Abstraction
A process of reducing complexity to formulate generalised fundamental ideas or concepts removed from specific details or situation. For example, the idea that a cricket ball is a sphere in the same way that a soccer ball is, or the concept that data can be organised in records made up of fields irrespective of whether the data are numbers, text, images or something else.
Address
Bar
Location in a web browser that displays the URL of the current page.
Aligment
How the content of a document
(text/graphics) is displayed in relation to the document's margins. Alignments include: Left aligned, right aligned, centred, and full justification.
Alt
A modifier key on your keyboard allowing additional actions when pressing keys or using the mouse.
Animation
Multiple images displayed quickly in sequence so that it appears to be seamlessly moving.
Application
A computer or tablet program.
Arrow
Keys
A set of keys on your keyboard allowing additional actions such as scrolling.
Attachment
A file that is sent along with an email.
Audio
Sounds produced by a computer or deivce.
Augmented
Reality
A technology that replicates, enhances or overlays extra information about the real-world environment, using computer-generated data such as global positioning systems (GPS), sound, videos and images. Examples include Pokemon
Go; a car windshield with a heads-up display that projects three-dimensional navigation information and virtual lanes; and a swimming telecast using a line to indicate the position of the record holder in relation to the actual swimmers in the race.
Avatar
An image that represents you online.
Backspace
Key on the keyboard which deletes text to the left of the cursor. In a browser it also allows you to go to the previous page.
Backup
An extra copy of a file or document.
Bee
-
Bot
Programmable floor robots that are in the shape of a bee.
Binary
A use of two states or permissible values to represent data, such as
ON and OFF positions of a light switch or transistors in a computer silicon chip that can be in either the electrical state of ON or OFF. Binary data are typically represented as a series of single digits referred to as binary digits (or bits) due to each taking on the value of either 0 or 1.
Bit
Smallest unit of data on a computer.
Can be either a 1 or a 0.
Block based programming language
Any programming language that lets users create programs by manipulating “blocks” or graphical programing elements, rather than writing code using text. Examples include
Code Studio, Scratch, Blockly, and Swift.
Blockly
The visual programming language used in Code.org's online learning system for K-5 students.
Blog
A website that was created to be an online journal.
Bluetooth
Short-range wireless technology that allows data to be transmitted wirelessly between devices.
Bold
A font weight which makes the selected text appear to be thicker and darker.
Bold
Not bold
Bookmark
A website link stored in the browser so you can easily access the website in the future.
Branching
Making a decision between one of two or more actions depending on sets of conditions and the data provided.
Browser
Software that allows you to graphically view information on the internet through the World
Wide Web. Examples include:
Chrome, Safari, Firefox, and
Internet Explorer.
Bug
An error in a program that causes incorrect or unexpected results.
Byte
8 bits combined together.
Cache
A temporary saved copy of everything you view online so webpages load faster.
Caps Lock
A key on the keyboard that makes all letters uppercase without holding the shift key down.
CAPTCHA
A graphic image (and audio for vision impaired) recognition test to confirm a human, rather than a computerautomated response to a request. It is an acronym for Completely Automated
Public Turing test to tell Computers and
Humans Apart. It is commonly used with online forms over the internet to reduce the chance of hackers using computer programs to automatically fill in multiple bogus online forms .
Character
Any number, symbol or letter typers.
! 1
# $ a n 4
>
Click
Pressing one of the mouse buttons down or pressing down on the trackpad.
Clip Art
Computer or hand drawn illustrations.
Clipboard
Specific location in computer memory used to store data that has been copied or cut.
Close
Exit out of a program or window.
Cloud
Online providing storage and computer services accessible via a browser. Cloud computing involves distributing computing over a network where storage of files, processing of data and/or access to software occurs automatically on interconnected server computers to which the user’s device is connected. Typically, people use the term to refer to accessing files and software over the internet.
Code
A set of algorithms and commands designed to be carried out by a computer.
Command
An instruction for the computer.
