Special Relativity Worksheet: Time Dilation, Length Contraction
advertisement

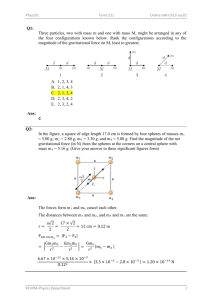
Einstein’s Special theory of Relativity (ESTR) ESTR is based on the number of concepts: The only constant number in the Universe is a speed of light 3x108 m/s Please watch following video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ttZCKAMpcAo and stipulate general principals of ESTR, use your own wording to explain each of them 1. 2. 3. 4. 1. Time dilation t - time measured on Earth or an observer time, relativistic time to - time measured on the spaceship or proper time v - velocity of the spaceship c - speed of light 𝒕= 𝒕𝒐 𝟐 √𝟏 − 𝒗𝟐 𝒄 Solve following problems: 1. An astronaut travels through space at a constant speed 2.95x108 m/s relative to Earth. According to his spaceship clock, his trip took 0.5 year. How long did the trip last according to the clock of his commander on Earth? ( you do not need to convert time to seconds, if you will use years in calculations, your result also will be in years). 2. An astronaut travels at a constant speed 2.7x108 m/s relative to Earth towards a distant star. If this trip takes 25 years as measured on Earth, how long does it take relative to the space vehicle? 3. If an astronaut’s trip through the space takes 25 years, as measured on Earth, and 1.5 years as measured by the clock on the spaceship, what was spaceship’s speed? 2. Length contraction 𝑣2 𝐿 = 𝐿0 √1 − ( 2 ) 𝑐 Lo – actual distance L - the distance measured by moving observer, this is relativistic length 1. A spaceship is 50m long and travels at 0.75c , c= 3x108 m/s past the observer standing on Eatrh. How long does the spaceship appear to the observer? Lo=50m, L-? 2. A spaceship travels at a constant speed o.955c parallel to a brick wall is 115m long. How long does this wall appear to an observer in the spaceship? Lo= 115m, L-? 3. Mass increase 𝑚= 𝑚0 2 √1 − 𝑣 2 𝑐 m - relativistic mass mo - real mass Calculate the relativistic mass of an electron (mass=9.11 x 10-31kg) that travels at 2.0 x 108 m/s. 4. Mass – Energy equivalence E= mc2 1. What mass is required to produce 2 x 1015 J of heat if 100% of the mass is converted into heat? 2. Calculate the energy produced if a 10 kg mass completely converts into heat.