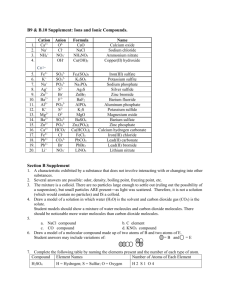
The Chemistry Name Game Contributed by Butane: The Carroll College Chemistry Club Main Science Idea for Kids As students play the Chemistry Name Game, they will learn why compounds form as they do. They will also learn how to correctly name chemical compounds and write chemical formulas. Grade Level 8th grade through high school How We Introduce this Activity We typically introduce this activity with an informal quiz about chemical formulas, asking students to tell us how many atoms are in a particular neutral ionic compound (e.g. How many aluminum atoms are in aluminum oxide?) or the name corresponding to a particular chemical formula. (e.g. What is the name of FeCl2?) This will give students a chance to think about the process and give the instructor an idea of just how well the students understand the concepts. The instructor should then continue the introduction by explaining the rules of the game and, more importantly, review the rules of naming for neutral ionic compounds and simple binary acids. The explanation of the rules for naming can also be done throughout the activity. Generally, students can gather in groups and are dealt a number of cards (see rules for the exact numbers). Then in a practice round, students should then take turns drawing cards and building neutral ionic compounds (i.e. a student who has one sodium ion and one chloride ion can make sodium chloride) where the number of dots exactly matches the number of holes. The instructor should ask all of the students to write each chemical formula and name each compound correctly. The instructor should also review the score for forming each compound. Scoring is described in step 5 of the procedure. This activity is a game but it is also meant to be a teaching tool for proper naming procedures. Students will hopefully learn by repeatedly practicing naming simple compounds. Instructors should emphasize team work and working together to have students teach and learn from each other. The instructor should move around to each group quizzing students on writing names and chemical formulas and provide guidance when required. Materials • • • • Playing cards o 100 cation cards including the alkali and alkaline earth metals and the most common transition elements in their most common oxidation states o 100 anion cards including the halogens, calcogens, and most basic polyatomic ions Game rules 4 or more score pads Pencils Optional For additional learning, samples of common household products can be made available to students to demonstrate the difference between similar compounds (e.g. sodium chloride and potassium chloride); in the event such products are used, goggles should be worn at all times. Notes about the Materials • The list of ions was based on a dry lab from J.A. Beran - Laboratory Manual for Principles of General Chemistry. • Each card has the name (in both the old system and the stock system) and the charge of the ion printed on the card. • All of the cation cards are printed with a corresponding number of "holes" (the holes are actually punched in the cards) to the appropriate oxidation state (a ferrous cation would have 2 holes while a ferric cation would have 3 holes). • Similarly, anion cards contain corresponding numbers of "dots" indicating the extra electrons available for bonding. • The dots on the cards are aligned such that a cation with two holes aligns exactly with the two dots of an anion card. • The cards may be used as a game with multiple players or as an individual study tool. Students can be given a list of chemical formulas or chemical compounds and use the cards to help write the other form. Procedure 1. Familiarize yourself with the guidelines for building and naming compounds. These are found at the Carroll College Chemistry Club website at http://orgs.cc.edu/chemclub/ChemistryNameGame.htm. 2. Shuffle the anion and cation cards together. Then deal cards to each player. The number of cards you deal will depend on the number of people playing. For example, 4 players would each receive 6 cards. 3. Each player then has the opportunity to draw a card from the top of the deck or take the top card from the discard pile. The current player has the opportunity to form neutral ionic compounds at any time during their turn. This is done by laying the cards out which make the complete compound (sodium chloride = 1 sodium cation + 1 chloride anion). For cards containing multiple dots or holes, the corresponding ion(s) must be the same (i.e. a compound made of 1 calcium cation, 1 chloride anion and 1 iodide anion is not a valid compound for this game). There are certainly exceptions to this rule, as upper level students might very well realize. 4. In addition to physically building the chemical compound with the cards the player has obtained, he or she must also write the correct chemical formula and the correct name of the chemical compound. 5. Scoring: The reward for building a correct chemical compound is receiving a number of points based on the number value of the cards played (i.e. sodium chloride would score 2 points, 1 point for the cation and one for the anion; similarly calcium chloride would score 4 points, two for the cation and one point for each of the anions). 