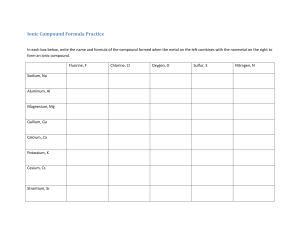
Predicting Products Type of Reaction Double Displacement (Precipitation) Both ionic solid reactants are soluble Switch cations to form products with other anions One new product is insoluble / forms a precipitate Verify which product is insoluble / (s) Properly formulate all compounds based on ionic charge Balance the equation Acid – Base Neutralization Acids begin with H+ion, Bases end with OH- ion Water is formed H(OH) H2O Other product is “salt” and is soluble Properly formulate all compounds based on ionic charge Balance the equation Single Displacement One reactant is a metallic element or a halide (F2, Cl2, Br2, I2) Switch lone element with its metallic or halide counterpart Properly formulate new compound based on ionic charge Balance the equation Combination (Synthesis) There will be only one product Metallic element and non-metallic element will form an ionic compound Properly formulate new compound based on ionic charge Balance the equation Decomposition There will be only one reactant It will break up into smaller compounds and / or elemental parts Binary ionic compounds can only break into elemental parts Balance the equation Combustion One reactant is a hydrocarbon (mostly hydrogen and carbon atoms) The other reactant is oxygen (O2) The two products formed in complete combustion are CO2 and H2O Balance the equation