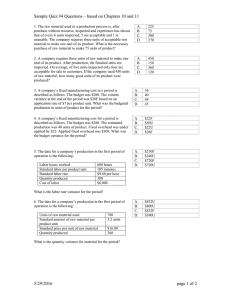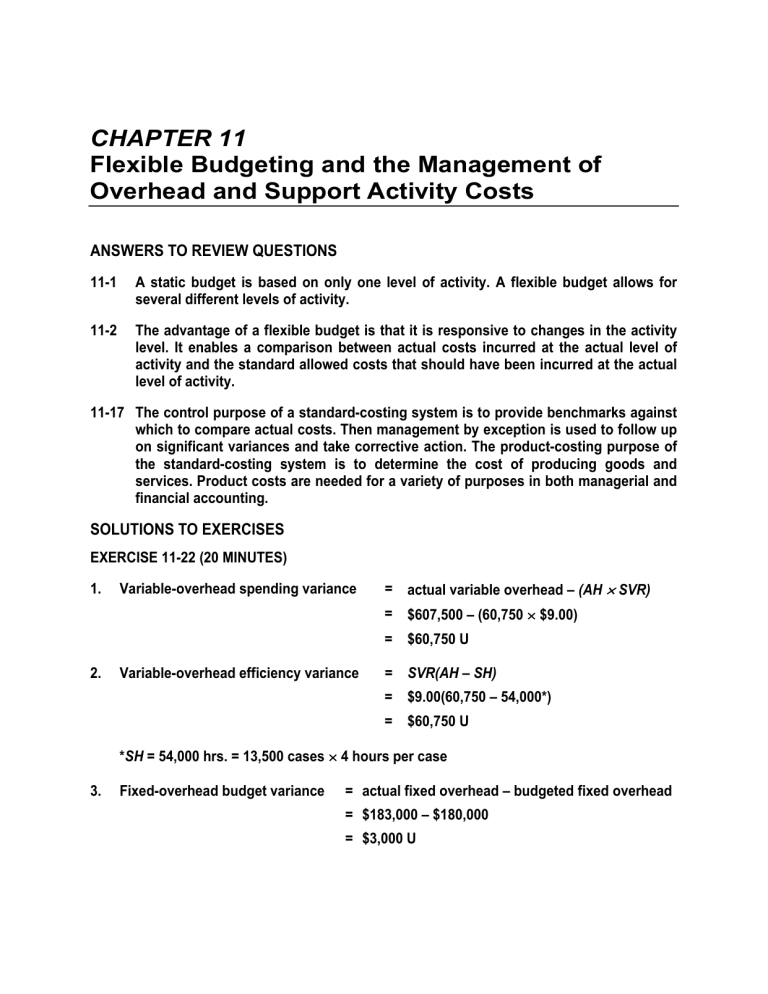
CHAPTER 11 Flexible Budgeting and the Management of Overhead and Support Activity Costs ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 11-1 A static budget is based on only one level of activity. A flexible budget allows for several different levels of activity. 11-2 The advantage of a flexible budget is that it is responsive to changes in the activity level. It enables a comparison between actual costs incurred at the actual level of activity and the standard allowed costs that should have been incurred at the actual level of activity. 11-17 The control purpose of a standard-costing system is to provide benchmarks against which to compare actual costs. Then management by exception is used to follow up on significant variances and take corrective action. The product-costing purpose of the standard-costing system is to determine the cost of producing goods and services. Product costs are needed for a variety of purposes in both managerial and financial accounting. SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES EXERCISE 11-22 (20 MINUTES) 1. Variable-overhead spending variance = actual variable overhead – (AH × SVR) = $607,500 – (60,750 × $9.00) = $60,750 U 2. Variable-overhead efficiency variance = SVR(AH – SH) = $9.00(60,750 – 54,000*) = $60,750 U *SH = 54,000 hrs. = 13,500 cases × 4 hours per case 3. Fixed-overhead budget variance = actual fixed overhead – budgeted fixed overhead = $183,000 – $180,000 = $3,000 U 4. Fixed-overhead volume variance = budgeted fixed overhead – applied fixed overhead = $180,000 – $162,000† = $18,000 (positive)** †Applied fixed overhead = ⎛ predetermined fixed ⎞ ⎛ standard allowed ⎞ ⎜⎜ ⎟⎟ × ⎜⎜ ⎟⎟ hours ⎝ overhead rate ⎠ ⎝ ⎠ = ⎛ $180,000 ⎞ ⎜ ⎟ × (13,500 × 4) ⎝ 15,000 × 4 ⎠ = $162,000 **Consistent with the discussion in the text, we choose not to interpret the volume variance as either favorable or unfavorable. Some accountants would designate a positive volume variance as "unfavorable" and a negative volume variance as "favorable." EXERCISE 11-30 (10 MINUTES) 1. 2. Flexible budgeted amounts, using activity-based flexible budget: a. Indirect material: $33,000 ($18,000 + $3,000 + $3,000 + $9,000) b. Utilities: $6,000 ($4,500 + $1,500) c. Inspection: $3,300 d. Test kitchen: $2,400 e. Material handling: $3,000 f. Total overhead cost: $64,800 ($45,000 + $7,800 + $2,400 + $3,000 + $6,600) Variance for setup cost: a. Using the activity-based flexible budget: $1,000 F (actual cost minus flexible budget = $3,500 – $4,500) b. Using the conventional flexible budget: $500 U (actual cost minus flexible budget = $3,500 – $3,000) EXERCISE 11-31 (45 MINUTES) Budgeted fixed overhead.................................................................... $ 25,000 Actual fixed overhead ........................................................................ $ 32,500a Budgeted production in units ............................................................ Actual production in units ................................................................. Standard machine hours per unit of output ..................................... Standard variable-overhead rate per machine hour ........................ Actual variable-overhead rate per machine hour............................. Actual machine hours per unit of output .......................................... Variable-overhead spending variance .............................................. Variable-overhead efficiency variance .............................................. Fixed-overhead budget variance ....................................................... Fixed-overhead volume variance....................................................... Total actual overhead.......................................................................... Total budgeted overhead (flexible budget)....................................... Total budgeted overhead (static budget).......................................... Total applied overhead........................................................................ 