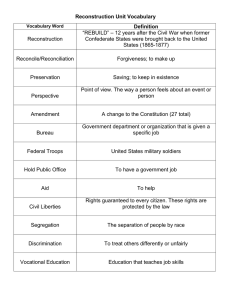
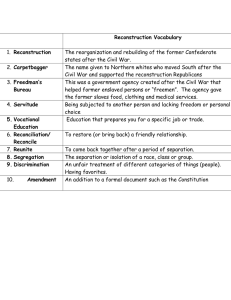
Secession/Civil War/Reconstruction Quiz Date: Name: 1. What agricultural invention, designed to increase production, had the e ect of increasing the number of slaves needed for labor in the Deep South? A. the wheat reaper B. C. the steel plow D. the rice mill 4. the cotton gin Who was the most important leader of the Underground Railroad? A. Harriet Tubman B. William Lloyd Garrison C. Phillis Wheatley D. Sarah Grimke 2. 5. The growing importance of cotton to the South created an economy and a society dominated by A. managers and professional people. A. universal su rage for citizens. B. small independent farmers. B. the gradual elimination of slavery. C. large landowners. C. the adoption of a state religion. D. abolition of state property taxes. D. industrial leaders. 6. 3. After the American Revolution, most Northern state constitutions called for What led the newspapers to speak of “Bleeding Kansas” in 1856? Prior to the Civil War, which group had the most political power in the South? A. ghting between pro-slavery and anti-slavery forces A. plantation owners B. B. attacks on job-seeking Irish immigrants C. urban merchants D. religious o C. con ict between cattle ranchers and farmers cattle ranchers cials D. reaction to the U.S. Supreme Court ruling against Dred Scott page 1 7. What is one reason that the Union strategy for defeating the South included a naval blockade of Southern ports? A. to cut the South o from its supply lines in the countries of Latin America B. to stop Southern attempts to establish slave plantations in Cuba and Mexico C. to prevent Southern e orts to sell cotton in Europe in exchange for war supplies 9. Use the graph below to answer the following question. D. to deprive the South of shing and whaling as a primary source of food According to the graph, which statement is true? A. The Missouri Compromise kept the number of free states and slave states in balance. B. The Missouri Compromise kept the total number of states in the Union the same. C. The Missouri Compromise increased the number of free states but did not change the number of slave states. D. The Missouri Compromise increased the number of slave states but did not change the number of free states. 8. Which crop was the biggest cash crop in the American South during the 1800s? A. cotton B. rice C. corn D. wheat 10. How did the cotton gin a ect the Southern economy from 1800 to 1860? A. It encouraged industrialization in the South. B. It promoted economic equality in the South. C. It strengthened Southerners' reliance on slavery. D. It increased Southerners' use of indentured servants. page 2 Secession/Civil War/Reconstruction Quiz 11. The Battle of Vicksburg was signi cant because it 14. Growth of the AfricanAmerican Population: A. marked the end of Confederate invasions into Union territory. B. destroyed the South's greatest city, devastating Confederate morale. 1648 C. gave the Union control of the Mississippi and split the Confederacy in two. 1680 1625 D. created a moment appropriate for President Lincoln to proclaim Emancipation. 23 300 1671 2,000 1700 16,390 3,000 1720 26,559 1740 60,000 1730 1775 30,000 210,000 Which explains the increase in the African-American population from 1625 to 1775? 12. Which action abolished slavery in the United States? A. suspension of habeas corpus B. passage of the Thirteenth Amendment C. passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1866 A. war B. jobs C. migration D. slavery D. delivery of the Gettysburg Address 15. 13. Which of these activities had the greatest economic impact on the southeastern United States between 1800 and 1860? A. ship building B. C. logging D. cotton farming How was Abraham Lincoln's victory in the 1860 presidential election a turning point in American history? A. Lincoln won the majority of electoral votes but not a majority of the popular vote. B. A coalition of Whigs, Know-Nothings, and Democrats ran a strong third-party candidate. C. The Crittenden Compromise attempted to resolve tensions aroused by the election. D. Lincoln's victory prompted Southern secession and the Civil War that followed. coal mining page 3 Secession/Civil War/Reconstruction Quiz 16. How did the end of the U.S. Civil War a ect American politics? A. Legislation passed that supported property rights and due process for women. B. Legislation passed that established voting rights for American Indians. C. Legislation passed that provided citizenship and legal protections for freed slaves. 18. Many Africans were brought to North America to be slaves for white landowners in the 1700s. In the space below, identify four characteristics of life under slavery in the late 1700s. 19. D. Legislation passed that enhanced individual states' rights. The term “secession” refers to which action taken by Southern states before the American Civil War? A. leaving the Union B. voting to be slave or free C. eliminating the Constitution D. compromising about slavery 17. That on the rst day of January, in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred and sixty-three, all persons held as slaves within any State or designated part of a State, the people whereof shall then be in rebellion against the United States, shall be then, thenceforward, and forever free; and the Executive Government of the United States, including the military and naval authority thereof, will recognize and maintain the freedom of such persons, and will do no act or acts to repress such persons, or any of them, in any e orts they may make for their actual freedom. 