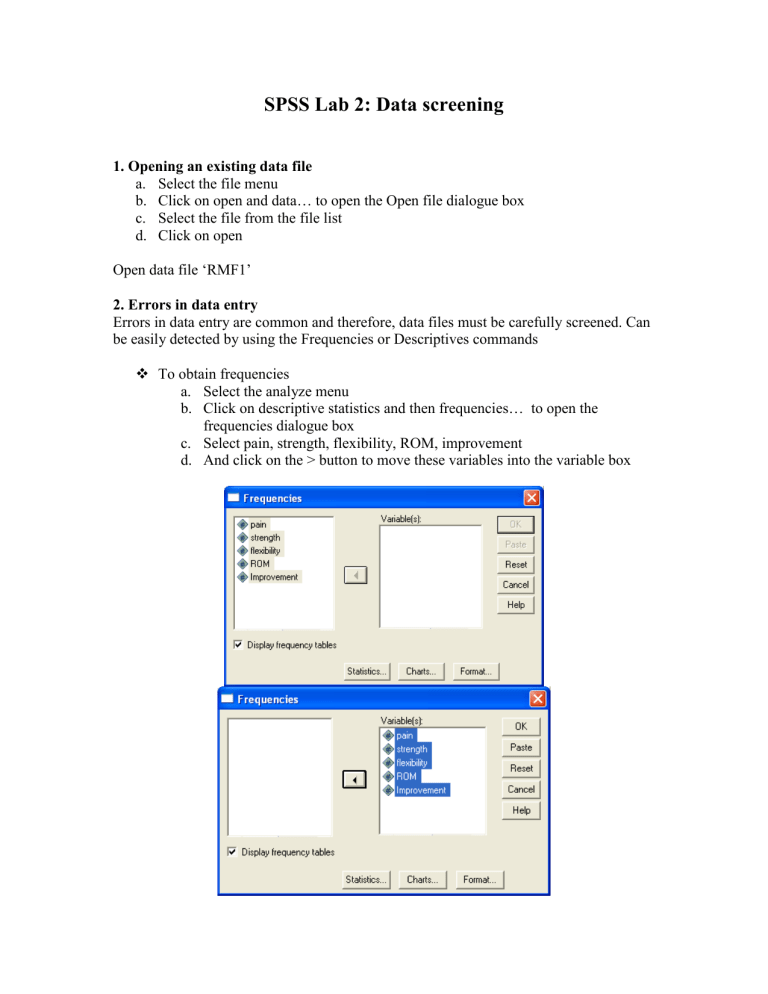
SPSS Lab 2: Data screening 1. Opening an existing data file a. Select the file menu b. Click on open and data… to open the Open file dialogue box c. Select the file from the file list d. Click on open Open data file ‘RMF1’ 2. Errors in data entry Errors in data entry are common and therefore, data files must be carefully screened. Can be easily detected by using the Frequencies or Descriptives commands To obtain frequencies a. Select the analyze menu b. Click on descriptive statistics and then frequencies… to open the frequencies dialogue box c. Select pain, strength, flexibility, ROM, improvement d. And click on the > button to move these variables into the variable box Frequencies Statistics pain N Valid Missing 22 0 strengt h 22 0 flexibility 22 0 ROM 22 0 Improvement 22 0 Frequency Table pa in Valid 2.00 3.00 4.00 5.00 6.00 7.00 8.00 Total Frequency 3 4 3 2 5 4 1 22 Percent 13.6 18.2 13.6 9.1 22.7 18.2 4.5 100.0 Valid Percent 13.6 18.2 13.6 9.1 22.7 18.2 4.5 100.0 Cumulative Percent 13.6 31.8 45.5 54.5 77.3 95.5 100.0 strength Valid 4.00 5.00 6.00 7.00 8.00 9.00 Total Frequency 1 4 6 5 4 2 22 Percent 4.5 18.2 27.3 22.7 18.2 9.1 100.0 Valid Percent 4.5 18.2 27.3 22.7 18.2 9.1 100.0 Cumulative Percent 4.5 22.7 50.0 72.7 90.9 100.0 fle xibi lity Valid poor good ex cellent Total Frequency 6 9 7 22 Percent 27.3 40.9 31.8 100.0 Valid Percent 27.3 40.9 31.8 100.0 Cumulative Percent 27.3 68.2 100.0 ROM Valid 12.00 13.00 14.00 15.00 16.00 21.00 22.00 Total Frequency 4 4 5 4 3 1 1 22 Percent 18.2 18.2 22.7 18.2 13.6 4.5 4.5 100.0 Valid Percent 18.2 18.2 22.7 18.2 13.6 4.5 4.5 100.0 Cumulative Percent 18.2 36.4 59.1 77.3 90.9 95.5 100.0 Improvement Valid no yes Total Frequency 7 15 22 Percent 31.8 68.2 100.0 Valid Percent 31.8 68.2 100.0 Cumulative Percent 31.8 100.0 3. Descriptive Statistics When we collect data, we sample from a population and, therefore, have several numbers from several different people. Generally, it is easier to refer to this group of data with one number, typically, the average or mean. The mean is a descriptive statistic for the data collected from the group. Other descriptive statistics of interest are the median, the range, the standard deviation and the standard error of the mean. We can get these descriptive statistics by clicking Analyse > Descriptive Statistics > Descriptives, selecting the desired variable (Pain) and dragging it into the Variable(s) box. Clicking the Options button will allow you to select further statistics, such as skewness. A better way to obtain the descriptive statistics is via the Explore function (Analyse > Descriptive Statistics > Explore) outlined below. 4. Assessing normality The assumption of normality is a prerequisite for many inferential statistical techniques. There are a number of different ways to explore this assumption graphically Histogram Stem and leaf plot Boxplot Normal probability plot Detrended normal plot Furthermore, a number of statistics are available to test normality Skewness Kurtosis Kolmogorov-Smirnov statistic, with a Lilliefors significance level and the Shapiro-Wilk statistic For our practical classes, we will use the SKEWNESS STATISTIC as the means to assess distribution when choosing a statistical test. There are several procedure available to obtain these graphs and statistics but the Explore procedure is the most convenient when both graphs and statistics are required. To obtain these graphs and statistics a. Select the analyze menu b. Click on Descriptive Statistics and the Explore… to open the Explore dialogue box c. Select the variable you require and click on the > button