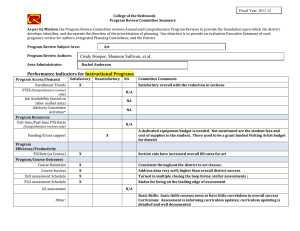
Cochrane Library Search Worksheet: Nursing Shortage Reviews
advertisement

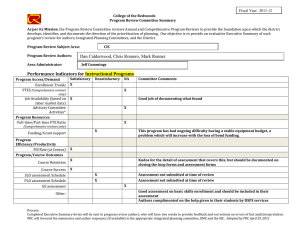
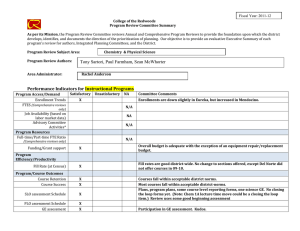
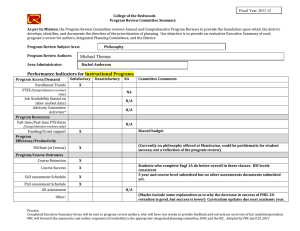
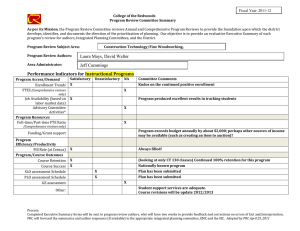
Cochrane Library Search and Find Student Name: Bilal Amtiaz The five dropdown tabs/ categories on the main page are: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Cochrane Reviews Trials Clinical answers About Help Click on Cochrane Reviews dropdown, then Search Reviews In the search box in the upper right corner, SELECT A SEARCH TERM related to your EBP clinical problem OR your NIH article clinical problem (after clicking search, make sure you are still in the Cochrane Reviews tab). My search TERM: Nursing shortage On the LEFT SIDE OF THE SCREEN: Set the SEARCH LIMITS 1. Set TYPE as INTERVENTION 2. Set DATE RANGE 3. CHOOSE a TOPIC. My limits were: 1. TYPE: INTERVENTION 2. DATE RANGE: 03/01/2016-03/15/2020 3. TOPIC: Effective practice & health systems Choose a review. You may copy & paste any sections EXCEPT AUTHOR’S CONCLUSIONS Systematic Review title: Hospital nurse‐staffing models and patient‐ and staff‐related outcomes Number of authors: 9 authors List the sections of the Abstract: Background, Objectives, Search methods, Selection criteria, Data collection and analysis, Main results, Authors’ conclusions Objective of the review: The purpose of this review was to explore the effect of hospital nurse‐staffing models on patient and staff‐related outcomes in the hospital setting, specifically to identify which staffing models are associated with: 1) better outcomes for patients, 2) better staff‐related outcomes, and, 3) the impact of staffing model(s) on cost outcomes. Search methods were (name the databases, etc.) CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase How many articles were found in the search? 69 How many of those articles were included in the review? 30 Author’s conclusions (summarize in your own words- DO NOT copy & paste The authors’ conclusion states that the evidence found in this article should be treated with caution because of the uncertainty to draw solid conclusions and because of the quality of the research. Having specialty nurses could possibly led to a small difference in patient outcome but not drastically. Cochrane Library Search and Find SECOND SEARCH: USE the SAME SEARCH TERM from 1st search. Now on the LEFT SIDE OF THE SCREEN: Adjust LIMITS for your search 1. TYPE remains INTERVENTION 2. Set DATE RANGE (may be the same) 3. CHOOSE A NEW TOPIC. My limits were: 1. TYPE: INTERVENTION 2. DATE RANGE: 03/01/2016-03/01/2020 3. TOPIC: Child health Choose a 2nd review. You may copy & paste any sections EXCEPT AUTHOR’S CONCLUSIONS 2nd Systematic Review title: Effectiveness of staffing models in residential, subacute, extended aged care settings on patient and staff outcomes Number of authors: 5 List the sections of the Abstract: Background, objectives, search methods, selection criteria, data collection and analysis, main results, authors’ conclusions Objective of the review: To identify which staffing models are associated with the best patient and staff outcomes. Search methods were (name the databases, etc.) CENTRAL, EPOC, MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHIL, Ageline How many articles were found in the search? 67 How many of those articles were included in the review? 19 Author’s conclusions (summarize in your own words- DO NOT copy & paste The two studies in the article are mainly in favor of patient care and demonstrate the best patient outcome but could be partially biased. Again, the evidence from these articles should be taken with caution because the evidence isn’t very clear as to which specific model of care works better for patients and health care providers. Below the “Abstract” should be a “Plain Language Summary.” In the box below compare/contrast the purpose of including both the Abstract and Plain Language Summary for Systematic Reviews in the Cochrane Library Database (hint - who is the audience, etc.). 50-100 words An abstract is a short paragraph about the purpose of the research article. It is always at the beginning of the article. A plain language summary also a short paragraph that focuses on the evidence from the article rather than an introduction. It describes the results from a systemic review in simple English that is understandable to a non-scientific audience. Both are used for clarity and to better grasp the concept of the research done.