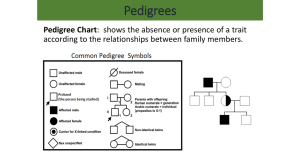
Short Cuts to Pedigree Chart Analysis Challenge Question: What process are we seeing here? • This is Mitosis happening in onion root cells • Can you spot any of the stages? • Hint: IPMAT How to read a pedigree chart Step 1. figure out which trait is dominant, the black or white individuals? There are 9 black and 7 white • Let’s assume black is dominant Step 2: Choose a letter (Like A) and assign genotypes to each individual • Its easiest to start with the recessive genotypes as these are homogenous so we know each white individual must have a genotype of ‘aa’ Step 3: Now you can work backwards from the recessive genotypes to figure out the genotypes of their parents using a punnet square • For example: • So if this offspring is genotype ‘aa’ what must the parents be? They are dominant (black) but are they heterozygous or homozygous? Try writing the genotypes for the rest of the pedigree chart for yourself… Short cuts: Fill in the table on your worksheet What does an autosomal dominant pedigree look like? In a pedigree this phenotype will appear with equal frequency in both sexes but it will not skip generations. Here is an example of an autosomal dominant pedigree: What does an autosomal recessive pedigree look like? Autosomal recessive pedigrees can look differently based on the genotype of the parents. Here is an example pedigree: One trick for identifying a recessive trait is that if a trait skips a generation in a pedigree, it is often an autosomal recessive trait These traits appear with equal frequency in both sexes. X-linked recessive pedigree • What does an X-linked recessive pedigree look like? • As you can see above, this trait is more likely to appear in males than females so the pedigree may contain more affected males than females • This trait is never passed from father to son, because a father carries the allele on his X chromosome, but always passes his Y chromosome on to any sons. • Here is a sample X-linked recessive pedigree: X-linked dominant • How can you identify an X-linked dominant trait • -This kind of trait affects both males and females equally and does not skip generations • -All affected males have an affected mother • -All affected females have an affected father or mother • -All female progeny of an affected male are affected