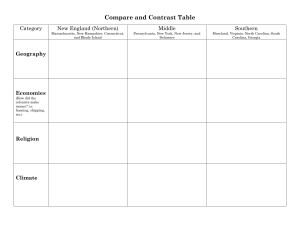
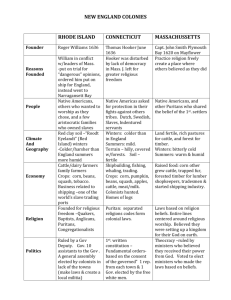
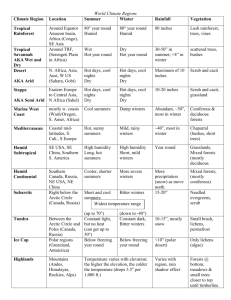
The New England Colonies Massachusetts Founders/Leaders William Bradford (1620 Pilgrims) New Hampshire Rhode Island John Wheelright (1638) Roger Williams Escape religious persecution in Massachusetts (Religious) Escape religious persecution in Massachusetts (Religious) John Winthrop (1630 Puritans) Anne Hutchinson (1644) Connecticut Thomas Hooker (1636) Reasons Founded Escape religious persecution in England (Religious) People Separatists known as British, Scottish, Irish Europeans Pilgrims and Puritans Native Americans Native Americans Dutch and Swedish Harbors Heavily forested Rocky Soil Hilly and Forested Rocky soil, heavy forest, fertile land Bitter cold winters with mild summers Bitter cold winters, warm and humid summers Rocky, fertile soil Colder Winters, short but humid summers Colder Winters, short but humid summers Shipping & Ship building Fishing, whaling Shipping Fishing, whaling Fur Shipping & Ship building Subsistence Farming Shipping & Ship building Lumber Fur Fishing Lumber Climate and Geography Economy Livestock and dairy farms Escape religious persecution in Massachusetts (Religious) Native Americans Subsistence Farming Livestock and dairy farms Rum-making Religious Views Lives centered around religious worship and the church Religious freedom Religious freedom Religious freedom Government Town meetings (self-government) Representative Assembly Town Meeting Town Meeting Governor and General Assembly Fundamental Orders of Connecticut (first written constitution) Laws based on religious beliefs Only white men in good standing with the church could vote The Middle Colonies (The Breadbasket Colonies) New York Founders/Leaders New Jersey Dutch Settlers (1624) Lord Berkley (1664) English (after military take-over) Pennsylvania William Penn (1681) Delaware Dutch Settlers English(after military take-over) Reasons Founded Profit (Economic) Profit and Trade (Economic) Escape from Profit and Trade religious persecution (Economic) in England Religious Freedom (Religious) (Religious) People Mixed Europeans (ethnic diversity/melting pot) Mixed Europeans (ethnic diversity/melting pot) Quakers and other religious groups Harbors Cold winters and hot, humid summers Fertile land with heavy forests Cool winters and mild/warm summers Hot, humid summers, cold winters forests Climate and Geography Fertile soil but had trees and rocks Longer growing season that New Hot humid summers, York bitter cold winters Moderate growing season Economy Farmers Fishing (“Breadbasket Colonies”) Merchants and tradesmen No natural harbor so not as much trade as NY Fur Small farms Lumber Dutch Swedish English Land contains iron ore Farms that produced lumber grains Fishing (“Breadbasket Colonies”) Dairy cattle Merchants and tradesmen lumber Shipping Religious Views Religious toleration Religious toleration Religious toleration Government Governor appointed by the King of England A royal colony where Political freedom colonists made their and self-government own local laws Representative (self-government) assembly Religious toleration Separate colony supervised by Pennsylvania’s governor The Southern Colonies Maryland Virginia North & South Carolina Georgia Founders/Leaders Lord Baltimore (1632) John Smith (Virginia Company 1607) Eight Lords who were friends with King Charles II (1663) Reasons Founded Religious Freedom for Catholics Investment to make money Given as a political gift New start for debtors who were in prison People Catholics Europeans seeking cheap land Europeans Debtors Indentured servants Europeans African slaves African slaves Chesapeake Bay was Mild winters, hot surrounded by fertile summers land Flat, fertile land Cold winters, hot Swampy in the east; and humid summers wooded mountains in the west Mild winters, hot summers Mild winters, hot summers Flat, fertile land Flat, fertile land Swampy in the east; wooded mountains in the west Swampy in the east; wooded mountains in the west Farms that raised grains, tobacco, flax crops such as tobacco, cotton, indigo and rice crops such as tobacco, crops such as cotton, indigo and rice tobacco, cotton, indigo and rice African slaves Climate and Geography Economy fishing James Oglethorpe (1732) Religious Views tolerant Church of England tolerant tolerant Government elected representatives House of Burgesses ruled by the King elected representatives to Common House of Assembly