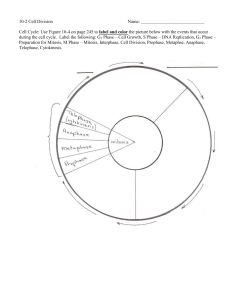
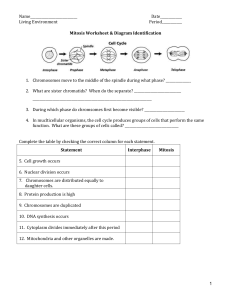
2.3 Cell Division and Death - Growth Development Maintaining health Healing from disease and injury Requires an intricate interplay between rate of mitosis and cytokinesis which divide the DNA and the rest of the cell, and apoptosis, a form of cell death. Adult – 30 trillion cells Cells die – normal development Apoptosis – “leaves falling from a tree” Genetically programmed sequence THE CELL CYCLE Cell cycle – series of events that enables a fertilized egg to develop into a many-trillion-celled organism Cell lining – small intestine’s inner wall Frequent mitosis -> rapid growth of fetus & embryo -> mitotic rate slows by birth -> mitosis maintains number and positions of specialized cells in tissues and organs TWO MAJOR STAGES: Interphase (not dividing) Mitosis (dividing) Mitosis (cell duplicates chromosomes) Cytokinesis (apportions/allocates one set of chromosomes, along with organelles, into each of two resulting cells called daughter cells) Meiosis (produces sperm or eggs, which have half the amount of genetic material that somatic cells do)