Many commands put together make up algorithms and computer programs.
Compression
A process of encoding information using fewer bits, that is,
0 or 1, than an original representation, to reduce file size – typically using mathematical formulas to remove repeated data, combine related data or simplify data (for example, a line segment can be represented by the position of the end points instead of every dot on it).
Comptational
Thinking
Mental processes and strategies that include: decomposition, pattern matching, abstraction, algorithms (decomposing problems into smaller, more manageable problems, finding repeating patterns, abstracting specific differences to make one solution work for multiple problems, and creating step-by-step algorithms).
Computer
An electronic machine that can store and process data. A computer has hardware, which is the machine itself, and software, which is a set of instructions.
Computer
Science
The study of computers and computational systems.
Conditionals
Statements that only run when certain conditions are met.
Control
A modifier key on a keyboard that allows users to perform a special operation. E.g. CTRL + C is copy
Cookie
File created by a web server through a browser to record your activities on a particular website.
Copy
Makes a duplication of the highlighted data and stores it in the clipboard.
CTRL + C
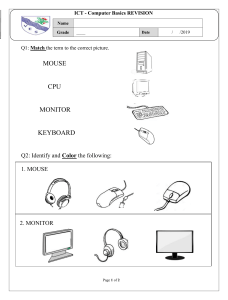
CPU
Central Processing Unit. The brains of the computer.
Crop
In computer graphics, to cut off the sides of an image to make it the proper size or to remove unwanted parts. Most graphics applications allow you to crop images with a clip feature.
Crowdsourcing
Getting help from a large group of people to finish something faster.
Cursor
Visual representation of your mouse movements on the computer screen.
Cut
Removes the highlighted content and stores it in the clipboard.
CTRL + X
Cyber bullying
Using technology to deliberately and repeatedly harass or harm others.
Data
Information stored on a computer.
Database
A place where data is organised and stored. It can be searched and updated.
Debugging
Finding and fixing errors in programs.
Desktop
The area of the screen in a computer where icons and windows appear.
Digital Citizen
An acceptance and upholding of the norms of appropriate, responsible behaviour with regard to the use of digital technologies. This involves using digital technologies effectively and not misusing them to disadvantage others. Digital citizenship includes appropriate online etiquette, literacy in how digital technologies work and how to use them, an understanding of ethics and related law, knowing how to stay safe online, and advice on related health and safety issues such as predators and the permanence of data.
Digital
Footprint
A digital trail you leave when you move through the internet.
Software can track your movements through the internet through your digital footprint.
Document
A file type that usually contains text and/or graphics.
Double
Click
Click the mouse button twice.
Used with both the left and right mouse buttons.
Download
Electronically transferring (saving) a file from the internet to a local computer.
Drag
Click and hold the mouse button down while moving the mouse.
Drag and
Drop
To do this, you click on something and hold the button down. This will move the object you clicked on and will leave it where you let go of the button. So it drags it and drops it.
Edit
Make changes to a file.
Eject
Remove media from the computer or device, such as a
DVD, a CD, or a USB flash drive.
Send a digital message to another person.
Encryption of data
A process in cryptography of encoding (converting) data, using mathematical formulas, into a form that only an intended recipient can decode, often including a personal digital signature (see digitally signed data). For example, when connecting to an online banking or shopping website, typically on login a secure communication is set up based on encryption provided at the website, and this will be represented by a https://URL and a lock symbol on the user’s internet browser.
Enter
A key on the keyboad that will submit information in a form, or allows you to skip to the beginning of the next line in a document.
File
A set of electornic records kept together.
File
Extension
Text after the period in a file name indicating what the file format is. E.g. .PDF is the file extension for portable Document
Files (PDF files).
File Transfer
Protocol
Transfer files back and forth between different computers.
Flash
Drive
A removable flash memory card format. These portable memory drives plug into a computer’s USB port.
Folder
Directory structure in a computer or deice that is visually represented with the image of a folder.
Font
A set of typed characters with particular size, typeface and style.
