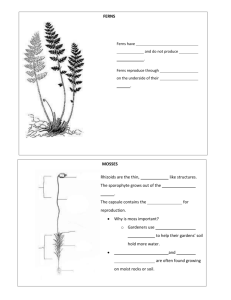
Nonvascular Plants Subtopics General Characteristics of Nonvascular Plants Bryophyta (mosses) Marchantiophyta (liverworts) Anthocerotophyta (hornworts) General Characteristics of Nonvascular Plants include the most primitive forms of land vegetation lack the vascular tissue system do not produce flowers, fruit, or seeds lack true leaves, roots, and stems typically appear as small, green mats of vegetation found in damp habitats exhibit alternation of generations and cycle between sexual and asexual reproductive phases Lack of Vascular Tissue System Metabolites and other nutrients are transferred between and within cells by osmosis, diffusion, and cytoplasmic streaming Cytoplasmic streaming is the movement of cytoplasm within cells for the transport of nutrients, organelles, and other cellular materials. Lack of genuine leaves, roots, and stems these plants have leaf-like, stem-like, and root-like structures that function similarly to leaves, stems, and roots have hair-like called rhizoids also filaments have a lobed leaf-like body called a thallus Alternations between sexual and asexual phases in their life cycles Gametophyte appears as green, leafy vegetation that remains attached to the ground or other growing surface. Sporophyte phase phase commonly appear as long stalks with sporecontaining caps on the end protrude from and remain attached to the gametophyte. Bryophyta (Mosses) small, dense plants that often resemble green carpets of vegetation Habitat thrive in moist areas and can grow on rocks, trees, sand dunes, concrete, and glaciers Mode of Nutrition acquire nutrients from the water and soil around them through absorption have rhizoids that keep them firmly planted to their growing surface Undergo photosynthesis in the thallus Ecological importance help to prevent erosion aid in the nutrient cycle, and serve as a source of insulation Reproduction in Mosses consists of a gametophyte phase and sporophyte phase develop from the germination of haploid spores that are released from the plant sporophyte Asexual reproduction is accomplished in mosses by fragmentation and gemmae development. Gemmae are cells that are contained within cup-like discs (cupules) formed by plant tissue in the plant body. Marchantiophyta (Liverworts) Their name is derived from the lobe-like appearance of their green plant body (thallus) that looks like the lobes of a liver. Two main types of liverworts Leafy liverworts closely resemble mosses with leaf-like structures that protrude upward from the plant base Thallose liverworts appear as mats of green vegetation with flat, ribbon-like structures growing close to the ground Habitat more commonly found in tropical habitats, but some species live in aquatic environments, deserts, and tundra biomes populate soil. areas with dim light and damp Mode of Nutrition acquire nutrients and water by absorption and diffusion also have rhizoids that function similarly to roots in that they hold the plant in place liverworts do not possess stomata to obtain carbon dioxide (they have air chambers below the surface of the thallus with tiny pores to permit gas exchange) Reproduction in Liverworts Anthocerotophyta (Hornworts) Have a flattened, leaf-like body (thallus) with long, cylindrically shaped structures that look like horns protruding from the thallus Habitat can be found around the globe and typically thrive in tropical habitats grow in aquatic environments, as well as in moist, shaded land habitats Mode of Nutrition Hornworts differ from mosses and liverworts in that their plant cells have a single chloroplast per cell have unicellular rhizoids that function to keep the plant fixed in place Reproduction in Hornworts https://www.thoughtco.com/non-vascular-plants-4126545 https://www.slideshare.net/Castro07apple/report-45854676 https://image.slidesharecdn.com/report-150315100333conversion-gate01/95/nonvascular-plants-6638.jpg?cb=1426414373 https://tentativeplantscientist.files.wordpress.com/2013/04/l eafy-and-thallose1.jpg https://image.slidesharecdn.com/liverworts-151006062625lva1-app6892/95/liverworts-5-638.jpg?cb=1444112895 https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images/wpcontent/uploads/sites/1842/2017/05/26231642/figure-25-0303f.jpeg http://www.mainevlmp.org/mciap/herbarium/images/Cer atDemFlower4.jpg https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/83/Ho rnwort_structures.jpg