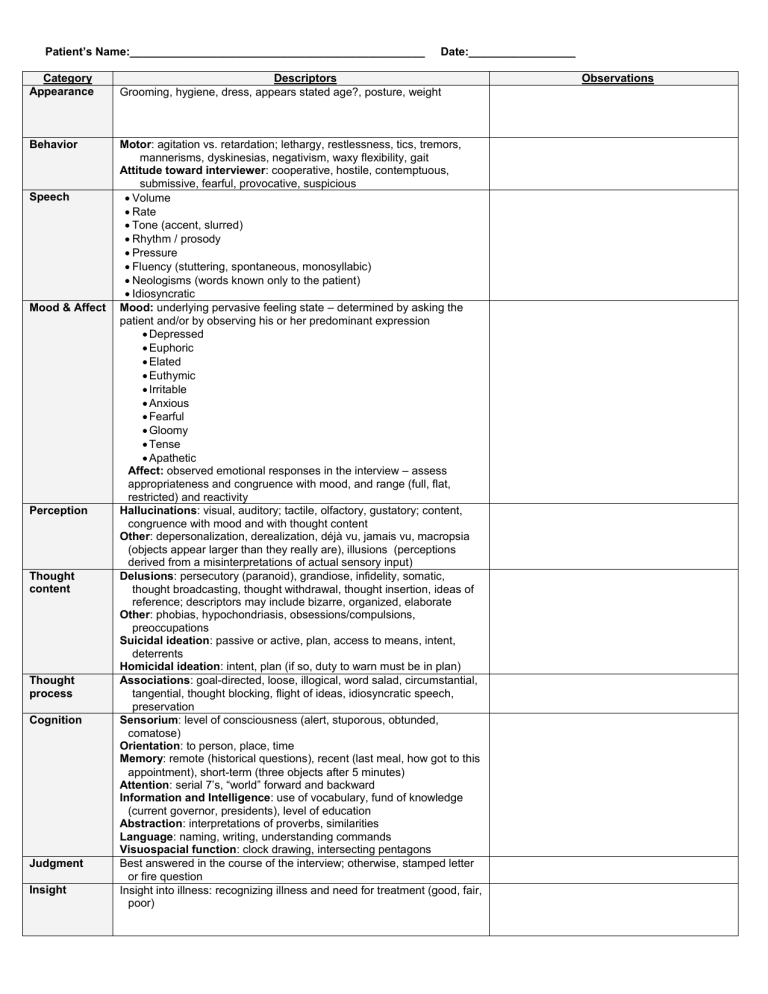
Patient’s Name:_______________________________________________ Date:_________________ Category Appearance Descriptors Grooming, hygiene, dress, appears stated age?, posture, weight Behavior Motor: agitation vs. retardation; lethargy, restlessness, tics, tremors, mannerisms, dyskinesias, negativism, waxy flexibility, gait Attitude toward interviewer: cooperative, hostile, contemptuous, submissive, fearful, provocative, suspicious Volume Rate Tone (accent, slurred) Rhythm / prosody Pressure Fluency (stuttering, spontaneous, monosyllabic) Neologisms (words known only to the patient) Idiosyncratic Mood: underlying pervasive feeling state – determined by asking the patient and/or by observing his or her predominant expression Depressed Euphoric Elated Euthymic Irritable Anxious Fearful Gloomy Tense Apathetic Affect: observed emotional responses in the interview – assess appropriateness and congruence with mood, and range (full, flat, restricted) and reactivity Hallucinations: visual, auditory; tactile, olfactory, gustatory; content, congruence with mood and with thought content Other: depersonalization, derealization, déjà vu, jamais vu, macropsia (objects appear larger than they really are), illusions (perceptions derived from a misinterpretations of actual sensory input) Delusions: persecutory (paranoid), grandiose, infidelity, somatic, thought broadcasting, thought withdrawal, thought insertion, ideas of reference; descriptors may include bizarre, organized, elaborate Other: phobias, hypochondriasis, obsessions/compulsions, preoccupations Suicidal ideation: passive or active, plan, access to means, intent, deterrents Homicidal ideation: intent, plan (if so, duty to warn must be in plan) Associations: goal-directed, loose, illogical, word salad, circumstantial, tangential, thought blocking, flight of ideas, idiosyncratic speech, preservation Sensorium: level of consciousness (alert, stuporous, obtunded, comatose) Orientation: to person, place, time Memory: remote (historical questions), recent (last meal, how got to this appointment), short-term (three objects after 5 minutes) Attention: serial 7’s, “world” forward and backward Information and Intelligence: use of vocabulary, fund of knowledge (current governor, presidents), level of education Abstraction: interpretations of proverbs, similarities Language: naming, writing, understanding commands Visuospacial function: clock drawing, intersecting pentagons Best answered in the course of the interview; otherwise, stamped letter or fire question Insight into illness: recognizing illness and need for treatment (good, fair, poor) Speech Mood & Affect Perception Thought content Thought process Cognition Judgment Insight Observations Patient’s Name:_______________________________________________ Date:_________________ Category Appearance Descriptors Grooming, hygiene, dress, appears stated age?, posture, weight Behavior Motor: agitation vs. retardation; lethargy, restlessness, tics, tremors, mannerisms, dyskinesias, negativism, waxy flexibility, gait Attitude toward interviewer: cooperative, hostile, contemptuous, submissive, fearful, provocative, suspicious Volume Rate Tone (accent, slurred) Rhythm / prosody Pressure Fluency (stuttering, spontaneous, monosyllabic) Neologisms (words known only to the patient) Idiosyncratic Mood: underlying pervasive feeling state – determined by asking the patient and/or by observing his or her predominant expression Depressed Euphoric Elated Euthymic Irritable Anxious Fearful Gloomy Tense Apathetic Affect: observed emotional responses in the interview – assess appropriateness and congruence with mood, and range (full, flat, restricted) and reactivity Hallucinations: visual, auditory; tactile, olfactory, gustatory; content, congruence with mood and with thought content Other: depersonalization, derealization, déjà vu, jamais vu, macropsia (objects appear larger than they really are), illusions (perceptions derived from a misinterpretations of actual sensory input) Delusions: persecutory (paranoid), grandiose, infidelity, somatic, thought broadcasting, thought withdrawal, thought insertion, ideas of reference; descriptors may include bizarre, organized, elaborate Other: phobias, hypochondriasis, obsessions/compulsions, preoccupations Suicidal ideation: passive or active, plan, access to means, intent, deterrents Homicidal ideation: intent, plan (if so, duty to warn must be in plan) Associations: goal-directed, loose, illogical, word salad, circumstantial, tangential, thought blocking, flight of ideas, idiosyncratic speech, preservation Sensorium: level of consciousness (alert, stuporous, obtunded, comatose) Orientation: to person, place, time Memory: remote (historical questions), recent (last meal, how got to this appointment), short-term (three objects after 5 minutes) Attention: serial 7’s, “world” forward and backward Information and Intelligence: use of vocabulary, fund of knowledge (current governor, presidents), level of education Abstraction: interpretations of proverbs, similarities Language: naming, writing, understanding commands Visuospacial function: clock drawing, intersecting pentagons Best answered in the course of the interview; otherwise, stamped letter or fire question Insight into illness: recognizing illness and need for treatment (good, fair, poor) Speech Mood & Affect Perception Thought content Thought process Cognition Judgment Insight Observations Patient’s Name:_______________________________________________ Date:_________________ Category Appearance Descriptors Grooming, hygiene, dress, appears stated age?, posture, weight Behavior Motor: agitation vs. retardation; lethargy, restlessness, tics, tremors, mannerisms, dyskinesias, negativism, waxy flexibility, gait Attitude toward interviewer: cooperative, hostile, contemptuous, submissive, fearful, provocative, suspicious Volume Rate Tone (accent, slurred) Rhythm / prosody Pressure Fluency (stuttering, spontaneous, monosyllabic) Neologisms (words known only to the patient) Idiosyncratic Mood: underlying pervasive feeling state – determined by asking the patient and/or by observing his or her predominant expression Depressed Euphoric Elated Euthymic Irritable Anxious Fearful Gloomy Tense Apathetic Affect: observed emotional responses in the interview – assess appropriateness and congruence with mood, and range (full, flat, restricted) and reactivity Hallucinations: visual, auditory; tactile, olfactory, gustatory; content, congruence with mood and with thought content Other: depersonalization, derealization, déjà vu, jamais vu, macropsia (objects appear larger than they really are), illusions (perceptions derived from a misinterpretations of actual sensory input) Delusions: persecutory (paranoid), grandiose, infidelity, somatic, thought broadcasting, thought withdrawal, thought insertion, ideas of reference; descriptors may include bizarre, organized, elaborate Other: phobias, hypochondriasis, obsessions/compulsions, preoccupations Suicidal ideation: passive or active, plan, access to means, intent, deterrents Homicidal ideation: intent, plan (if so, duty to warn must be in plan) Associations: goal-directed, loose, illogical, word salad, circumstantial, tangential, thought blocking, flight of ideas, idiosyncratic speech, preservation Sensorium: level of consciousness (alert, stuporous, obtunded, comatose) Orientation: to person, place, time Memory: remote (historical questions), recent (last meal, how got to this appointment), short-term (three objects after 5 minutes) Attention: serial 7’s, “world” forward and backward Information and Intelligence: use of vocabulary, fund of knowledge (current governor, presidents), level of education Abstraction: interpretations of proverbs, similarities Language: naming, writing, understanding commands Visuospacial function: clock drawing, intersecting pentagons Best answered in the course of the interview; otherwise, stamped letter or fire question Insight into illness: recognizing illness and need for treatment (good, fair, poor) Speech Mood & Affect Perception Thought content Thought process Cognition Judgment Insight Observations Patient’s Name:_______________________________________________ Date:_________________ Category Appearance Descriptors Grooming, hygiene, dress, appears stated age?, posture, weight Behavior Motor: agitation vs. retardation; lethargy, restlessness, tics, tremors, mannerisms, dyskinesias, negativism, waxy flexibility, gait Attitude toward interviewer: cooperative, hostile, contemptuous, submissive, fearful, provocative, suspicious Volume Rate Tone (accent, slurred) Rhythm / prosody Pressure Fluency (stuttering, spontaneous, monosyllabic) Neologisms (words known only to the patient) Idiosyncratic Mood: underlying pervasive feeling state – determined by asking the patient and/or by observing his or her predominant expression Depressed Euphoric Elated Euthymic Irritable Anxious Fearful Gloomy Tense Apathetic Affect: observed emotional responses in the interview – assess appropriateness and congruence with mood, and range (full, flat, restricted) and reactivity Hallucinations: visual, auditory; tactile, olfactory, gustatory; content, congruence with mood and with thought content Other: depersonalization, derealization, déjà vu, jamais vu, macropsia (objects appear larger than they really are), illusions (perceptions derived from a misinterpretations of actual sensory input) Delusions: persecutory (paranoid), grandiose, infidelity, somatic, thought