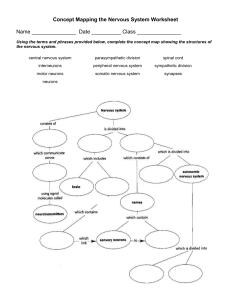
The Nervous System Key words: Central Nervous System, Peripheral nervous system, Receptors and Neurons The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. It's sometimes called the "co-ordinator" because it makes sense of the messages it receives from the sense organs and co-ordinates responses by the muscles and glands. The peripheral nervous system consists of the bundles of nerves that relay messages between the sense organs, the central nervous system and the muscles and glands. This system is spread out through the entire body, as shown on the right. Receptors are cells that allow us to detect different types of stimuli. For example, olfactory receptor cells located in the nose detect odour molecules in the air. There are five primary types of receptors: Chemoreceptors are sensitive to chemicals, such as odour molecules in the air, and are located in the nose and tongue. Mechanoreceptors are sensitive to touch, pressure, sound and motion and are located in the skin, the inner ear and muscles. Pain receptors are sensitive to chemical changes in damaged cells and are located throughout the body, but most are located in the skin. Thermoreceptors are sensitive to temperature changes and are located in the skin. Photoreceptors are sensitive to light and are located in the eyes. Neurons Neurons are specialized cells that transmit messages, in the form of electrical signals, to and from, and within, the central nervous system. They act something like the wires of an electric circuit. There are a number of different types of neurons: Sensory neurons transm it messages from receptors to the central nervous system. Interneurons transmit messages from sensory neurons to motor neurons. Motor neurons transmit messages from the central nervous system to "effectors" such as muscles and glands to initiate a response. Although they have different roles, neurons generally have the same structure. They are made up of dendrites (branches that receive messages), a cell body (where the nucleus is found), axons (that transmit a message away from the cell body) and myelin sheaths (a fatty layer that insulates the axon and sometimes a dendrite). Label the diagram below