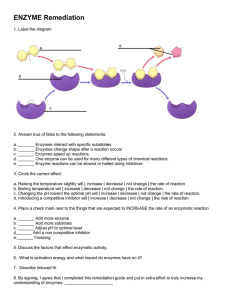
Class: 4 4.1 ( Name: ) Date: Enzymes and metabolism Metabolism (Book 1A, p. 4-3) (1) _______________ (新陳代謝) is the sum of chemical reactions that take place in an organism. It includes (2) _______________ (分解代謝) and (3) _______________ (合成代謝). Catabolism Anabolism energy complex molecule energy simple molecules simple molecules complex molecule The (4) ______________ (breaking-down / The (6) ______________ (breaking-down / building-up) reactions in an organism. building-up) reactions in an organism. Energy is (5) _______________ (released / Energy is (7) _______________ (released / required). required). 4.2 The role of enzymes in metabolism (Book 1A, p. 4-4) For every reaction, a certain amount of energy must be supplied to the reactants before the reaction can occur. This is called the (1) _______________ _______________ (活化能). In our body, (2) _______________ (酶) are present which function as biological catalysts (催化劑). They help (3) _______________ (raise / lower) the activation energy so that chemical reactions can take place at body temperature at a faster rate. energy level activation energy (without enzyme) activation energy (with enzyme) reactants products progress of reaction New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology (Second Edition) - 28 - ◄ Enzymes work by lowering the activation energy Oxford University Press 2014 Go to Practical 4.1 Demonstration of the breaking-down action of enzymes (Book 1A, p. 4-5; Practical Workbook for SBA 1A, p. 4-1) Practical 4.2 Demonstration of the building-up action of enzymes (Book 1A, p. 4-6; Practical Workbook for SBA 1A, p. 4-4) 4.3 A Actions and properties of enzymes How do enzymes work? (Book 1A, p. 4-7) (Book 1A, p. 4-7) On each enzyme molecule, there is an (1) _______________ _______________ (活性部位). An enzyme molecule only binds to (2) _______________ (受質) molecules that fit the shape of its active site. A metabolic reaction begins when the substrate molecule(s) bind to the active site of an enzyme to form an (3) _______________-_______________ _______________ (酶受質複合物). Its formation (4) _______________ (raises / lowers) the activation energy of the reaction. The substrate(s) are converted into product(s). The enzyme molecule is released in its (5) _______________ form. Catabolic reactions shapes fit together substrate enzyme-substrate complex products enzyme unchanged enzyme active site enzyme can be reused Anabolic reactions enzyme-substrate complex substrates shapes fit together enzyme product enzyme unchanged active site enzyme can be reused ▲ Enzyme action in metabolic reactions The specificity of enzyme actions can be explained by the (6) ___________- _____________ _____________ _______________ (鎖鑰假說). New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology (Second Edition) - 29 - Oxford University Press 2014 B What are the properties of enzymes? Property (Book 1A, p. 4-8) Description Enzymes are biological Enzymes speed up metabolic reactions by lowering the (7) _______________. (8) _______________ energy of the reactions. The actions of enzymes are An enzyme only acts on substrates that fit into its (9) _______________. (10) _______________ _______________. Enzymes are The structures and hence the activity of enzymes are easily (11) _______________. affected by temperature and pH. Most enzymes are (12) _______________ (變性) at high temperatures. Enzymes are Enzymes remain unchanged after reactions. They can bind to (13) _______________. other substrate molecules after the reaction is complete. Enzymes are needed in relatively Since enzymes can be (15) _______________, they are (14) _______________ amounts. usually needed in small amounts only. 4.4 Factors affecting the rate of enzymatic reactions (Book 1A, p. 4-10) A Temperature (Book 1A, p. 4-10) reaction rate maximum rate enzymes are denatured enzymes are inactive temperature (℃) 10 20 30 40 50 60 optimum temperature for this enzyme ▲ Effect of temperature on the rate of an enzymatic reaction New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology (Second Edition) - 30 - Oxford University Press 2014 At low temperatures, enzymes are (1) ______________ (不活躍). The enzyme and substrate molecules move slowly and the chance for them to (2) _______________ with each other is low. Therefore, the reaction rate is (3) _______________. As the temperature rises, both enzyme and substrate molecules move around more rapidly and collide with each other more (4) ______________. This increases the chance of forming (5) _____________-_____________ ______________. As a result, the rate of the enzymatic reaction (6) _______________. The rate of enzymatic reaction