broadcasting, thought withdrawal, thought insertion, ideas of reference; descriptors may include bizarre, organized, elaborate Other: phobias, hypochondriasis, obsessions/compulsions, preoccupations Suicidal ideation: passive or active, plan, access to means, intent, deterrents Homicidal ideation: intent, plan (if so, duty to warn must be in plan) Associations: goal-directed, loose, illogical, word salad, circumstantial, tangential, thought blocking, flight of ideas, idiosyncratic speech, preservation Sensorium: level of consciousness (alert, stuporous, obtunded, comatose) Orientation: to person, place, time Memory: remote (historical questions), recent (last meal, how got to this appointment), short-term (three objects after 5 minutes) Attention: serial 7’s, “world” forward and backward Information and Intelligence: use of vocabulary, fund of knowledge (current governor, presidents), level of education Abstraction: interpretations of proverbs, similarities Language: naming, writing, understanding commands Visuospacial function: clock drawing, intersecting pentagons Best answered in the course of the interview; otherwise, stamped letter or fire question Insight into illness: recognizing illness and need for treatment (good, fair, poor) Speech Mood & Affect Perception Thought content Thought process Cognition Judgment Insight Observations Patient’s Name:_______________________________________________ Date:_________________ Category Appearance Descriptors Grooming, hygiene, dress, appears stated age?, posture, weight Behavior Motor: agitation vs. retardation; lethargy, restlessness, tics, tremors, mannerisms, dyskinesias, negativism, waxy flexibility, gait Attitude toward interviewer: cooperative, hostile, contemptuous, submissive, fearful, provocative, suspicious Volume Rate Tone (accent, slurred) Rhythm / prosody Pressure Fluency (stuttering, spontaneous, monosyllabic) Neologisms (words known only to the patient) Idiosyncratic Mood: underlying pervasive feeling state – determined by asking the patient and/or by observing his or her predominant expression Depressed Euphoric Elated Euthymic Irritable Anxious Fearful Gloomy Tense Apathetic Affect: observed emotional responses in the interview – assess appropriateness and congruence with mood, and range (full, flat, restricted) and reactivity Hallucinations: visual, auditory; tactile, olfactory, gustatory; content, congruence with mood and with thought content Other: depersonalization, derealization, déjà vu, jamais vu, macropsia (objects appear larger than they really are), illusions (perceptions derived from a misinterpretations of actual sensory input) Delusions: persecutory (paranoid), grandiose, infidelity, somatic, thought broadcasting, thought withdrawal, thought insertion, ideas of reference; descriptors may include bizarre, organized, elaborate Other: phobias, hypochondriasis, obsessions/compulsions, preoccupations Suicidal ideation: passive or active, plan, access to means, intent, deterrents Homicidal ideation: intent, plan (if so, duty to warn must be in plan) Associations: goal-directed, loose, illogical, word salad, circumstantial, tangential, thought blocking, flight of ideas, idiosyncratic speech, preservation Sensorium: level of consciousness (alert, stuporous, obtunded, comatose) Orientation: to person, place, time Memory: remote (historical questions), recent (last meal, how got to this appointment), short-term (three objects after 5 minutes) Attention: serial 7’s, “world” forward and backward Information and Intelligence: use of vocabulary, fund of knowledge (current governor, presidents), level of education Abstraction: interpretations of proverbs, similarities Language: naming, writing, understanding commands Visuospacial function: clock drawing, intersecting pentagons Best answered in the course of the interview; otherwise, stamped letter or fire question Insight into illness: recognizing illness and need for treatment (good, fair, poor) Speech Mood & Affect Perception Thought content Thought process Cognition Judgment Insight Observations Patient’s Name:_______________________________________________ Date:_________________ Category Appearance Descriptors Grooming, hygiene, dress, appears stated age?, posture, weight Behavior Motor: agitation vs. retardation; lethargy, restlessness, tics, tremors, mannerisms, dyskinesias, negativism, waxy flexibility, gait Attitude toward interviewer: cooperative, hostile, contemptuous, submissive, fearful, provocative, suspicious Volume Rate Tone (accent, slurred) Rhythm / prosody Pressure Fluency (stuttering, spontaneous, monosyllabic) Neologisms (words known only to the patient) Idiosyncratic Mood: underlying pervasive feeling state – determined by asking the patient and/or by observing his or her predominant