Atomic Structure Worksheet: Protons, Neutrons, Electrons
advertisement

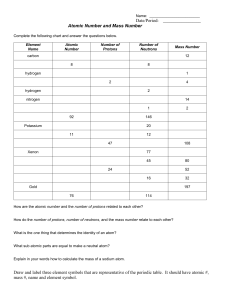
ATOMS: The Atom http://www.epsnews.eu/wp-content/uploads/2013/06/art_quantum.jpg Using page 4 of your Pearson Science 9 textbook, fill in the following table: Subatomic Particles Table: Subatomic particle Proton Neutron Electron Charge (positive, Where it can be negative or neutral) found in the atom Its mass in amu (atomic mass units) Nuclear Symbols: This is how an element is represented as a nuclear symbol: So helium would be written as Atomic Number: Using your Periodic Table, you will see that every element has an atomic number. For example, helium (He) above has an atomic number of 2. *Note that the symbols are always a capital letter if there is only 1 letter (such as H), and a capital letter followed by a lowercase letter if there are 2 letters (such as He). The atomic number = number of protons that the atom has. Atomic Mass: Atomic mass = number of protons + number of neutrons Using your periodic table, fill in the blanks for the first 20 elements below. Don’t forget that in order for the atom to be neutrally charged, the number of electrons = number of protons. The first two have been completed for you: Atomic number Element 1 Nuclear Symbol Atomic Mass (amu) Number of protons Number of neutron s Number of electron s Hydrogen 1 1 0 1 2 Helium 4 2 2 2 3 Lithium 7 3 4 Beryllium 9 4 5 Boron 6 Carbon 7 Nitrogen 8 Oxygen 9 Fluorine 4 3 7 6 14 7 8 19 6 8 9 10 Neon 10 11 Sodium 12 Magnesium 13 Aluminium 14 Silicon 15 Phosphorus 31 16 Sulfur 32 17 Chlorine 35 18 Argon 19 Potassium 20 Calcium 23 10 11 12 27 13 16 16 17 18 39 12 22 19