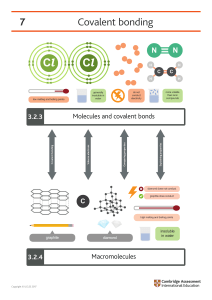
Covalent Bonding: Revision Questions Bronze: 1. What is a covalent bond? 2. What do covalent bonds form between? 3. Right the formula for the following molecules: nitrogen, oxegen, water, chlorine, carbon dioxide and hydrogen. 4. How many carbon atoms make up Buckminsterfullerene? 5. Draw dot-cross diagrams for: hydrogen chlorine, ammonia and chlorine. 6. Diamond and grafite are both giant covalent structures that are made from which element? Silver: 1. Fullerenes in the name used to describe what? 2. How many bonds does each carbon atom in a) diamond and b) graphite form? 3. Draw dot cross diagrams for: methane, oxygen and nitrogen. 4. Why does diamond have such a high melting point 5. State some of the potential uses of graphene, linking to it’s structure. 6. Looking at the dot cross diagram for ethane on the right, what is the molecular formula for this molecule? 7. Describe the following properties for simpel covalent substances: melting/boiling points and ability too conduct electricity. Gold: 1. Explain why substances that consist of small molecules are usually gasses or liquids with low melting/boiling points. 2. Diamond is used for drill bits, and graphite for electrodes and as a lubricant. explain these uses, linking to the properties. 3. Describe the limitations of using dot-cross, ball and stick and 2/3D diagrams to represent molecules or giant structures. 4. Compear and contrast the bonding in water with that of silicon dioxide. Link to the difference in boiling points, and why neither can conduct electricity. 5. Explain why CF4 has a lower boiling point that CCl4. 6. Explain, why the melting point of hydrogen chloride is -115oC, whereas sodium chloride’s melting point is 801oC. Find the 10 incorrect spellings/grammar errors and highlight in green pen.