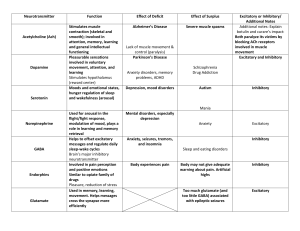
AP Psych Review Unit 1-history of Psych Subfields of psychology Biological Cognitive Etc William James Function over structure Wilhelm Wundt Introspection Freud Unconscious mind Skinner? Unit 2 – research methods Case study Survey Observations Unit 3 – Biology Brian page 101 Brainstem o Automatic survival Medulla o Controls hearts and breathing Thalamus o Relays messages Cerebellum o Controls balance Reticular Formation o Widespread connections o Reticular activation system Maintains Limbic system o Hypothalamus o pituitary gland o o amygdala emotions hippocampus memory Lobes o Frontal Abstract thinking o Partial Sensory o Temporal Hearing o Occipital Sight Neurotransmitter Acetylcholine (ACH) Dopamine Serotonin Norepinephrine GABA Glutamate Endorphins Type Function Problems with Surplus Excitatory – muscle function – learning and memory – attention Muscle spasms Alzheimer’s disease Inhibitory – mood and emotion – arousal Schizophrenia, drug addiction Parkinson’s disease Inhibitory – mood regulation – hunger and sleep Hallucinations Depression and mood disorders Excitatory – arousal and alertness, especially in fight-or-flight response – mood elevation Anxiety Mental disorders, specifically depression Inhibitory – brain’s main inhibitory neurotransmitter – regulates sleepwake cycles Sleep and eating disorders Anxiety, epilepsy, insomnia, Huntington’s disease Excitatory – brain’s main excitatory neurotransmitter – basis of learning and long-term memory Overstimulation of brain, which can cause migraines and seizures N/A Artificial highs, inadequate response to pain Potential involvement in addiction, especially opiates Inhibitory – pain control – stress reduction – positive emotions Problems with Deficit Unit 4 – Sensation and Perception 1. Physical energy received 2. Transduction 3. Action Eyes Retina Lens Cornea Pupil Rods (Detect light) o Located in the retina o 12 million Cones (Colors) o Located in the retina o 6 million Processing Bottom up processing Top down processing Ear flap Outer ear o Ear canal o Hammer Middle Ear o Anvil o Ear drum Inner ear o Cochlea o Auditory nerve o Eustachian tube Ear Place theory Different hairs vibrate in the cochlea when they hear different pitches Frequency theory All hair vibrate but at different speeds Unit 5 – States of consciousness Id – unconscious part of the mind Ego – conscious part of the mind Super ego – subconscious part of the mind Hypnosis Only people who allow themselves Sleep Circadian rhythms Waves Sleep cycle o REM Dreams Manifest content o Storyline Latent content o The reason for the dream o NREM-1 o NREM-2 o NREM-3 Sleep deprivation REM rebound o Increase of REM sleep after a night of little to no REM sleep Drugs Depressants o Relaxes the body o Slows bodily functions Stimulants o Speeds up bodily functions Hallucinogen o Causes hallucinations Unit 6 – Learning Operant conditioning Reinforcer o Positive reinforcement Add something desirable o Negative reinforcement Take away something unpleasant Punishment o Positive punishment o Negative reinforcement Classical conditioning Pavlov’s dogs Extinction Skinner Skinner box o Mouse presses a button and gets food Result: Teaches the mouse to press the button for food Watson Baby Albert experiment Unit 7 Memory Encoding (input) o Semantic meaning o Acoustic Sound o Visual sight Storage o Sensory memory Shortest of the memory Generally, 5 seconds o Working memory Short term memory Generally, 20 seconds o Long term memory Declarative memory Episodic memory o Tiny episodes Rehearsal Flashbulb memory Vivid memories Retrieval (output) Amnesia Retrograde o Make new memories Anterograde o Cannot make new memories Memory cues Recall Recognition Misinformation effect A reconstrued memory The question can cause this o How fast were the cars going when they bumped into each other? o How fast were the cars going when they smashed into each other? Language Babbling stage One-word stage Two-word stage Telegraphic speech People Loftus – psychologist Chomsky – linguist Unit 8 – Motivation, Emotion and Stress Motivation Drive reduction theory o When individuals experience a need or a drive, they’re motivated to reduce the drive Homeostasis o Instinct Theories Incentive Theories o Push and pull theory Drive theory Incentive theory Arousal theory o Yerkes-Dodson Law We perform most activities better when we are moderately aroused Stress and eating Emotions Physiological thoughts Expressive behaviors and conscious James-Lange Theory o Fear inside then fear outside Cannon-Bard o Fear in and our simulators Two-factor theory o Fear inside Thought Heart pounding o Fear outside Stress and Health Personality types Type A o o o Type B o o Competitive Hard driving Aggressive Easy going Relaxed Unit 9 People Freud o Psychosexual Piaget o Cognitive Erikson o Psychosocial Kohlberg o Moral Vygotsky o Cognitive (scaffolding) Harlow o Attachment The one with the money and the fake mothers Piaget Sensori-motor (birth-2 years) Preoperational (2-7 years) Concreate operational (7-11 years) Formal operational (12 years +) Kohlberg Preconventional o Punishment and obedience o Mutual Benefit Conventional Postconventional Authoritarian 95% of Indian parents o Super strict o Too many rules Passive Do whatever kids want o Not enough rules o Stupid Authoritative Passive and Authoritarian o Freedom with restriction Unit 10 – Personality Freud Psychoanalytic theory o Id – unconscious part of the mind o Ego – conscious part of the mind o Super ego – subconscious part of the mind Adler Psychodynamic Jung Psychodynamic Maslow Hierarchy of needs Humanistic Rogers Humanistic Bandura Triat Defense mechanisms Regression Reaction formation Displacement Personality tests Myers-Briggs OCEAN Unit 11 – Testing and individual behavior IQ Average score is 100 Used to place students in classes 𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝑐ℎ𝑟𝑜𝑛𝑜𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑖𝑐𝑎𝑙 𝑎𝑔𝑒 × 100 Reliability Test can be repeated and get similar scores Validity Test is supposed to test the material Gardner Eight intelligences o Interpersonal o Intrapersonal o Bodily-kinesthetic o Linguistic Binet Created the original IQ test Unit 12 – Abnormal behavior Anxiety disorders OCD o Excessive cleanliness Genialized Anxiety disorder o Anxiety all the time PTSD o Traumatic event causes extreme anxiety o Has a clear cause Phobia o Extreme fear Panic disorder o Panic attack Mood disorders Bipolar disorder o Mania to Depression Depression o 2 consecutive weeks to be diagnosed o Extreme sadness Personality Disorder Dissociative identity disorder o Split personality Eating disorder Bulimia Anoxia Unit 13 – Treatment of Abnormal behavior Therapy Client centered o Self understanding Psychodynamic o interpreting conflicts Behavioral o Teaching patients Cognitive Cognitive-behavioral Group and family Aversion o Classical conditioning Unit 14 – Social psychology Milgram Shock experiment Obedience Conformity Group think Ash Stanford prison experiment