Cell Wall
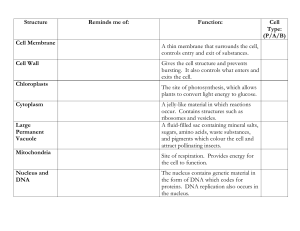
A strong layer around the cell membrane in plants, algae, and come bacteria.
Cell
Membrane
A thin flexible outer layer that protects and surrounds the cell.
Regulates what enters and leaves the cell
(selective permeable).
Nucleus
Contains the cell’s genetic material and controls the cell’s activities.
Nucleolus
Where the assembly of ribosomes begins.
Found in the nucleus.
Ribosomes
Small particles in the cell where proteins are made/assembled.
Attached or freefloating.
Nuclear
Envelope
Double-membrane layer that surrounds the nucleus of a cell.
Nuclear Pore
A tiny hole in the membrane that surrounds the nucleus of a cell. Allows material to move in and out of the nucleus.
Chromosome
A threadlike structure in the nucleus that contains the genetic information that is passed on from one generation to the next.
Golgi
Apparatus
A stack of membranes that modify, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for delivery to targeted destinations.
Mitochondria
Where cellular respiration occurs.
Involves the conversion of chemical energy in foods to chemical energy in ATP.
A network of protein
Cytoskeleton filaments to help the cell maintain its shape and help the cell with movement.
Smooth
Endoplasmic
Reticulum
Involved in the synthesis of lipids, oils, phospholipids, and steroids.
Rough
Endoplasmic
Reticulum
Makes additional membrane for itself and proteins destined for secretion.
Lysosome
Filled with digestive enzymes that surround and break down worn out cell parts.
Flagella
Propels a cell by a whip-like motion.
Arranged in a 9+2 pattern.
Cilia
Short hair-like structures that help some cells move. Arranged in a 9+2 pattern.
Chloroplast
Converts light energy to chemical energy of sugar molecules by photosynthesis.
Vacuole
Can provide structural support in plants. Also used as storage, waste disposal, and protection.
Vesicle
Help to move molecules from one place to another and secrete substances from the cell.
Pili
Help bacteria cells attach to specific surfaces or to other cells.