20. Which African custom and tradition brought by slaves had the greatest in uence on Southerners? A. foods B. books C. clothing D. religion Abraham Lincoln, A Proclamation, January 1, 1863 How was issuing the Emancipation Proclamation a turning point in the Civil War? A. It proposed a peace treaty with the Confederate states. B. It established a Freedmen's Bureau to help freed slaves. C. 21. It provided a plan for Reconstruction. D. It freed slaves in the Confederate states. One goal of post—Civil War Congressional Reconstruction was to A. repay Confederate war debts. B. ensure civil rights for former slaves. C. preserve the plantation system. D. rebuild the Southern naval system. page 4 Secession/Civil War/Reconstruction Quiz 22. During Reconstruction, the Freedmen's Bureau A. relocated many former slaves to the North. B. created a system for tenant farming. C. gave forty acres and a mule to former slaves. 23. D. established schools for former slaves. One of the functions of the Freedmen's Bureau was to A. discourage segregation in the South. B. relocate former slaves to urban areas. C. provide assistance to former slaves. D. reward veterans with land and money. page 5 Secession/Civil War/Reconstruction Quiz Read and study documents 1 through 4 about the Reconstruction era in Louisiana. Use the documents to answer the following questions. DOCUMENT 1 Portions of the Black Code of St. Landry Parish, Louisiana, 1865 Sec. 1. Be it ordained by the police jury of the parish of St. Landry, That no negro shall be allowed to pass within the limits of said parish without special permit in writing from his employer. Whoever shall violate this provision shall pay a ne of two dollars and fty cents, or in default thereof [if unable to pay the ne] shall be forced to work four days on the public road, or su er corporeal [physical] punishment as provided hereinafter. Sec. 3. No negro shall be permitted to rent or keep a house within said parish. Any negro violating this provision shall be immediately ejected [removed] and compelled [required] to nd an employer; and any person who shall rent, or give the use of any house to any negro, in violation of this section, shall pay a ne of ve dollars for each o ence. Sec. 4. Every negro is required to be in the regular service of some white person, or former owner, who shall be held responsible for the conduct of said negro. But said employer or former owner may permit said negro to hire his own time by special permission in writing, which permission shall not extend over seven days at any one time. Sec. 5. No public meetings or congregations of negroes shall be allowed within said parish after sunset; but such public meetings and congregations may be held between the hours of sunrise and sunset, by the special permission in writing of the captain of patrol, within whose beat such meetings shall take place. Sec. 6. No negro shall be permitted to preach, exhort, or otherwise declaim [speak] to congregations of colored people, without a special permission in writing from the president of the police jury. Sec. 7. No negro who is not in the military service shall be allowed to carry re-arms, or any kind of weapons, within the parish, without the special written permission of his employers, approved and indorsed by the nearest and most convenient chief of patrol. Sec. 8. No negro shall sell, barter, or exchange any articles of merchandise or tra c within said parish without the special written permission of his employer, specifying the article of sale, barter or tra c. Sec. 11. It shall be the duty of every citizen to act as a police o cer for the detection of o ences and the apprehension [arrest] of o enders, who shall be immediately handed over to the proper captain or chief of patrol. page 6 Secession/Civil War/Reconstruction Quiz DOCUMENT 2 Picture and Speech about the New Orleans Riot, 1866 Louisiana Republicans called a constitutional convention in 1866 and invited over two hundred African American men to participate. They met in a building called the Mechanics' Institute in New Orleans. A group of whites, aided by the police, attacked the convention, resulting in over thirty deaths and many injuries. The picture and quotation below relate to these events. The Riot in New Orleans—Murdering Negroes in the Rear of Mechanics' Institute Excerpt from President Andrew Jonson's Speech in St. Louis, September 8, 1886 Pehaps if you had a word or two on the subject of New Orleans, you might understand more about it than you do. . . If you will take up the riot at New ORleans and trace it back to its source, or to its immediate cause, you will nd out who was responsible for the blood that was shed there. If you will take up the riot at New Orleans and trace it back to the Radical Congress, you will nd that the riot at New Orleans was substantially planned—if you will take up the proceedings in their caucuses [meetings] you will understand that they there knew that a conversation was to be called which was extinct, by its powers having expired; that it was said, and the intention was that a new Government was to be organized; and in the organization of that Government the intention was to enfranchise one portion of the population called the colored population, who had just been emancipated, and at the same time disfranchise white men. page 7 Secession/Civil War/Reconstruction Quiz DOCUMENT 3 Excerpt from the First Reconstruction Act of 1867, Passed by the Congress over the Veto of President Andrew Johnson Whereas no legal State governments or adequate protection for life or property now exists in the rebel States of Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, Mississippi, Alabama, Louisiana, Florida, Texas, and Arkansas; and whereas it is necessary that peace and good order should be enforced in said States until loyal and republican State governments can be legally established: Therefore, Be it enacted by the Senate and House of Representatives of