expression Depressed Euphoric Elated Euthymic Irritable Anxious Fearful Gloomy Tense Apathetic Affect: observed emotional responses in the interview – assess appropriateness and congruence with mood, and range (full, flat, restricted) and reactivity Hallucinations: visual, auditory; tactile, olfactory, gustatory; content, congruence with mood and with thought content Other: depersonalization, derealization, déjà vu, jamais vu, macropsia (objects appear larger than they really are), illusions (perceptions derived from a misinterpretations of actual sensory input) Delusions: persecutory (paranoid), grandiose, infidelity, somatic, thought broadcasting, thought withdrawal, thought insertion, ideas of reference; descriptors may include bizarre, organized, elaborate Other: phobias, hypochondriasis, obsessions/compulsions, preoccupations Suicidal ideation: passive or active, plan, access to means, intent, deterrents Homicidal ideation: intent, plan (if so, duty to warn must be in plan) Associations: goal-directed, loose, illogical, word salad, circumstantial, tangential, thought blocking, flight of ideas, idiosyncratic speech, preservation Sensorium: level of consciousness (alert, stuporous, obtunded, comatose) Orientation: to person, place, time Memory: remote (historical questions), recent (last meal, how got to this appointment), short-term (three objects after 5 minutes) Attention: serial 7’s, “world” forward and backward Information and Intelligence: use of vocabulary, fund of knowledge (current governor, presidents), level of education Abstraction: interpretations of proverbs, similarities Language: naming, writing, understanding commands Visuospacial function: clock drawing, intersecting pentagons Best answered in the course of the interview; otherwise, stamped letter or fire question Insight into illness: recognizing illness and need for treatment (good, fair, poor) Speech Mood & Affect Perception Thought content Thought process Cognition Judgment Insight Observations Patient’s Name:_______________________________________________ Date:_________________ Category Appearance Descriptors Grooming, hygiene, dress, appears stated age?, posture, weight Behavior Motor: agitation vs. retardation; lethargy, restlessness, tics, tremors, mannerisms, dyskinesias, negativism, waxy flexibility, gait Attitude toward interviewer: cooperative, hostile, contemptuous, submissive, fearful, provocative, suspicious Volume Rate Tone (accent, slurred) Rhythm / prosody Pressure Fluency (stuttering, spontaneous, monosyllabic) Neologisms (words known only to the patient) Idiosyncratic Mood: underlying pervasive feeling state – determined by asking the patient and/or by observing his or her predominant expression Depressed Euphoric Elated Euthymic Irritable Anxious Fearful Gloomy Tense Apathetic Affect: observed emotional responses in the interview – assess appropriateness and congruence with mood, and range (full, flat, restricted) and reactivity Hallucinations: visual, auditory; tactile, olfactory, gustatory; content, congruence with mood and with thought content Other: depersonalization, derealization, déjà vu, jamais vu, macropsia (objects appear larger than they really are), illusions (perceptions derived from a misinterpretations of actual sensory input) Delusions: persecutory (paranoid), grandiose, infidelity, somatic, thought broadcasting, thought withdrawal, thought insertion, ideas of reference; descriptors may include bizarre, organized, elaborate Other: phobias, hypochondriasis, obsessions/compulsions, preoccupations Suicidal ideation: passive or active, plan, access to means, intent, deterrents Homicidal ideation: intent, plan (if so, duty to warn must be in plan) Associations: goal-directed, loose, illogical, word salad, circumstantial, tangential, thought blocking, flight of ideas, idiosyncratic speech, preservation Sensorium: level of consciousness (alert, stuporous, obtunded, comatose) Orientation: to person, place, time Memory: remote (historical questions), recent (last meal, how got to this appointment), short-term (three objects after 5 minutes) Attention: serial 7’s, “world” forward and backward Information and Intelligence: use of vocabulary, fund of knowledge (current governor, presidents), level of education Abstraction: interpretations of proverbs, similarities Language: naming, writing, understanding commands Visuospacial function: clock drawing, intersecting pentagons Best answered in the course of the interview; otherwise, stamped letter or fire question Insight into illness: recognizing illness and need for treatment (good, fair, poor) Speech Mood & Affect Perception Thought content Thought process Cognition Judgment Insight Observations Patient’s Name:_______________________________________________ Date:_________________ Category Appearance Descriptors Grooming, hygiene, dress, appears stated age?, posture, weight Behavior Motor: agitation vs. retardation; lethargy, restlessness, tics, tremors, mannerisms, dyskinesias, negativism, waxy flexibility, gait Attitude toward interviewer: cooperative, hostile, contemptuous, submissive, fearful, provocative, suspicious Volume Rate Tone (accent, slurred) Rhythm / prosody Pressure Fluency (stuttering, spontaneous, monosyllabic) Neologisms (words known only to the patient) Idiosyncratic Mood: underlying pervasive feeling state – determined by asking the patient and/or by observing his or her predominant expression Depressed Euphoric Elated Euthymic Irritable Anxious Fearful Gloomy Tense Apathetic Affect: observed emotional responses in the interview – assess appropriateness and congruence with mood, and range (full, flat, restricted) and reactivity Hallucinations: visual, auditory; tactile, olfactory, gustatory; content, congruence with mood and with thought content Other: depersonalization, derealization, déjà vu, jamais vu, macropsia (objects appear larger than they really are), illusions (perceptions derived from a misinterpretations of actual sensory input) Delusions: persecutory (paranoid), grandiose, infidelity, somatic, thought broadcasting, thought withdrawal, thought insertion, ideas of reference; descriptors may include bizarre, organized, elaborate Other: phobias, hypochondriasis, obsessions/compulsions, preoccupations Suicidal ideation: passive or active, plan, access to means, intent, deterrents Homicidal ideation: intent, plan (if so, duty to warn must be in plan) Associations: goal-directed, loose, illogical, word salad, circumstantial, tangential, thought blocking, flight of ideas, idiosyncratic speech, preservation Sensorium: level of consciousness (alert, stuporous, obtunded, comatose) Orientation: to person, place, time Memory: remote (historical questions), recent (last meal, how got to this appointment), short-term (three objects after 5 minutes) Attention: serial 7’s, “world” forward and backward Information and Intelligence: use of vocabulary, fund of knowledge (current governor, presidents), level of education Abstraction: interpretations of proverbs, similarities Language: naming, writing, understanding commands Visuospacial function: clock drawing, intersecting pentagons Best answered in the course of the interview; otherwise, stamped letter or fire question Insight into illness: recognizing illness and need for treatment (good, fair, poor) Speech Mood & Affect Perception Thought content Thought process Cognition Judgment Insight Observations Patient’s Name:_______________________________________________ Date:_________________ Category Appearance Descriptors Grooming, hygiene, dress, appears stated age?, posture, weight Behavior Motor: agitation vs. retardation; lethargy, restlessness, tics, tremors, mannerisms, dyskinesias, negativism, waxy flexibility, gait Attitude toward interviewer: cooperative, hostile, contemptuous, submissive, fearful, provocative, suspicious Volume Rate Tone (accent, slurred) Rhythm / prosody Pressure Fluency (stuttering, spontaneous, monosyllabic) Neologisms (words known only to the patient) Idiosyncratic Mood: underlying pervasive feeling state – determined by asking the patient and/or by observing his or her predominant expression Depressed Euphoric Elated Euthymic Irritable Anxious Fearful Gloomy Tense Apathetic Affect: observed emotional responses in the interview – assess appropriateness and congruence with mood, and range (full, flat, restricted) and reactivity Hallucinations: visual, auditory; tactile, olfactory, gustatory; content, congruence with mood and with thought content Other: depersonalization, derealization, déjà vu, jamais vu, macropsia (objects appear larger than they really are), illusions (perceptions derived from a misinterpretations of actual sensory input) Delusions: persecutory (paranoid), grandiose, infidelity, somatic, thought broadcasting, thought withdrawal, thought insertion, ideas of reference; descriptors may include bizarre, organized, elaborate Other: phobias, hypochondriasis, obsessions/compulsions, preoccupations Suicidal ideation: passive or active, plan, access to means, intent, deterrents Homicidal ideation: intent, plan (if so, duty to warn must be in plan) Associations: goal-directed, loose, illogical, word salad, circumstantial, tangential, thought blocking, flight of ideas, idiosyncratic speech, preservation Sensorium: level of consciousness (alert, stuporous, obtunded, comatose) Orientation: to person, place, time Memory: remote (historical questions), recent (last meal, how got to this appointment), short-term (three objects after 5 minutes) Attention: serial 