12,500 12,000c 4 hours $8.00 $9.00b 3d $ 36,000 U $ 96,000 F $ 7,500 U $ 1,000g (positive or U*) $356,500 $409,000e $425,000f $408,000 *Some accountants would designate a positive fixed-overhead volume variance as unfavorable. Explanatory Notes: a. Fixed-overhead budget variance = actual fixed overhead – budgeted fixed overhead $7,500 U = X – $25,000 X = $32,500 = actual fixed overhead b. Total actual overhead = actual variable overhead + actual fixed overhead $356,500 = X + $32,500 X = $324,000 = actual variable overhead Variable-overhead spending variance = actual variable overhead – (AH × SR) $36,000 U = $324,000 – (AH × $8) $8AH = $288,000 AH = 36,000 Actual variable-overhead rate per machine hour = actual variable overhead actual hours = $324,000 = $9 per hour 36,000 EXERCISE 11-31 (CONTINUED) c. Fixed-overhead rate = budgeted fixed overhead budgeted machine hours = $25,000 (12,500 units)(4 hrs. per unit) = $.50 per hr. Total standard overhead rate = standard variable overhead rate + fixed-overhead rate $8.50 = $8.00 + $.50 Total applied overhead = total standard hours × total standard overhead rate $408,000 = X × $8.50 X = 48,000 = total standard hrs. d. e. Actual production = total standard hrs. standard hrs. per unit = 48,000 = 12,000 units 4 Actual machine hrs. per unit of output = total actual machine hrs. actual production = 36,000 hrs. = 3 hrs. per unit 12,000 units Total budgeted overhead (flexible budget) = budgeted fixed overhead + (SVR × SH) = $25,000 + ($8.00 × 12,000 units × 4 hrs. per unit) = $409,000 EXERCISE 11-31 (CONTINUED) f. g. Total budgeted overhead (static budget) = ⎛ total standard ⎞⎛ budgeted ⎞⎛ standard hrs. ⎞ ⎜⎜ ⎟⎟⎜⎜ ⎟⎟⎜⎜ ⎟⎟ ⎝ overhead rate ⎠⎝ production ⎠⎝ per unit ⎠ = ($8.50)(12,500)(4) = $425,000 = budgeted fixed overhead – applied fixed overhead = $25,000 – ($.50)(12,000 × 4) = $1,000 (positive)* Fixed overhead volume variance *Consistent with the discussion in the text, we choose not to interpret the volume variance as either favorable or unfavorable. Some accountants would designate a positive volume variance as "unfavorable" and a negative volume variance as "favorable." PROBLEM 11-44 (40 MINUTES) 1. Susan Porter recommended that EduSoft use flexible budgeting in this situation because a flexible budget would allow Mark Fletcher to compare EduSoft's actual selling expenses (based on current month's actual activity) with budgeted selling expenses. In general, flexible budgets: • Provide management with the tools to evaluate the effects of varying levels of activity on costs, revenues, and profits. • Enable management to improve planning and decision making. • Improve the analysis of actual results. 2. EDUSOFT CORPORATION REVISED MONTHLY SELLING EXPENSE REPORT FOR OCTOBER Advertising ...................................................... Staff salaries ................................................... Sales salariesa ................................................. Commissionsb ................................................. Per diem expensec .......................................... Office expensesd ............................................. Flexible Budget $3,300,000 250,000 230,400 992,000 316,800 732,000 Actual $3,320,000 250,000 230,800 992,000 325,200 716,800 Variance $20,000 (U) 0 400 (U) 0 8,400 (U) 15,200 (F) Shipping expensese ........................................ Total expenses................................................ 