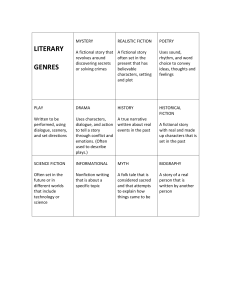
Literary Elements Plot—is the series of related events that make up the story Introduction-tells who the main character or characters are Complication—develop the characters and the struggles with different possible solutions Climax—main character makes a final decision Resolution—writer suggests what the characters feel or do, now the conflict is over and story is wrapped up Character—is a person or other figure that is part of a story. Setting—is the time and place in which story events occur. Theme—is the major idea or lesson that a story conveys about life Though there are exceptions, authors seldom state there intended them directly in so many words. It is usually up to the readers to discover the theme for themselves Some stories may have more than one theme Different readers may find different themes in the same story Tone—is the attitude or style of expression used to write Mood/Atmosphere—is the general feeling in a story. It refers to the emotion or emotions a writer makes the reader feel. Point of view—is the vantage point from which a story is told 1st person—main character in the story is telling the story (I, me, we…) 3rd person—we see the story events from the viewpoint of just one of the characters (he she….) Omniscient—the narrator knows what everyone in the story is feeling, thinking, and doing Figurative Language—refers to any language that uses images or language that makes different comparisons. Appeals to the senses Simile/metaphor Foreshadowing—means suggesting beforehand what is going to happen later in the story Flashback—occurs when the author tells about an even that happened before the time of the story Genre Poetry—verse that evokes an emotional response…instead of being written in paragraphs it is written in stanzas (Shel Silverstein books, Edger Allen Poe) Biography—is a nonfiction type of writing that talks about a person’s life or a specific event in a person’s life (The life of Helen Keller) Realistic Fiction—a story that is fictional, takes place in modern times and there is a possibility that the story could happen (Hank Zipzer stories) History—a story that is fictional, takes place in the past and the story could only happen in the setting that it is. Events are mixed with real and fictional events (Watsons go to Birmingham 1963, The Outsiders) Folk, Fairy Tales, and Mythology— (Johnny Appleseed, Hercules, Two Sisters) Does not have a single or identifiable author Originates in oral telling Fantasy or unrealistic elements Happened a long time ago or once upon a time Mystery—everything in the story revolves around a puzzle or unusual problem to solve (Chasing Vermeer or Nancy Drew) Fantasy—major events in the story could not really happen, it usually takes in modern times, and magic or impossible strategies are used to solve the conflict (Harry Potter) Science Fiction—major events in the story could happen, based on scientific facts that we know to be true, usually takes place in the future, and solve problems using scientific data.