7’s, “world” forward and backward Information and Intelligence: use of vocabulary, fund of knowledge (current governor, presidents), level of education Abstraction: interpretations of proverbs, similarities Language: naming, writing, understanding commands Visuospacial function: clock drawing, intersecting pentagons Best answered in the course of the interview; otherwise, stamped letter or fire question Insight into illness: recognizing illness and need for treatment (good, fair, poor) Speech Mood & Affect Perception Thought content Thought process Cognition Judgment Insight Observations Patient’s Name:_______________________________________________ Date:_________________ Category Appearance Descriptors Grooming, hygiene, dress, appears stated age?, posture, weight Behavior Motor: agitation vs. retardation; lethargy, restlessness, tics, tremors, mannerisms, dyskinesias, negativism, waxy flexibility, gait Attitude toward interviewer: cooperative, hostile, contemptuous, submissive, fearful, provocative, suspicious Volume Rate Tone (accent, slurred) Rhythm / prosody Pressure Fluency (stuttering, spontaneous, monosyllabic) Neologisms (words known only to the patient) Idiosyncratic Mood: underlying pervasive feeling state – determined by asking the patient and/or by observing his or her predominant expression Depressed Euphoric Elated Euthymic Irritable Anxious Fearful Gloomy Tense Apathetic Affect: observed emotional responses in the interview – assess appropriateness and congruence with mood, and range (full, flat, restricted) and reactivity Hallucinations: visual, auditory; tactile, olfactory, gustatory; content, congruence with mood and with thought content Other: depersonalization, derealization, déjà vu, jamais vu, macropsia (objects appear larger than they really are), illusions (perceptions derived from a misinterpretations of actual sensory input) Delusions: persecutory (paranoid), grandiose, infidelity, somatic, thought broadcasting, thought withdrawal, thought insertion, ideas of reference; descriptors may include bizarre, organized, elaborate Other: phobias, hypochondriasis, obsessions/compulsions, preoccupations Suicidal ideation: passive or active, plan, access to means, intent, deterrents Homicidal ideation: intent, plan (if so, duty to warn must be in plan) Associations: goal-directed, loose, illogical, word salad, circumstantial, tangential, thought blocking, flight of ideas, idiosyncratic speech, preservation Sensorium: level of consciousness (alert, stuporous, obtunded, comatose) Orientation: to person, place, time Memory: remote (historical questions), recent (last meal, how got to this appointment), short-term (three objects after 5 minutes) Attention: serial 7’s, “world” forward and backward Information and Intelligence: use of vocabulary, fund of knowledge (current governor, presidents), level of education Abstraction: interpretations of proverbs, similarities Language: naming, writing, understanding commands Visuospacial function: clock drawing, intersecting pentagons Best answered in the course of the interview; otherwise, stamped letter or fire question Insight into illness: recognizing illness and need for treatment (good, fair, poor) Speech Mood & Affect Perception Thought content Thought process Cognition Judgment Insight Observations Patient’s Name:_______________________________________________ Date:_________________ Category Appearance Descriptors Grooming, hygiene, dress, appears stated age?, posture, weight Behavior Motor: agitation vs. retardation; lethargy, restlessness, tics, tremors, mannerisms, dyskinesias, negativism, waxy flexibility, gait Attitude toward interviewer: cooperative, hostile, contemptuous, submissive, fearful, provocative, suspicious Volume Rate Tone (accent, slurred) Rhythm / prosody Pressure Fluency (stuttering, spontaneous, monosyllabic) Neologisms (words known only to the patient) Idiosyncratic Mood: underlying pervasive feeling state – determined by asking the patient and/or by observing his or her predominant expression Depressed Euphoric Elated Euthymic Irritable Anxious Fearful Gloomy Tense Apathetic Affect: observed emotional responses in the interview – assess appropriateness and congruence with mood, and range (full, flat, restricted) and reactivity Hallucinations: visual, auditory; tactile, olfactory, gustatory; content, congruence with mood and with thought content Other: depersonalization, derealization, déjà vu, jamais vu, macropsia (objects appear larger than they really are), illusions (perceptions derived from a misinterpretations of actual sensory input) Delusions: persecutory (paranoid), grandiose, infidelity, somatic, thought broadcasting, thought withdrawal, thought insertion, ideas of reference; descriptors may include bizarre, organized, elaborate