Footer
Text or images displayed at the bottom of a document.
For Loop
A loop with a beginning, end and incremental step.
Function
Code that performs a task and can be called over and over again.
GIF
Graphic Interchange File - An image file commonly used to make animated images.
To search for information about
(someone or something) on the
Internet using the search engine
Google.
Graphic
An image created using a computer.
Hardcopy
A paper printout of data displayed on the screen.
Hard
Drive
The hardware in a computer that reads and writes data.
Hardware
The physical components of a computer. E.g. CD -Rom drives, hard drives and CPU.
Header
Text or images found at the top of a document.
Headphones
Speakers that fit next to a person's ears alllowing a single person to hear audio from a device or computer.
Highlight
Using the mouse or input device to select text or image. The selected text or image will have a background different than normal.
Homepage
The first page you see when you open your browser. You can make any page your homepage.
Hyperlink
A link from a file or text to another file or location.
Icon
Graphical symbol that represents a computer/tablet application or data file.
Input
Enter data into a computer. A compuer mouse, keyboard and touch screen are all examples of ways to input data.
Internet
A worldwide network of computers connected together to transmit and exchange data.
iPad
A handheld computing device released by Apple Inc. The iPad is designed for consumers who want a mobile device that is bigger than a smartphone but smaller than a laptop for entertainment multimedia.
Italic
A font style with letters slanting to the right.
Italic
Not italic
Iteration
A repetition of a process or set of instructions in computer programming where each repeated cycle builds on a previous set of instructions.
JPEG
A lossy file format for JPEG file types. Best used for photographic images.
Key
A physical button on a keyboard.
Keyboard
Computer input device made of a set of keys.
Landscape
A document layout in which the document is wider than it is tall.
Laptop
A small portable computer.
Launch
Start or open a computer application.
Layout
The plan or visual design of a file. A common term used when desinging a graphical document or website.
Link
Shortened version or hyperlink.
Log In
/
Log On
Entering your username and password to a computer or website to gain access to files or systems.
Log
Out
/
Off
Will end the session for the computer or website you were logged into to. You will not be able to access your account until you log in again. Sometimes also called the Sign Out/Off, the
Log Out/Off button.
Loop
In a loop structure, the program asks a question, and if the answer requires an action, it is performed and the original question is asked again until the answer is such that the action is no longer required. For example, a program written to compute a company ’ s weekly payroll for each individual employee will begin by computing the wages of one employee and continue performing that action in a loop until there are no more employee wages to be computed, and only then will the program move on to its next action. Each pass through the loop is called an iteration. Loops constitute one of the most basic and powerful programming concepts.
Lossless
Compression
A type of compression algorithm that retains sufficient information to allow the original data to be perfectly reconstructed from the compressed data. It is used when it is important for the original data to be perfectly preserved, for example, in text documents, programming source code, application files or for archival purposes.
Lossy Compression
A type of compression algorithm that compresses data by discarding information that is not necessary to reproduce the original data with sufficient detail for the user not to notice the difference. It is used primarily for reducing the size of multimedia assets such as video, audio and photos, especially when streaming or transmitting the data over the internet. The original data cannot be restored from the compressed version, as is noticeable when attempting to increase the size of a compressed jpeg file.
Malware
Malicious software designed to interfere with the regular operation of a computer system.
Often used to gain access to other people’s computers or to gather sensitive information, it is usually hidden in other software to avoid user detection. Examples can include viruses, Trojan horses, key loggers and spyware. Anti-malware software is often relied on to help users detect and remove malware from their computers.
Margin
Blank space that surrounds the text on a page.
Maximise
Enlarge the window to full size/screen. Opposite of minimise.
Megabyte
1,000 kilobytes or 1,000,000 bytes.
Memory
This is the data that a computer stores. Long term memory must be saved to the hard drive.
Menu
A list of options available to a computer user.
Minimise
Shrink a program so it is no longer visible. The minimised program goes to the taskbar.
Modem
Device that uses a telephone or other communication line to connect to the internet.
