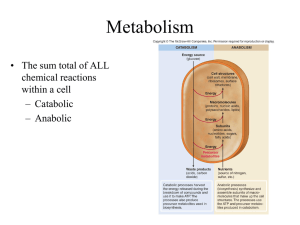
Adjei Frederick UEB3401318 Microbial Metabolism Metabolism is the sum total of chemical reactions in an organism which involves breaking down of complex substances to release energy or building up of complex substances from simple ones, metabolism in microbes is so unique and it helps them to survive in conditions other organisms cannot survive. Metabolism is divided into two classes; Catabolism, which is the breakdown of complex organic compounds into simpler ones to release energy, Anabolism, which is the building up of complex organic substances from simpler ones (it requires energy) Catabolic reactions provide building blocks and the energy needed for anabolic reactions, energy derived from catabolic reactions are stored in ATP(adenosine triphosphate). When a phosphate group is detached from ATP to produce ADP the energy stored is released and used to furnish a reaction mostly an anabolic reaction and after a catabolic reaction the energy produced adds a phosphate group to ADP to produce ATP. There are many pathways by which microbes produce energy these include; glycolysis, Krebs cycle, the electron transport chain, Doudroff pathway the pentose phosphate pathway and many others Some microbes can produce energy only in presence of oxygen others produce energy in the absence of oxygen some tolerate both conditions. Microbes can be identified in a test by looking for their intermediate substances and end product of their metabolic pathways, with this we can identified the organism into details; whether its aerobic or anaerobic, pathogenic or nonpathogenic. Microbial process that are widely used in the food industry, pharmaceuticals and in many other industries ie; Fermentation are very essential, fermentation it is any metabolic pathway that release energy from a sugar or other molecules and does not require oxygen, fermentation of ethanol, acetic acid, lactic acid, propionic acid, citric acid are very prominent in the food industry, fermentation of acetone, butanol, glycerol, sorbose are also very essential in the pharmaceutical industry. Other microbes are also essential to animal life they live in animals to help undertake many processes and help to prevent the entry of other pathogenic microbes