6. At the end of each turn a player must discard one card from their hand unless they have made a compound in which they need to refill their hand. 7. When playing in a group there are three rounds, where each round ends after one player has successfully made 5 compounds (this can be changed as desired). The Chemistry Explanation This activity is designed to help students with naming chemical compounds and writing chemical formulas. It can also be used to help develop an understanding of balancing formulas and later chemical equations. Why We Like this Activity We like this activity because it brings some life to chemical naming, which many students find difficult and tedious. In addition it takes a different approach to learning than just repetition. This activity was developed based on the idea that people learn in different ways, and this game could be a tool for those who learn better "by doing". If students have a tool that they can use to understand the process rather than regurgitate the material, then they will be able to do assignments based on understanding rather than from repetition. About Us Butane frequently visits elementary schools and the local children’s museum to demonstrate of the wonders of chemistry to children and adults alike. They also educate and entertain middle school children who visit their campus each year. The members of Butane maintain a chemistry club website where they point to outstanding online science resources and answer science questions submitted by students, teachers, and parents. Butane: The Carroll College Chemistry Club Waukesha WI Ca 2+ calcium 2+ Sr strontium 2+ Ba barium 2+ Mg Ca 2+ calcium 2+ Sr strontium 2+ Ba barium 2+ Mg magnesium magnesium 3+ 3+ Al aluminum Al aluminum Ca 2+ calcium 2+ Sr strontium Ba 2+ barium 2+ Mg magnesium 1+ Rb rubidium 1+ Na sodium K 1+ Li 1+ Na sodium 1+ Na sodium potassium K 1+ potassium potassium 1+ Li 1+ 1+ lithium 1+ Rb rubidium C 4+ carbon lithium 1+ Cs cesium C 4+ carbon K 1+ Rb rubidium 1+ Cs cesium Li 1+ lithium Fe 2+ iron (II)/ferrous 3+ Fe Fe 2+ 3+ Fe iron (II)/ferrous iron (II)/ferric 4+ 4+ Sn Sn iron (II)/ferric tin(IV)/stannic tin(IV)/stannic 2+ 2+ 2+ Sn tin(II)/stannous 2+ Zn zinc 1+ Cu copper (I) cuprous Sn tin(IV)/stannous 2+ Cu copper (II) cupric 1+ Cu copper (I) cuprous Zn zinc 2+ Cu copper (II) cupric Cr 2+ chromium (II) chromous Cr 2+ Cr 2+ Cr 3+ Cr 3+ chromium (II) chromous chromium (II) chromous Pb Pb Pb Pb Pb Mn Mn Mn Co Co Co 4+ lead (IV) plumbic 2+ lead (II) plumbous 2+ manganese (II) manganous 2+ cobalt (II) cobaltous 4+ lead (IV) plumbic 2+ lead (II) plumbous 2+ manganese (II) manganous 2+ cobalt (II) cobaltous chromium (III) chromic chromium (III) chromic 2+ lead (II) plumbous 2+ manganese (II) manganous 2+ cobalt (II) cobaltous Hg 2+ mercury (II) mercuric Hg 2+ 2 Hg 2+ mercury (II) mercuric Hg 2+ 2 Hg 2+ mercury (II) mercuric Hg 2+ 2 mercury (I) mercurous mercury (I) mercurous Mn manganese (III) manganic Mn manganese (III) manganic Co 3+ Ni Ni Co 3+ 3+ 2+ nickel (II) 1+ Ag silver 3+ 2+ nickel (II) 1+ Ag silver mercury (I) mercurous cobalt (III) cobaltic cobalt (III) cobaltic 1+ Ag silver H 1+ hydrogen Fe 2+ iron (II)/ferrous 4+ Sn Cd tin(IV)/stannic Cd 2+ Ni 2+ cadmium nickel (II) Sc 3+ scandium 2+ cadmium 2+ Zn zinc 1+ Cu copper (I) cuprous Sc 3+ scandium 2+ Sn tin(II)/stannous Cd 2+ cadmium H 1+ hydrogen 2+ Cu copper (II) cupric Cs cesium 1+ 1+ NH4 ammonium H 1+ hydrogen NH4 ammonium H 1+ As arsenic 5+ As V 1+ NH4 ammonium Pb 4+ lead (IV) plumbic hydrogen 5+ arsenic 1+ 5+ vanadium V 5+ vanadium 1- Cl Cl I I chloride 1- chloride 1- 1- iodide 1- Cl I chloride 1- iodide 1- iodide 1- 1- Br Br Br O O O bromide bromide 2- oxide F bromide 2- oxide 1- fluoride F 1- fluoride 2- oxide F 1- fluoride 1- 1- 1- Cl Cl I I Br Br chloride chloride 1- 1- iodide F bromide bromide F OH O O 1- hydroxide 2- 2 peroxide 2- 2 2- 2 peroxide peroxide 3- 3- N nitride 1- hydroxide fluoride fluoride O 1- 1- 1- OH iodide N nitride 1- 1- OH OH OH hydroxide S 2- sulfide hydroxide S 2- sulfide 2- 1- hydroxide S 2- sulfide 2- 2- CO3 CO3 CO3 carbonate carbonate carbonate 2- 2- 2- SO4 SO4 SO4 sulfate sulfate sulfate 2- 2- 2- SO3 SO3 SO3 sulfite sulfite sulfite CN 1- cyanide 1- CN CN cyanide cyanide 1- 1- 1- 1- NO3 NO3 NO3 nitrate nitrate nitrate 1- 1- 1- NO2 NO2 NO2 nitrite nitrite 2- nitrite 2- CrO4 CrO4 chromate 2- chromate 2- 2- CrO4 chromate 2- Cr2O7 Cr2O7 Cr2O7 dichromate dichromate dichromate 1- 1- 2- HCO3 HCO3 S2O3 bicarbonate 1- ClO hypochlorite 1- ClO hypochlorite 1- bicarbonate thiosulfate 2- S2O3 thiosulfate 1- thiosulfate 1- ClO2 ClO2 chlorite chlorite 1- chlorate 1- ClO4 ClO perchlorate S2O3 1- ClO4 ClO3 perchlorate 2- hypochlorite 1- ClO3 chlorate 1- ClO2 chlorite 1- C2H3O2 acetate 3- 3- AsO4 AsO4 arsenate arsenate 1- 1- C2H3O2 C2H3O2 acetate 3- BO3 borate 3- PO3 phosphite 3- PO4 phosphate acetate 2- C2O4 oxalate 3- BO3 borate 2- C2O4 oxalate 3- PO3 phosphite 3- PO4 phosphate P P 3- phosphide 3- phosphide 1- 2- 2- HCO3 MnO4 MnO4 bicarbonate manganate 2- 1- manganate 1- MnO4 MnO4 MnO4 manganate permanganate 1- 2- permanganate 1- ClO4 C2O4 MnO4 perchlorate 1- ClO3 chlorate oxalate permanganate