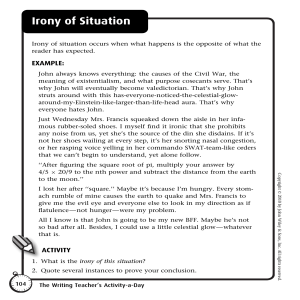
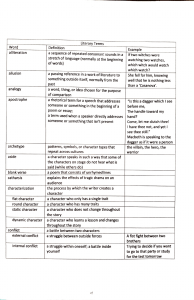
FIGURES OF SPEECH 1. Simile – indirect comparison using “like,” “as,” or “seem.” a. You eat like a pig! 2. Metaphor – direct comparison of two unlike things or ideas. a. Money is time. 3. Hyperbole – from “over-casting”; an exaggeration of ideas for the sake of emphasis. a. She nearly drowned in her tears. b. I am so hungry; I could eat a horse! 4. Apostrophe – from “turning away”; addressing an imaginary character (ie, non-existent person or an abstract idea) as if it were present and capable of understanding feelings. a. Mountains and hills, come and fall on me. b. Ninoy, are the Filipinos worth dying for? 5. Irony – words are used in such a way that their intended meaning is different from the actual meaning of the words. a. Verbal Irony – contrast between what is said and what is meant. i. It was very kind of you to remind me of my humiliation. b. Situational Irony – the contrast between the actual result of a situation and what was expected to happen. i. The student who did not study passed the test. c. Dramatic Irony – a situation in which the audience knows something that the character does not know. i. In a scary movie, the character walks into the house and the audience knows the killer is in the house. 6. Antithesis – juxtaposition of opposing or contradicting ideas (statements) in the sentence. a. Love is an ideal thing, marriage a real thing. 7. Oxymoron – conjoining contradictory terms or words. a. Deafening silence; bitter sweet; open secret; original copy; old news 8. Alliteration – series of words that begin with the same consonant. a. Fred fried frogs. 9. Assonance – repetition of vowel sounds. a. I feel depressed and restless. 10. Climax – structure of ideas from an important to most important idea. a. I came, I saw, I conquer. 11. Anticlimax - structure of ideas from an important to least important idea. a. We married, we got engaged, we met. 12. Metonymy – substituting the name of an attribute of something for the name of the thing itself. a. The pen is mightier than the sword. b. “Laurel” for glory; “guts” for courage; “sweat” for hardwork. 13. Onomatopoeia - the formation or use of words that imitate the sound associated with something. a. The thunder came roaring. b. The lighting flowed flashing. 14. Synecdoche - a figure of speech in which a part of something is used to represent the whole. a. “ABC’s” for alphabet; “a pair of eyes” for a person; “wheels” for car. 15. Periphrasis – the use of excessive and longer words to convey a meaning which could have been conveyed with a shorter expression or in a few words. a. The land of the rising sun – Japan 16. Personification - the attribution of human qualities to inanimate or abstract beings a. The trees are dancing. b. I see the moon smiling at me. 17. Rhetorical Question - a question asked for effect that neither expects nor requires an answer a. A person enters a dark room and asks out loud, has someone turned off the lights?