will eventually reach a maximum at (7) _______________ _______________ (最適溫度). High temperatures may cause (8) _______________ change (i.e. a change in shape) in the active site of the enzyme molecule. The enzyme is said to be (9) _______________. The substrate molecule can no longer fit into the active site of the enzyme. As a result, the rate of the enzymatic reaction (10) _______________. B pH (Book 1A, p. 4-12) Most enzymes work in a (11) _______________ (wide / narrow) range of pH. They work best at their (12) _______________ pH. Similar to the effect of high temperatures, an unsuitable pH will cause (13) _______________ of the enzyme. Therefore the rate of the enzymatic reaction (14) _______________. many enzymes in mammals (e.g. salivary amylase) pancreatic lipase reaction rate pepsin 2 4 optimum pH 6 8 10 12 14 pH optimum optimum pH pH ▲ Different enzymes have their own optimum pH New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology (Second Edition) - 31 - Oxford University Press 2014 C Inhibitors (Book 1A, p. 4-15) (15) _______________ (抑制劑) are chemicals that can decrease the rate of enzymatic reactions. Cyanides and (16) _______________ _______________ (重金屬) such as mercury ions, lead(II) ions and copper(II) ions are examples of inhibitors. Go to Practical 4.3 Investigation of the effect of temperature on enzyme activity (Book 1A, p. 4-11; Practical Workbook for SBA 1A, p. 4-8) Practical 4.4 Design an investigation of the effect of pH on enzyme activity (Book 1A, p. 4-13; Practical Workbook for SBA 1A, p. 4-12) Practical 4.5 Investigation of the effect of inhibitors on enzyme activity (Book 1A, p. 4-15; Practical Workbook for SBA 1A, p. 4-17) 4.5 Applications of enzymes (Book 1A, p. 4-18) Enzymes produced by organisms also work well outside the organisms. They are extracted and used to produce various commercial products. Examples of products and the enzymes used: Enzyme used Product I Biological washing powders a Protease II Stonewashed jeans (石磨藍牛仔褲) b Lipase III Contact lens cleaners c Cellulase IV Meat tenderizers d Papain (木瓜酶) V e Pectinase (果膠酶) Cheese VI Fruit juices I: (1) _______ & (2) _______ II: (3) _______ III: (4) ______ IV: (5) _______ V: (6) _______ VI: (7) ______ New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology (Second Edition) - 32 - Oxford University Press 2014 Advantages and limitations of using enzymes in the production of commercial products: Advantage Limitation Enzymes can speed up chemical Enzymes are sensitive to reactions. This (8) _______________ the (15) _______________ and production time and allows the (16) ________ changes. High (9) _______________ production of temperatures and unsuitable pH can cause products. (17) _______________ of enzymes. Enzymes are (10) _______________ in Enzymes are easily affected by action. This can reduce the production (18) _______________. All containers of (11) _______________ products. that are used in the production processes Enzymes are (12) _______________ and have to be (19) _______________. This are needed in small amounts only. This prevents the containers from lowers the (13) ______________ of (20) _______________ with inhibitors. production. Many enzymes work at (14) _______________ conditions. Using enzymes in the production processes does not require extreme conditions. Go to Practical 4.6 Investigation of the effectiveness of different biological washing powders (Book 1A, p. 4-20; Practical Workbook for SBA 1A, p. 4-20) Practical 4.7 Design an investigation of protease activities in different fruit juices (Book 1A, p. 4-21; Practical Workbook for SBA 1A, p. 4-24) New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology (Second Edition) - 33 - Oxford University Press 2014 Answers Ch 4 Enzymes and metabolism 4.1 1 Metabolism 2 catabolism 3 anabolism 6 building-up 7 required activation energy 2 1 active site 5 4 enzymes 3 lower 2 substrate 3 enzyme-substrate complex original 6 lock-and-key hypothesis 9 specific 10 active site 14 small 15 reused 1 inactive 2 collide 5 enzyme-substrate complexes 8 conformational 9 13 denaturation 1 breaking-down 5 released 4 lowers 4.2 1 4.3 7 catalysts 8 activation 13 reusable 11 proteins 12 denatured 3 low 4 frequently 6 increases 7 optimum temperature denatured 10 decreases 11 narrow 14 decreases 15 Inhibitors 16 heavy metals a 2 b 3 c 4 6 a 7 e 8 shortens 11 unwanted 12 reusable 13 16 pH 17 denaturation 18 4.4 12 optimum a 5 d 9 mass 10 specific cost 14 moderate 15 temperature inhibitors 19 clean 20 contaminating 4.5 New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology (Second Edition) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) - 34 - Oxford University Press 2014