Other: phobias, hypochondriasis, obsessions/compulsions, preoccupations Suicidal ideation: passive or active, plan, access to means, intent, deterrents Homicidal ideation: intent, plan (if so, duty to warn must be in plan) Associations: goal-directed, loose, illogical, word salad, circumstantial, tangential, thought blocking, flight of ideas, idiosyncratic speech, preservation Sensorium: level of consciousness (alert, stuporous, obtunded, comatose) Orientation: to person, place, time Memory: remote (historical questions), recent (last meal, how got to this appointment), short-term (three objects after 5 minutes) Attention: serial 7’s, “world” forward and backward Information and Intelligence: use of vocabulary, fund of knowledge (current governor, presidents), level of education Abstraction: interpretations of proverbs, similarities Language: naming, writing, understanding commands Visuospacial function: clock drawing, intersecting pentagons Best answered in the course of the interview; otherwise, stamped letter or fire question Insight into illness: recognizing illness and need for treatment (good, fair, poor) Speech Mood & Affect Perception Thought content Thought process Cognition Judgment Insight Observations Patient’s Name:_______________________________________________ Date:_________________ Category Appearance Descriptors Grooming, hygiene, dress, appears stated age?, posture, weight Behavior Motor: agitation vs. retardation; lethargy, restlessness, tics, tremors, mannerisms, dyskinesias, negativism, waxy flexibility, gait Attitude toward interviewer: cooperative, hostile, contemptuous, submissive, fearful, provocative, suspicious Volume Rate Tone (accent, slurred) Rhythm / prosody Pressure Fluency (stuttering, spontaneous, monosyllabic) Neologisms (words known only to the patient) Idiosyncratic Mood: underlying pervasive feeling state – determined by asking the patient and/or by observing his or her predominant expression Depressed Euphoric Elated Euthymic Irritable Anxious Fearful Gloomy Tense Apathetic Affect: observed emotional responses in the interview – assess appropriateness and congruence with mood, and range (full, flat, restricted) and reactivity Hallucinations: visual, auditory; tactile, olfactory, gustatory; content, congruence with mood and with thought content Other: depersonalization, derealization, déjà vu, jamais vu, macropsia (objects appear larger than they really are), illusions (perceptions derived from a misinterpretations of actual sensory input) Delusions: persecutory (paranoid), grandiose, infidelity, somatic, thought broadcasting, thought withdrawal, thought insertion, ideas of reference; descriptors may include bizarre, organized, elaborate Other: phobias, hypochondriasis, obsessions/compulsions, preoccupations Suicidal ideation: passive or active, plan, access to means, intent, deterrents Homicidal ideation: intent, plan (if so, duty to warn must be in plan) Associations: goal-directed, loose, illogical, word salad, circumstantial, tangential, thought blocking, flight of ideas, idiosyncratic speech, preservation Sensorium: level of consciousness (alert, stuporous, obtunded, comatose) Orientation: to person, place, time Memory: remote (historical questions), recent (last meal, how got to this appointment), short-term (three objects after 5 minutes) Attention: serial 7’s, “world” forward and backward Information and Intelligence: use of vocabulary, fund of knowledge (current governor, presidents), level of education Abstraction: interpretations of proverbs, similarities Language: naming, writing, understanding commands Visuospacial function: clock drawing, intersecting pentagons Best answered in the course of the interview; otherwise, stamped letter or fire question Insight into illness: recognizing illness and need for treatment (good, fair, poor) Speech Mood & Affect Perception Thought content Thought process Cognition Judgment Insight Observations Patient’s Name:_______________________________________________ Date:_________________ Category Appearance Descriptors Grooming, hygiene, dress, appears stated age?, posture, weight Behavior Motor: agitation vs. retardation; lethargy, restlessness, tics, tremors, mannerisms, dyskinesias, negativism, waxy flexibility, gait Attitude toward interviewer: cooperative, hostile, contemptuous, submissive, fearful, provocative, suspicious Volume Rate Tone (accent, slurred) Rhythm / prosody Pressure Fluency (stuttering, spontaneous, monosyllabic) Neologisms (words known only to the patient) Idiosyncratic Mood: underlying pervasive feeling state – determined by asking the patient and/or by observing his or her predominant expression Depressed Euphoric Elated Euthymic Irritable Anxious Fearful Gloomy Tense Apathetic Affect: observed