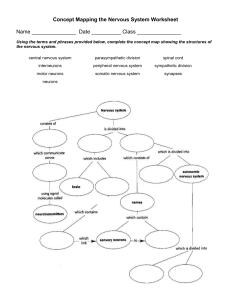
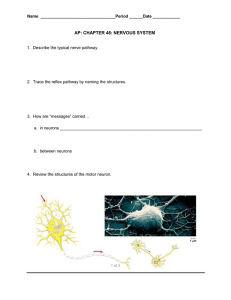
The Nervous System Chapter 9 Learning Objectives: ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Describe the structure and function of neurons and neuroglia Differentiate between white matter and gray matter Describe the function of afferent and efferent nerves List the components of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system Differentiate between the autonomic and somatic nervous system Describe the process of depolarization and repolarization of neurons (action potential) Identify the structures of the synapse and explain their functions Understand excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters and describe their role in the conduction of nerve impulses Describe the structure and function of the cerebrum, cerebellum, diencephalon, and brainstem Describe the connective tissue layer that surrounds the brain and spinal cord Explain the functions of cerebrospinal fluid List the cranial nerves and describe their function Differentiate between the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system Differentiate between autonomic and somatic reflexes Describe the components of the reflex arc Describe the stretch reflex, withdrawal reflex, crossed extensor reflex, palpebral reflex, and pupillary light reflex Introduction to the Nervous System Major Functions: � Control � Coordinate � Communicate How does it do these things? � Signal reception � Signal integration � Signal transmission Neurons and Supporting Cells The Neuron Figure 9-1, Page 229 Neuroglia Organizational Schemes of the Nervous System � Anatomic location � Direction of impulse transmission � Function Anatomic Location Direction of Impulse Transmission Function Organization of the Nervous System Overview Neuron Function: The Action Potential Overview: The Action Potential Resting State- Sodium Potassium Pump creates electrochemical gradient Depolarization- Sodium gates open Repolarization- Potassium gates open Sodium- Potassium Pump brings back to Resting State SodiumPotassium Pump The Action Potential Figure 9-5, Page 233 All or Nothing Principle Saltatory Conduction How Neurons Communicate: The Synapse The Synapse Figure 9-7, Page 336 National Geographic: Mapping the Brain (Synapse) Neurotransmitters Types of Neurotransmitters ● Excitatory- Depolarize ○ Cause postsynaptic membrane to become more positive with the influx of sodium ● Inhibitory- Hyperpolarize ○ Cause the postsynaptic membrane to become more negative with the influx of chloride or outflux of potassium Specific Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine- excitatory (somatic) and inhibitory (parasympathetic) Catecholamines ● ● ● Norepinephrine- excitatory in fight or flight Epinephrine- excitatory in fight or flight Dopamine- excitatory and inhibitory in brain Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and Glycine- inhibitory in brain and spinal cord (tranquilizers) Neurotransmitter Recycling The Central Nervous System Central Nervous System (Figure 9-8, Page 239) Meninges Figure 9-10, Page 240 Cerebrospinal Fluid Blood Brain Barrier Cranial Nerves Table 9-1, Page 243 Know name, number and key functions of all. Spinal Cord Figure 9-11, Page 244 The Autonomic Nervous System Structure of the Autonomic System Figure 9-12, Page 245 Sympathetic System Parasympathetic System Functions of the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous System Table 9-3, Page 246 Sympathetic Parasympathetic Heart rate Increases Decreases Force of heart contraction Increases Decreases Diameter of bronchioles Dilates Contricts Diameter of pupil Dilates Constricts Gastrointestinal function Decreases Increases Diameter of skin and kidney blood vessels Decreases No significant effect Diameter of muscle blood vessels Increases Decreases Neurotransmitters at the Postganglionic Receptor, Figure 9-13, Page 247 Neurotransmitter Use in the Parasympathetic and Sympathetic Nervous Systems Reflexes and Reflex Arcs Stretch Reflex, Figure 9-14, Page 248 Withdrawal Reflex, Figure 9-15, Page 249 Crossed Extensor Reflex, Figure 9-16, Page 250 Palpebral reflex and Pupillary light reflex Clinical Neurology and Functional Neuroanatomy from University of Georgia