Monitor
Output device that displays information from a computer.
Mouse
Input device that allows you to control the cursor on your computer screen.
Multimedia
A combination of text, graphics, sound, movies and animations.
Network
A system of connected computers. The internet is an example of a network.
Offline
Not connected to the internet.
Online
Connected to the internet.
Operating
System
Software that controls the running of computer programs.
Output
Data sent from the computer to be displayed on an output device. A monitor or a printer is a common output device.
Ozobot
Miniature robot.
Parameter
An extra piece of data passed to a function.
Password
A secret word or phrase that allows a user to access a system.
Paste
To copy an object from a buffer (or clipboard) to a file.
In word processing, blocks of text are moved from one place to another by cutting and pasting.
CTRL + V
Peripheral
Device
A digital component that can be connected to a digital system but are not essential to the system, for example, printer, scanner, digital camera.
Pixel
The smallest unit of an image or picture.
Portable
Document
Format
File format to display documents independent of the original software that created them.
Portrait
A page with portrait orientation, typical for letters, memos, and other text documents. It is taller than it is wide.
Preview
An image that shows how the document wil look after it is printed.
Data sent to the printer, creating a physical copy.
CTRL + P
Printer
An output device that prints data received from a computer or device.
Program
A sequence of instructions a computer can understand and run.
Programming
The process of creating a computer program.
RAM
Random Access
Memory. Short term computer memory that is used by programs when the computer is on.
Reboot
Turn off the computer/deivce then turn it back on.
Return
A key on the keyboard that will submit information in a form, or allows you to skip to the beginning of the next line in a document.
Right click
When you right click on the mouse, you are given a menu of options.
Save
Write or record data on a computer.
CTRL + S
Save As
Write or record data on a computer with a different file name, format or location.
Scanner
An input device which takes a physical image and digitises it.
Screen
The physical display on a computer monitor or device.
Script
Another term for macro or batch file, a script is a list of commands that can be executed without user interaction.
Scroll
Move through graphics or text that do not fit on the screen.
Search
Find a specific word or phrase.
Search
Engnine
Computer software or websites that allow you to do keyword searches to find information.
Select
Using an input device (such as a mouse) to highlight text or images which can be modified or changed.
Select All
Select everything in a file or on the screen.
CTRL + A
Sequence
One of the three basic logic structures in computer programming. The other two logic structures are selection and loop.
Server
A computer or device on a network that manages network resources.
Shift
A modifier key on the keyboard allowing letters to be typed in uppercase.
Software
A computer program.
Spam
This is an abbreviation for Sending Particularly
Annoying Messages. It stands for unwanted e-mail.
Sphero
A spherical robot.
Tab
Key on a keyboard or word processor that moves the cursor over a set space to the next tab marker.
Task bar
The bar beside the
Start button that shows what programs are open.
Text
Words.
Text
Box
In a software program, it is a box that is created to hold text or that text will be typed into.
Tool
Bar
A row of button icons that allow the user to quickly access menu commands, such as printing, launching a program or changing a file.
Transition
A visual effect added between the switching of two slides in a presentation.
Underline
Line drawn underneath text.
Undo
Cancel the last action that was performed.
CTRL + Z
Upload
Transfer a file from one computer to another. Examples are uploading files to the internet from your computer or uploading files from a flash drive to your computer.
URL
The address of documents and resources on the
Internet.
USB
Universal Serial Bus. A port on the computer allowing input and output devices to be plugged in.
Username
The name of a user's account in a network.
Variable
A placeholder for a piece of information that can change.
Virus
Computer software which is harmful to files or other programs on the computer.
While Loop
A continuous loop that runs while a condition is met.
Wi Fi
A wireless method of sending information using radio waves.
Window
A rectangular part of a computer screen that contains a display different from the rest of the screen.
World
Wide
Web
Group of Internet servers linking computers around the world.
Zoom
Make a particular area of the screen larger, showing more detail, or smaller, showing less detail.