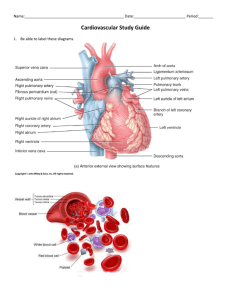
The City College 55 East Road London, N1 6AH cover image by Kevin Howdeshell first publishes 2018 custom edition 1 copyright Daniel Scott 2018 Published by the City College No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise without prior written permission of the publisher. Copyright Licensing agency UK UNIT 12: PHYSIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES FOR HEALTH AND SOCIAL CARE UNIT CODE: A/601/1608 QCF LEVEL: 4 CREDIT VALUE: 15 . HAND IN DATE 5 /4 / 2018 The successful completion of this workbook comprises 20% of the assessment for this unit. The Unit can’t be passed without completing the workbook. The assessments with in this book are intended to consolidate and develop your learning of anatomy, physiology and the language of these subjects. You are encouraged to use whatever resources you have at your disposal to enable you to complete this task effectively Lectures. These will be held in the college and will cover essential material. Regular attendance is essential in order to achieve a sound understanding of physiological concepts. Textbooks and linked electronic resources. Textbooks and webbased resources will help to embed your learning. Formation of study groups. Students have often reported that one of the most enriching learning activates is engaging with others studying the same subject. This can be helpful in two ways firstly a peer can be a good person to help you understand a topic and secondly one of the best ways to really learn something is to explain it to someone else. Please note, even if you tackle the work in this book with other students the work submitted in this book MUST be your own. Make sure your answers are you’re own, and written in your own words, please read the College's guidelines on plagiarism and collusion . Contents Direction and moment Talking about anatomy Major muscles Chemistry introduction Cells Blood Cardio systems Gastrointestinal system Hormones Kidney Immune system Define the Planes and directions in anatomical language sagittal coronal transverse 1 superior 2 medial 3 proximal 5 inferior 6 lateral 7 distal 4 superficial 8 deep DEFINE THE FOLLOWING TERMS Write a short definition for each term Physiology: study of the functioning of living organisms, animal or plant, and of the functioning of their constituent tissues or cells Anatomy: is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts Chemistry: Chemistry is a branch of science that involves the study of the composition, structure and properties of matter. Biology: study of living things and their vital processes Psychology: Psychology is the study of behavior and the mind Haematology: is the branch of medicine concerned with the study: of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. homeostasis: Homeostasis is the tendency of organisms to auto-regulate and maintain their internal environment in a stable state Pathology: is a branch of medical science that involves the study and diagnosis of disease Embryology: is the branch of biology concerned with the development of new organisms Lable as many muscles as you can 12 1. temporalis 2 orbicularis oculi 3 zygomatis 4 buccinator 5 steernocleidomastoid 6 supraspinatus 7 deltoid 8 pectoralis major 9 external oblique 10 intercostals 11 transverse abdominis 12 internal oblique 13 rectus abdominis 14 rectus sheath 15 biceps femoris 16 flexor carpi ulnaris 17 extensor digitorum 18 extensor carpi ulnaris 19 adductors 20 satorius 21 vastus lateralis 22 rectus femoris 23 quadriceps 24 gastrocnemius 25 soleus 26 extensor digitorum longus 27 tibialis anterior Label the main bones 1. sphenoid 16. mandible 2. cervical vertebra 17. clavicle 3.costal cartilage 18. sternum 4. anterior rib 19. humerus 5. thoracic vertebra 20. posterior rib 6. vertebral facet 21. radius 7. lumbar vertebra 22. ulnar 8. ilium 23. metacarpals 9. sacrum 24. phalanges 10. coccyx 25. femur 11. pubis 26. patella 12. pubic ramus 27. tibia 13. pubic symphysis 28. fibula 14. maxilla 29. talus 15. teeth Label the main section of the Spine 1- cervical spine c1 to c7 2- thoracic spine t1 to t12 3- lumbar spine l1 to l5 6- atlas 7- axis Chemistry of the body Students of physiology need to have some understanding of basic biological chemistry. these questions help to review your knoladge 1) Water is essential to life. List four main properties of water and explain their role in the maintenance of living cells 1. cohesion which is the property of water to stick to other water molecules to hydrogen bonds. 2. adhesion which is the tendency of water to stick to other substances. 3. high specific heat and high heat of vaporization allows it to moderate temperature 4. low density of ice 2) Briefly describe the process of Osmosis a process by which molecules of a solvent tend to pass through a semipermeable membrane from a less concentrated solution into a more concentrated one. 3) What are Enzymes are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products 4) What are Proteins made of ? Proteins are made up of smaller building blocks called amino acids, joined together in chains. Chemistry of the body Define the function of the five type of Leucocytes 1) neutrophils The primary function of neutrophils is phagocytosis 2) eosinophils responsible for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections in vertebrates 3) basophils play a role in mast cells in the effector response to allergens and parasites 4) monocytes Monocytes and their macrophage and dendritic-cell progeny serve three main functions in the immune system. These are phagocytosis, antigen presentation, and cytokine production. 5) lymphocytes Effector lymphocytes function to eliminate the antigen, either by releasing antibodies (in the case of B cells), cytotoxic granules (cytotoxic T cells) or by signaling to other cells of the immune system (helper T cells). 