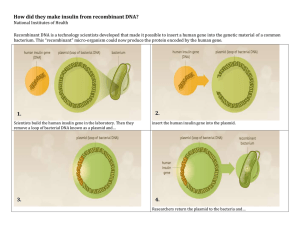
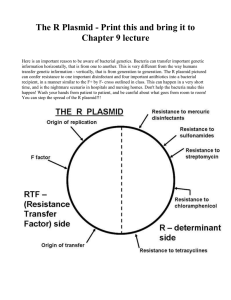
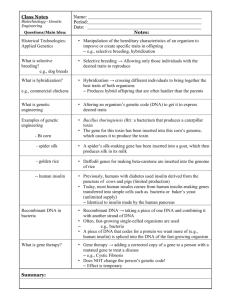
Monday, 10 February 2020 What is genetic engineering? Learning Objective: To identify why genetic engineering is carried out Learning Outcomes: Must define the term genetic engineering Should describe how genetic engineering is carried out Could evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of genetic engineering Starter Do you think the following plants and animals have been genetically engineered? Why would we want to be able to change the genes of an organism? Modern uses of genetic engineering: Finding out where genes are expressed in the body Manufacturing insulin Crops which produce a greater yield Crops resistant to disease But what is “Genetic Engineering”? • Genetic engineering is the deliberate modification (changing) of an organism’s genes. • GE = Genetic engineering • GM = Genetically modified (organisms which have been genetically engineered) Manufacturing Insulin Human cell Nucleus Chromosomes Gene for producing insulin Harmless Bacteria Plasmid (DNA) Insulin gene is removed using restriction enzymes Enzymes are used to cut open the Human insulin gene is placed in the Human insulin gene is placed in the Plasmid is replaced in bacteria Bacteria reproduce rapidly All of these bacteria have the gene to make human Genetic engineerin g in action The insulin these bacteria make saves lives every day Chromosomes 1 4 7 2 5 Insulin gene is removed using restriction enzymes Human insulin gene is placed in the plasmid 3 8 6 Plasmid is replaced in bacteria 9 Enzymes are used to cut open the plasmid 10 1. DNA taken from a human cell 2. Use a restriction enzyme to cut out the gene for insulin from the DNA 3. Use an enzyme called lysozyme to cut the Plasmid (ring of DNA) out of a bacterial cell 4. Use the same restriction enzyme to cut a section of DNA from the plasmid 5. Insert the gene for insulin into the plasmid 6. Use an enzyme called ligase to join the ends of the DNA 7. Put the plasmid with the insulin gene back into a bacterial cell 8. Leave the bacteria to divide Multiple copies of the bacteria which produces insulin 9. Insulin is removed and purified 10. Ready for use in humans! The process of cutting out a gene from the DNA of one organism and inserting it into the DNA of another is called gene splicing Task • Complete the revision grid to summarise your notes from today’s lesson • Include as much information as possible What is your opinion? • What are the advantages and disadvantages of genetic engineering? • What is your opinion? • Support each point that you make with evidence! Social, economical, ethical? Social How it affects groups of people. Economical Anything to do with money. Ethical People’s ideas of right and wrong. Social, economical, ethical? The issue 1. We have developed plants that are resistant to pests and disease. 2. Unborn children will be genetically screened and then aborted if their genetic make-up is faulty. 3. Cross pollination of GM crops could cause a natural ‘weed’ to become resistant to herbicides. 4. GE means we can produce crops that can grow in drought areas. 5. Parents could choose the genetic makeup of their child – known as ‘designer babies’. Social Economic Ethical