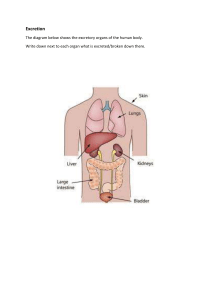
SNC 2D – UNIT REVIEW: BIOLOGY – TISSUES, ORGANS, and SYSTEMS of LIVING THINGS NOTE: Our test will be based on all that we have learned this unit, starting with cell theory, cell structure, and cell division, then moving on to plant systems, tissues/organs/organ systems, and applications related to stem cell research, medical imaging technology, and public health strategies. This review is only intended to be a guide. CHAPTER 2 – CELLS, CELL DIVISION, and CELL DIFFERENTIATION 1. List the three main components of Cell Theory. 2. What advancement in technology made it possible for Robert Hooke to study cells? 3. How can we calculate the total magnification of a microscope? What is the total magnification if obj. mag. = 10 and the oc. mag. = 10? 4. Be able to identify the following organelles and describe their function: cell membrane cytoplasm mitochondrion ribosome endoplasmic reticulum vacuole chloroplast cell wall cell plate nucleolus nucleus Golgi body 5. Compare and contrast the structure and the organelles found in plant and animal cells. 6. Explain the difference between diffusion and osmosis. What happens to a cell that is placed in an isotonic solution? Hypertonic? Hypotonic? 7. Define the following terms, then use all four in a coherent sentence: gene, DNA, chromosomes, nucleus 8. How many chromosomes are present in somatic cells? How many chromosomes are found in a human sperm or egg cell? 9. Why do multicellular organisms divide? List the three main reasons. 10. Summarize the three stages of the cell cycle. 11. Explain the major events that take place during interphase and describe each of the major checkpoints. 12. Identify and explain—using words and diagrams—the four phases of mitosis, and the key events that occur in each phase. 13. Explain how the two stages of cell division—mitosis and cytokinesis—are different. 14. How is cytokinesis in plant cells different from cytokinesis in animal cells? 15. Why do some cells in the body undergo mitosis more often than others? Give an example. 16. Define the following terms: tumour, benign tumour, malignant tumour, cancer 17. Review and be able to explain each of the medical imagining technologies discussed in your unit package, and what they are used for. 18. Define the following terms: cell differentiation, tissue, organ, organ system, organism, meristematic cell, stem cell (both kinds) CHAPTER 3 – ANIMAL SYSTEMS 1. Identify and describe the function of the four main types of tissue found in the human body, and provide examples of each. 2. Trace the passage of food through the following organs of the digestive system, beginning with the mouth. 3. Describe the structure and function of arteries, veins, and capillaries. 4. Be able to locate the following structures of the circulatory system: right atrium left atrium right ventricle pulmonary artery aorta left ventricle superior vena cava inferior vena cava 5. Be able to trace the passage of blood flow through the heart. 6. Name and trace the passage of air through the structures of the respiratory system, beginning with the nasal cavity. 7. Explain how the human circulatory and respiratory systems are related. What is coronary artery disease? What is a heart attack? 8. What is a public health strategy? Describe public health strategies related to AIDS, the West Nile Virus, and tobacco smoke. 9. Define the following terms and explain how they are used to ensure public health: vaccination, immunization, cancer screening, DNA screening 10. List the four components of blood, along with their composition and characteristics. 11. Explain how the liver, pancreas, and gall bladder work together in the human digestive system. What name is given to these organs? 12. In diabetic patients, what organ is affected? What enzyme is over- or under-produced in diabetic patients? 13. What are the alveoli? Where are they located? What is their function? CHAPTER 4 – PLANT SYSTEMS 1. Be able to label and describe the function of the following plant tissues/cells: dermal tissue ground tissue vascular tissue wax cuticle epidermal cells palisade tissue xylem cells phloem cells vascular bundle spongy mesophyll guard cells stomata 2. Explain the function of plant stems, roots, and flowers. 3. What is photosynthesis? What is transpiration? Explain these processes. 4. Which image represents a fibrous root system? A tap root system? Label the diagrams below. Label the 3 types of root tissue appendix SUGGESTED TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS Chapter 2 Review: p. 64, #4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 11, 12, 15, 19 p. 66, #6, 9, 10, 11, 15 Chapter 3 Review: p. 116, #1, 2, 5, 7, 8, 9, 11, 13, 16, 22 p. 118, #1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 9, 12, 17, 18, 19 Chapter 4 Review: p. 150, #1, 4, 5, 9, 11, 22, 23, 26, 27, 28 p. 152, #1, 3, 6, 8, 9, 22 Unit Review: p. 158, #1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 17, 18, 25, 51, 73