to move this variable into the Dependent List box d. Select the variable Pain e. Click on the Plots… command pushbutton to obtain the Explore: Plots subdialogue box. f. Click on the histogram check and the Normality plots with tests check box, and ensure that the Factor levels together radio button is selected in the Boxplots display. g. Click on Continue h. In the Display box, ensure that Both is activated i. Click on the Options….. command pushbutton to open the Explore: Options sub-dialogue box. j. In the Missing Values box, click on the Exclude cases pairwise radio button. If this option is not selected then, by default, any variable with missing data will be excluded from the analysis. That is, plots and statistics will be generated only for cases with complete data k. Click on Continue and then OK Results of output 1. Descriptive Statistics Table 2. Histogram Histogram 5 Frequency 4 3 2 1 Mean = 4.8182 Std. Dev. = 1.89326 N = 22 0 2.00 3.00 4.00 5.00 6.00 7.00 8.00 pain Above is the histogram of pain. The values on the vertical axis indicate the frequency of cases. The values on the horizontal axis are midpoints of value ranges. The shape of the distribution is considered abnormal 2. Boxplots 8.00 7.00 6.00 5.00 4.00 3.00 2.00 pain To determine whether a distribution is normal, you look at the median that should be positioned in the centre of the box. If the median is closer to the top of the box, then the distribution is negatively skewed, and if it is closer to the bottom of the box, then it is positively skewed. This boxplot is negatively skewed. 3. Normal probability plots In a normal probability plot, each observed value is paired with its expected value from the normal distribution. If the sample is from a normal distribution, then the cases fall more or less in a straight line. Normal Q-Q Plot of pain 2 Expected Normal 1 0 -1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Observed Value This is not normally distributed It is also possible to plot the actual deviations of the points from a straight line. If the sample is from a normal distribution, then there is no pattern to the clustering of points; the points should assemble around a horizontal line through zero. The plot below does not assemble around a horizontal line through zero. Detrended Normal Q-Q Plot of pain 0.3 Dev from Normal 0.2 0.1 0.0 -0.1 -0.2 -0.3 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Observed Value 4. Kolmogorov-Smirnov and Shapiro-Wilk Statistics The Kolmogorov-Smirnov statistic with a Lilliefors significance level for testing normality is produced with the normal probability and detrended probability plots. If the significance level is greater than 0.05 then normality is assumed. The Shapiro-Wilk statistic is also calculated if the sample size is less than one hundred. Tests of Normality a pain Kolmogorov-Smirnov Statistic df Sig. .188 22 .041 Shapiro-Wilk Statistic df .920 22 Sig. .075 a. Lilliefors Significance Correction The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was < 0.05 which would indicate that the data is not normally distributed. However, the Shapiro-Wilk test was >0.05 indicating that the data was normally distributed. Task Assess the other variables for normal distribution Answer 1. Strength Normally distributed Yes No Why? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Flexibility Normally distributed Yes No Why? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. ROM Normally distributed Yes No Why? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 4. Improvement Normally distributed Yes No Why? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________