1,985,000 $7,806,200 Supporting calculations: aMonthly salary for salesperson $216,000 ÷ 90 = $2,400. Budgeted amount $2,400 × 96 = $230,400. bCommission rate $896,000 ÷ $22,400,000 = .04. Budgeted amount $24,800,000 × .04 = $992,000. ÷ 90) ÷ 15 days = $220 per day. ($220 × 15) × 96 = $316,800. c($297,000 – 6,000,000) ÷ 54,000 = $40 per order. ($6,000,000 ÷ 12) + ($40 × 5,800) = $732,000. d($8,160,000 – ($6 × 2,000,000)] ÷ 12 = $125,000 monthly fixed expense. e[$13,500,000 $125,000 + ($6 × 310,000) = $1,985,000. PROBLEM 11-45 (45 MINUTES) Missing amounts for case A: 2. $21.00a per hour 3. $28.50b per hour 6. $294,150c 9. $7,500 Ud 10. $9,000 Fe 1,953,000 $7,787,800 32,000 (F) $18,400 (F) 11. $(126,000) (Negative)f (The negative sign means that applied fixed overhead exceeded budgeted fixed overhead.) 12. $24,150 underappliedg 13. $135,000 overappliedh 16. 6,000 unitsi 19. $270,000j 20. $756,000k Explanatory notes for case A: aBudgeted direct-labor hours = budgeted production × standard direct-labor hours per unit = 5,000 units × 6 hrs. = 30,000 hrs. Fixed overhead rate = = bTotal budgeted fixed overhead budgeted direct-labor hours $630,000 = $21per hr. 30,000 hrs. standard overhead rate = variable overhead rate + fixed overhead rate = $7.50 + $21.00 = $28.50 cVariable-overhead spending variance = actual variable overhead – (actual direct-labor hours × standard variable overhead rate) $16,650 U = actual variable overhead – (37,000 × $7.50) Actual variable overhead = $294,150 dVariable-overhead efficiency variance = SVR(AH – SH) = $7.50(37,000 – 36,000) = $7,500 U eFixed-overhead budget variance = actual fixed overhead – budgeted fixed overhead = $621,000 – $630,000 = $9,000 F fFixed-overhead volume variance = budgeted fixed overhead – applied fixed overhead = $630,000 – (36,000 × $21) = $126,000 (negative sign) gUnderapplied variable overhead = actual variable overhead – applied variable overhead = $294,150 – (36,000 × $7.50) = $24,150 underapplied hOverapplied fixed overhead = actual fixed overhead – applied fixed overhead = $621,000 – (36,000 × $21) = $135,000 overapplied iActual production jApplied = standard allowed direct-labor hours standard hrs. per unit = 36,000 = 6,000 units 6 variable overhead = SH × SVR = 36,000 × $7.50 = $270,000 kApplied fixed overhead = SH × fixed overhead rate = 36,000 × $21 = $756,000 Missing amounts for case B: 1. $4.00a per hour 2. $9.00b per hour 4. $25,600c 5. $72,000d 6. $32,000e 7. $76,320f 12. $6,400 underappliedg 13. $18,720 underappliedh 14. 1,000 unitsi 16. 800 unitsj 19. $25,600k 20. $57,600l Explanatory notes for case B: aTo find the standard variable overhead rate: Variable-overhead efficiency variance = SVR(AH – SH) $1,600 F = SVR(6,000 – 6,400) SVR = $4 bStandard fixed-overhead rate = total standard overhead rate – SVR = $13 – $4 = $9 cFlexible budget for variable overhead = SH × SVR = 6,400 × $4 = $25,600 dFlexible budget for fixed overhead = applied fixed overhead + volume variance = (6,400 × $9) + $14,400 = $72,000 eActual variable overhead = applied variable overhead + spending variance + efficiency variance = (6,400 × $4) + $8,000 U – $1,600 F = $32,000 fActual fixed overhead = budgeted fixed overhead + fixed-overhead budget variance = $72,000 + $4,320 U = $76,320 gUnderapplied variable overhead = spending variance + efficiency variance = $8,000 U* + $1,600 F* = $6,400 underapplied *Note that the signs cancel when adding variances of different signs. hUnderapplied fixed overhead = fixed-overhead budget variance + volume variance = $4,320 U + $14,400 (positive) = $18,720 underapplied iBudgeted direct-labor hours = = $72,000 $9 = 8,000 Budgeted production = = jActual production kApplied budgeted fixed overhead fixed-overhead rate budgeted direct-labor hours standard hours per unit 8,000 = 1,000 units 8 = standard allowed hours standard hours per unit = 6,400 = 800 units 8 variable overhead = SH × SVR = 6,400 × $4 = $25,600 lApplied fixed overhead = SH × standard fixed-overhead rate = 6,400 × $9 = $57,600