3) Heamoglobin (Red Blood Cells) are specialised for oxygen transport A) What is Haemoglobin comprised of It is composed of four protein chains, two alpha chains and two beta chains, each with a ring-like heme group containing an iron atom. B) How many molecules of Oxygen can haemoglobin carry hemoglobin molecule can bind (carry) up to four oxygen molecules. C) Why is this important to the function of Heamoglobin The major role of hemoglobin is to carry oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and return carbon dioxide (CO2) from the tissue to the lungs. Oxygen binds to hemoglobin with high affinity in an oxygen-rich environment and leaves hemoglobin in an environment where there is not enough oxygen.this helps it to carry more oxygen. Colour in sections Colour in sections Label A -to - F yourself A)Left and right atria _____Chambers that receive blood returning from your body through your veins B)Left and right ventricles_____Chambers where blood is pumped to your body through your arteries C)Mitral valve ____The mitral valve controls the flow of oxygen-rich blood from the left atrium to the left ventricle D)Tricuspid valve ____The tricuspid valve controls the flow of oxygen-poor blood from the right atrium to the right ventricle E)Aortic valve_____The aortic valve controls flow of oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle to the body F)Pulmonary valve____The pulmonary valve controls flow of oxygen-poor blood from the right ventricle to the lungs oesophagus stomach liver pancreas gall bladder large intestine small intestine rectum Draw and lable the following areas of the digestive system and try to add in the Accessory digestive organs: • Oesophagus. • Stomach. • Small Intestine. • Large Intestine. • Rectum. Accessory digestive organs: liver, gallbladder, pancreas. Chemistry of the body 1)Briefly describe the following kidney functions A) Filtration Filtration is the mass movement of water and solutes from plasma to the renal tubule that occurs in the renal glomerulus. the glomuerulus is a semi permeable allowing for this sieving mechanism. B) Osmoregulation is the maintenance of constant osmotic pressure in the fluids of an organism by the control of water and salt concentrations.salt and water are excreted or retained according the fluid balance in the body. 2) What is the main force pushing water and solutes out of the blood The force of hydrostatic pressure in the glomerulus (the force of pressure exerted from the pressure of the blood vessel itself) is the driving force that pushes filtrate out of the capillaries and into the slits in the nephron. 3) Briefly explain how Kidney filtration rate is maintained and regulated. GFR is one of the many ways in which homeostasis of blood volume and blood pressure may occur. In particular, low GFR is one of the variables that will activate the renin–angiotensin feedback system, a complex process that will increase blood volume, blood pressure, and GFR. This system is also activated by low blood pressure itself, and sympathetic nervous stimulation, in addition to low GFR. 4) Why is the tubular reabsorption so important to the function of the kidney Tubular reabsorption is the process by which solutes and water are removed from the tubular fluid and transported into the blood. Reabsorption is a finely tuned process that is altered to maintain homeostasis of blood volume, blood pressure, plasma osmolarity, and blood pH. Reabsorbed fluids, ions, and molecules are returned to the bloodstream through the peri-tubular capillaries, and are not excreted as urine. DEFINE THE FOLLOWING TERMS Write a short definition for each term Oestrogen: oestrogen, is the primary female sex hormone. It is responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics Testostorone Testosterone is the key male sex hormone that regulates fertility, muscle mass, fat distribution, and red blood cell production and male sexual characteristics Progesterone:It is secreted by the ovary during the second half of the menstrual cycle. It plays important roles in the menstrual cycle and in maintaining the early stages of pregnancy. Exocrine Glands are glands that produce and secrete substances onto an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Endocrine Gland: secrete their products, hormones, directly into the blood rather than through a duct Steroid:biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes which alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Histamine an important component of the immune and neurologic systems and is involved in the process of inflammation. Histamine causes a variety of symptoms depending on where it is released and what receptors it binds to. Lymph: fluid that circulates throughout the lymphatic system containing interstitial fluid. Plasma: is the liquid straw colored component of blood that suspends the blood cells. Chemistry of the body Antibodies, also called immunoglobulins, are proteins manufactured by the body that help fight against foreign substances. Briefly how do Antibodies work in the body? Neutralisation, in which neutralizing antibodies block parts of the surface of a bacterial cell or virion to render its attack ineffective Agglutination, in which antibodies "glue together" foreign cells into clumps that are attractive targets for phagocytosis Complement activation (fixation), in which antibodies that are latched onto a foreign cell encourage complement to attack it with a membrane attack complex, Please give some examples of Antigens Exogenous antigens are antigens that have entered the body from the outside, for example, by inhalation, ingestion or injection for example drugs, foods, pollen, dander. Endogenous antigens are generated within normal cells as a result of normal cell metabolism, or because of viral or intracellular bacterial infection. Briefly describe Autoimmune diseases. Autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells and tissues. Any disease that results from such an aberrant immune response is termed an "autoimmune disease". such include rheumatoid arthritis wherby the immune system attacks joints of the person. Notes notes