teh United States of America in Congress assembled, That said rebel States shall be divided into military districts and made subject to the military authority of the United States. . . Sec. 5 And be it further enacted, That when the people of any one of said rebel States shall have formed a constitution of government in conformity with the Constitution of the United States in all respects, framed by a convention of delegates elected by the male citizens of said State, twenty–one years old and upward, of whatever race, color, or previous condition, who have been resident in said State for one year previous to the day of such election. . . and when such constitution shall provide that the elective franchise [vote] shall be enjoyed by all such persons as have the quali cations herein stated for the electors of the delegates, and when such constitution shall be rati ed by a majority of the persons voting. . . and when such constitution shall have been submitted to the Congress for examination and approval, and Congress shall have aproved the same,. . . said State shall be declared entitled to representation in Congress. page 8 Secession/Civil War/Reconstruction Quiz DOCUMENT 4 The Louisiana Constitution of 1868 The illustration below shows a portion of a print titled, “Extract from the reconstructed Constitution of the state of Louisiana, with portraits of the distinguished members of the Convention & Assembly, A.D. 1868.” Excerpts from the Louisiana Constitution of 1868 appear on the sides of the illustration and are also shown below. On the Left Side of the Illustration: Bill of Rights Article 13 All persons shall enjoy equal rights and privileges upon any conveyance of a public character; and all places of business or of public resort, shall be deemed places of a public character, and shall be opened to the accomidation and patronage [use] of all persons without distiction or discrimination on account of race or COLOR. On the Right Side of the Illustration: Public Education Article 135 All children of this State shall be admited to the Public Schools or other Institutions of learning sustained or established by the State in COMMON, without distinction of RACE, COLOR, or PREVIOUS CONDITION. THere shall be no separate schools or institutions of learning established exclusively for any Race by the State of Louisiana. page 9 Secession/Civil War/Reconstruction Quiz 24. 27. Which statement best describes supporters of Radical Reconstruction? A. They emphasized the need for rearmament of the South. A. Freed slaves served as public o cials for the rst time. B. They encouraged the appointment of rebel leaders to high government posts. B. Carpetbaggers had di culty voting or holding elected o ce. C. They promoted advances in rights that would later be undermined. C. The Democratic Party was in control of most state legislatures. D. State governments had more power than the federal government. D. They focused on industrialization in the South. 25. Which best describes Southern politics during Reconstruction? Why did Congress pass laws protecting civil rights during Reconstruction? A. to reverse the Dred Scott decision B. to abolish black codes in the South C. to punish former Confederate soldiers 28. D. to help former slaves migrate to the North What main goal did many Republicans in the North share during Reconstruction? A. allowing government o cials to enforce black codes B. building strong support for groups like the Ku Klux Klan C. helping freedmen move North to work in factories D. adding numbers to their political party by helping freedmen 26. Which of these is the strongest evidence of the federal government showing its power over state governments during the Reconstruction period? A. the creation of the sharecropping system B. the migration of carpetbaggers into southern states C. the military occupation of former Confederate states 29. D. the creation of the Freedmen's Bureau How did the Freedmen's Bureau assist freed slaves in the South after the Civil War? A. It helped them start small businesses. B. It gave them each forty acres of land. C. It set up a sharecropping system for them. D. It created educational opportunities for them. page 10 Secession/Civil War/Reconstruction Quiz 30. Which action best describes the role of the Democratic Party in Reconstruction in Louisiana? A. Democrats proposed gradually increasing civil rights for African Americans. B. Democrats attempted to restore pre-war social conditions. C. Democrats focused on developing new sources of jobs for whites. D. Democrats supported new limits on immigration. page 11 Secession/Civil War/Reconstruction Quiz Problem-Attic format version 4.4.375 c 2011–2018 EducAide Software _ Licensed for use by Zena Buras Terms of Use at www.problem-attic.com Secession/Civil War/Reconstruction Quiz 1/31/2020 1. Answer: Points: B 1 15. Answer: Points: D 1 2. Answer: Points: C 1 16. Answer: Points: C 1 3. Answer: Points: A 1 17. Answer: Points: D 1 4. Answer: Points: A 1 5. Answer: Points: B 1 Objective: Points: Slaves could not vote, were not paid for their work, could not own land, and did not have control over keeping their families together. OH 5.B 1 6. Answer: Points: A 1 7. Answer: Points: 19. Answer: Objective: Points: A OH 8.G 1 C 1 8. Answer: Points: 20. Answer: Points: A 1 A 1 9. Answer: Objective: Points: 21. Answer: Points: B 1 A LA G-1A-M2 1 22. Answer: Points: D 1 10. Answer: Points: C 1 23. Answer: Points: C 1 11. Answer: Points: C 1 12. Answer: Points: 24. Answer: Objective: Points: C LA H-1D-M2 1 B 1 13. Answer: Points: 25. Answer: Points: B 1 D 1 14. Answer: Points: 26. Answer: Points: C 1 D 1 27. Answer: Points: A 1 18. Answer: Teacher's Key 28. Answer: Points: D 1 29. Answer: Points: D 1 30. Answer: Objective: Points: B LA H-1D-M2 1 Page 2