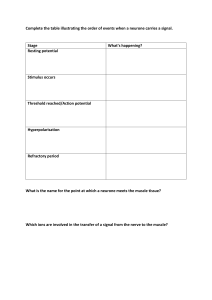
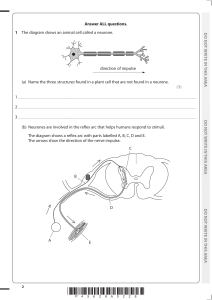
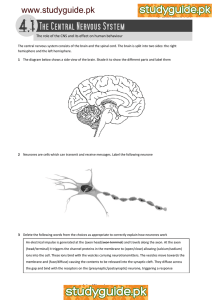
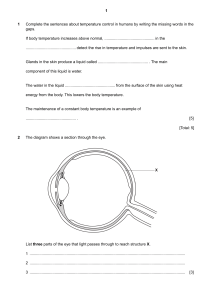
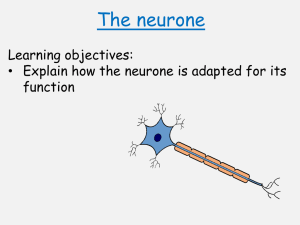
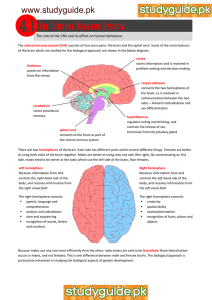
Synapses Voltage change during an action potential Outline the sequence of events that leads to an action potential being passed across a synapse. Label the diagram below to show which areas of the graph represent the following key words: resting potential, hyperpolarisation, resting potential restored, depolarisation, repolarisation, refractory period Non-myelinated neurones Outline how an action potential is transmitted through a non-myelinated neurone. Myelinated neurones Synapses Label the diagram of a synapse with as many key terms as possible. With reference to the diagram above, outline how an action potential is transmitted through a myelinated neurone Structure of neurones Resting potential Label the neurone with the following terms: cell body, axon, nucleus, dendrites, Schwann cells, nodes of Ranvier, axon terminals. Reflex arc Label the sensory, relay and motor neurones, a synapse, receptor and spinal cord. Describe how the structures above are used to maintain the resting potential of a cell. The cell above is a motor neurone. It carries electrical impulses from the central nervous system to the effector. Draw a simple sketch Action potential of and name where the following neurones transmit information from and to: Sensory neurone Relay neurone What is the: Stimulus? Effector? Receptors Receptor Energy change it detects Response? Definitions Generator potential Action potential Describe how the structures above are used to create an action potential following a stimulus in a cell.