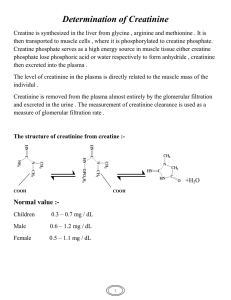
Serum Creatinine test • Creatinine is a waste product, anhydride form of creatine and creatine phosphate. • • CH3 CH3 • │ │ • H2C ------ N H2C ------ N • │ │ │ │ • 0═C C ═ NH C ═ NH • │ │ │ │ • OH NH2 O ═ C --------N • │ • H • • Creatine Creatinine • Creatine is synthesized in the liver and pancreas from three amino acids: arginine, glycine, and methionine. After synthesis, creatine diffuses into the vascular system and is supplied to many kinds of cells, particularly the muscle, where it is phosphorylated by ATP to creatine phosphate. ● Creatine and creatine phosphate total approximately 400 mg/ 100g of muscle. ● Creatine is filtered by glomeruli but is largely reabsorbed at the proximal tubule: hence there is very little excretion of creatine in the urine. ● Both creatine and creatine phosphate are spontaneously converted largely in muscles into creatinine at a rate of approximately 2% per day by irreversible nonenzymatic removal of water. ● The body content of creatine is proportional to muscle mass; therefore, the level of creatinine in the body is also proportional to muscle mass; ● Creatinine is removed from the plasma by glomerular filteration. No reabsorption of creatinine occurs in the renal tubules; i.e. creatinine has high clearance rate as compared to urea. Clinical Significance • Serum creatinine determination is significantly more reliable than plasma urea determination since it is not affected by dietary protein. • Because kidney can also secrete creatinine through the tubules, blood creatinine levels in renal disease do not increase untile kidney function is severely impaired (~50% of function test). • Increase in creatinine above 2-4 mg/dl is suggestive of moderate to severe kidney damage. • Minor changes in blood creatinine concentration may be of significant and indicate impairment of renal function. • ● Simultaneous determination of urea and creatinine is of value in the differential diagnosis of prerenal, renal, and postrenal hyperuremia. • ■ Normal rate of urea/creatinie is between 15/1 to 24/1. urea/creatinie ratio -INCREASED UREA:CREATININE RATIO dehydration/prerenal failure corticosteroids haemorrhage protein-rich diet severe catabolic state -DECREASED UREA:CREATININE RATIO severe liver dysfunction intrinsic renal damage malnutrition pregnancy low protein diet Creatinine clearance Tests The creatinine clearance is a very sensitive indicator of glomerular filtration rate (GFR). The creatinine clearance test helps provide information about how well the kidneys are working. The test compares the creatinine level in urine with the creatinine level in blood. How the Test is Performed This test requires both a urine sample and blood sample. You will collect your urine for 24 hours and then have blood taken. • The creatinine clearance (CrCl ) is calculated from the following formula: • • Urine Volume • CrCl (ml / min) = ---------------------------• S.Cr*24*60 • 24 hours • 60 second (1minute) Normal range(CrCl) Male 90-140ml/minute Female 80-125 ml/minute Increased serum creatinine: -Doing strenuous exercise two days before testing • -Eating high amounts of meat (eight ounces) within 24 hours of testing -Impaired renal function – Vary large muscle mass: body builders, giants, acromegaly patients – Athletes taking oral creatine – Drugs: • Probenecid • Cimetidine • Triamterene • Trimethoprim • Amiloride • When you do S.Creatinine? doctor may order a creatinine blood test to assess the • creatinine levels if there are signs of kidney disease. These symptoms include: trouble sleeping • a loss of appetite • lower back pain near the kidneys • changes in urine output and frequency • high blood pressure • nausea • vomiting • Normal range • • • • • • Male: 0.6 -1.4 mg/dl (53- 93 µmol/l) Female: 0.5- 0.9 mg/dl (44- 80 µmol/l)) Urine 24hrs Male 1.0 – 2.0 g/day Female 0.8 – 1.8 g/day Specimen -One can analyze serum, plasma, or diluted urine(1:100). -The common anticoagulants (fluoride and heparin) do not cause interference,. -Storage 7 days at 4-25oC At least 3 months at -20oC Interferences 1- Hemolysis, bilirubin may cause falsely results. 2- Ascorbic acid, and some antibiotics interfere also with the determination of creatinine according to Jaffe method Methods for creatinine determination The methods used to measure creatinine are based on the Jaffe reaction: •Kinetic method •Enzymatic method Determination of creatinine by kinetic method Principle Creatinine reacts with picric acid under alkaline condition to form a yellow complex. The absorbance of the color produced, measured at a wavelength 492 nm, is directly proportional to creatinine concentration in the sample.. Creatinine + picric acid Alkaline pH yellow complex Serum creatinine procedure • Procedure Standerd 1ml Sample 1 ml Working reagent (0.5ml R1+0.5ml R2) Distilled water -----------Standard 100 µl -----Sample ------100 µl • Mix well. After 30 seconds, record absorbance A1 at 490 nm against reagent blank or distilled water. Exactly 2 minutes after the first reading, record absorbance A2. Calculation A2-A1 = ∆Asample or ∆Astandard ∆Asample --------------------- × standard conc. = Conc. Of creatinine (mg/dl or µmol/l) ∆Astandard Home work A 19-year-old woman is hospitalized for acute kidney injury (AKI) associated with bloody diarrhea that developed after she returned from a trip to South America. She also has nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fever, chills, and decreased urine output. Medical history is otherwise unremarkable, and she takes no medications. On physical examination, temperature is 37.8°C (100.0°F), blood pressure is 135/90 mm Hg, and pulse rate is 110/min. The oral mucosa is dry. There is diffuse abdominal pain with guarding. The remainder of the physical examination is normal. Laboratory studies show haptoglobin 8 mg/dL (80 mg/L), hemoglobin 5.2 g/dL (52 g/L), leukocyte count 20,000/µL (20 × 109/L), platelet count 36,000/µL (36 × 109/L), reticulocyte count 7.8%, serum creatinine 5.7 mg/dL (504 µmol/L) and lactate dehydrogenase 2396 units/L. Peripheral blood smear showed many schistocytes and urinalysis many erythrocytes and erythrocyte casts. Urine protein creatinine ratio is 0.5 mg/mg. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's acute kidney injury? A. Acute tubular necrosis B.. Hemolytic uremic syndrome C. Postinfectious glomerulonephritis D. Scleroderma renal crisis