emotional responses in the interview – assess appropriateness and congruence with mood, and range (full, flat, restricted) and reactivity Hallucinations: visual, auditory; tactile, olfactory, gustatory; content, congruence with mood and with thought content Other: depersonalization, derealization, déjà vu, jamais vu, macropsia (objects appear larger than they really are), illusions (perceptions derived from a misinterpretations of actual sensory input) Delusions: persecutory (paranoid), grandiose, infidelity, somatic, thought broadcasting, thought withdrawal, thought insertion, ideas of reference; descriptors may include bizarre, organized, elaborate Other: phobias, hypochondriasis, obsessions/compulsions, preoccupations Suicidal ideation: passive or active, plan, access to means, intent, deterrents Homicidal ideation: intent, plan (if so, duty to warn must be in plan) Associations: goal-directed, loose, illogical, word salad, circumstantial, tangential, thought blocking, flight of ideas, idiosyncratic speech, preservation Sensorium: level of consciousness (alert, stuporous, obtunded, comatose) Orientation: to person, place, time Memory: remote (historical questions), recent (last meal, how got to this appointment), short-term (three objects after 5 minutes) Attention: serial 7’s, “world” forward and backward Information and Intelligence: use of vocabulary, fund of knowledge (current governor, presidents), level of education Abstraction: interpretations of proverbs, similarities Language: naming, writing, understanding commands Visuospacial function: clock drawing, intersecting pentagons Best answered in the course of the interview; otherwise, stamped letter or fire question Insight into illness: recognizing illness and need for treatment (good, fair, poor) Speech Mood & Affect Perception Thought content Thought process Cognition Judgment Insight Observations Patient’s Name:_______________________________________________ Date:_________________ Category Appearance Descriptors Grooming, hygiene, dress, appears stated age?, posture, weight Behavior Motor: agitation vs. retardation; lethargy, restlessness, tics, tremors, mannerisms, dyskinesias, negativism, waxy flexibility, gait Attitude toward interviewer: cooperative, hostile, contemptuous, submissive, fearful, provocative, suspicious Volume Rate Tone (accent, slurred) Rhythm / prosody Pressure Fluency (stuttering, spontaneous, monosyllabic) Neologisms (words known only to the patient) Idiosyncratic Mood: underlying pervasive feeling state – determined by asking the patient and/or by observing his or her predominant expression Depressed Euphoric Elated Euthymic Irritable Anxious Fearful Gloomy Tense Apathetic Affect: observed emotional responses in the interview – assess appropriateness and congruence with mood, and range (full, flat, restricted) and reactivity Hallucinations: visual, auditory; tactile, olfactory, gustatory; content, congruence with mood and with thought content Other: depersonalization, derealization, déjà vu, jamais vu, macropsia (objects appear larger than they really are), illusions (perceptions derived from a misinterpretations of actual sensory input) Delusions: persecutory (paranoid), grandiose, infidelity, somatic, thought broadcasting, thought withdrawal, thought insertion, ideas of reference; descriptors may include bizarre, organized, elaborate Other: phobias, hypochondriasis, obsessions/compulsions, preoccupations Suicidal ideation: passive or active, plan, access to means, intent, deterrents Homicidal ideation: intent, plan (if so, duty to warn must be in plan) Associations: goal-directed, loose, illogical, word salad, circumstantial, tangential, thought blocking, flight of ideas, idiosyncratic speech, preservation Sensorium: level of consciousness (alert, stuporous, obtunded, comatose) Orientation: to person, place, time Memory: remote (historical questions), recent (last meal, how got to this appointment), short-term (three objects after 5 minutes) Attention: serial 7’s, “world” forward and backward Information and Intelligence: use of vocabulary, fund of knowledge (current governor, presidents), level of education Abstraction: interpretations of proverbs, similarities Language: naming, writing, understanding commands Visuospacial function: clock drawing, intersecting pentagons Best answered in the course of the interview; otherwise, stamped letter or fire question Insight into illness: recognizing illness and need for treatment (good, fair, poor) Speech Mood & Affect Perception Thought content Thought process Cognition Judgment Insight Observations
![[100% HDQ]**[VIDEO] Sully Full HD online streaming Watch](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/018201909_1-d9e42526408b40da0a9798833ad4d3be-300x300.png)


