AM2 U2 Gilded Age and Progressivism with Infusion updated July 11, 2019
advertisement

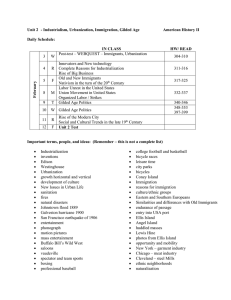
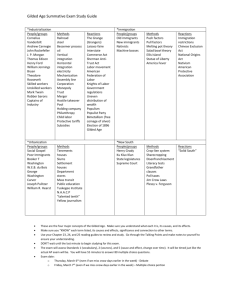
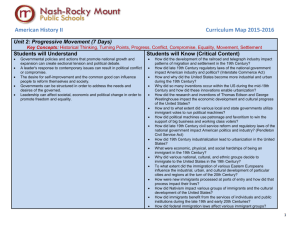
WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer Subject(s) Social Studies Grade/Course American History 2 Unit of Study Unit 2: Industrialism, Urbanization, Immigration, the Gilded Age and Progressivism (3.4, 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 5.1, 8.1, 8.3, 8.4) Unit Title The Gilded Age and Progressivism Pacing 12 Days Conceptual Lenses ● Urbanization ● Immigration ● Power ● Reform Unit Overview The second unit of American History 2 examines the Gilded Age and Progressive Era through the lenses of urbanization, immigration, power and reform. The Gilded Age: Industrialization and Immigration By the 1880s, industrialization takes hold of the northern and Midwestern portions of the United States. Technological innovations helped speed up production in factories and aided in the growth of cities. Urbanization reaches new heights, both figuratively and literally. Not only do many Americans migrate to the cities to find work, but the hope for work and a chance at the “American Dream” brings millions of immigrants to the United States. From 1870 to 1900, approximately twelve million immigrants arrived in the United States. The majority of these immigrants traveled from Europe and were processed on the East Coast at Ellis Island, while a smaller number of immigrants, mostly from Asia, entered the United States through the western processing center at Angel Island. These “huddled masses” endured long voyages in hopes of improving their quality of life. Once through the stressful ordeal of being processed, most of the immigrants traveled to large cities, settled in neighborhoods that became distinct ethnic communities, and became factory workers. The Gilded Age: Political Machines and Captains of Industry Local and state politicians would use the naivety of immigrants to gain votes and secure their positions of power. Once in power, a system of patronage and favoritism was used to maintain their power in the political arena, essentially creating “political machines”. “Political machines” could be found in major cities around the country, and once in place, they were difficult to dismantle and riddled with corruption. The politicians in control would use their power to grant favors to businesses and workers in return for monetary support and votes. By supporting “political machines”, industrialists were able ensure a “laissez faire” government that would not interfere with business practices. These practices included a variety of measures to increase the wealth and power of large business owners, often at the expense of small businesses, workers, and consumers. “Robber Barons” and “Captains of Industry” were able to rise to the top by eliminating competition through the creation of monopolies. While many defended their business tactics and treatment of workers by citing Darwin’s “survival of the fittest” theory, others used their money and power to give back to the communities. Progressivism: Moving Towards Reform Rapid urbanization presented new obstacles for cities. Sanitation and housing became major issues as the population in major cities grew. Concerns over fire safety grew as top floors in buildings became out of reach for longest fire department ladders. The masses needed a way to decompress and enjoy the little leisure time they had. Some of these obstacles would be fuel for the Progressive Era and help change the nature of American entertainment. Life in urban areas changed as a result of the huge numbers of immigrants. The mass influx of diverse cultures led to the development of ethnic neighborhoods that continued the cultural aspects of “home”. Unfortunately, life in the big city was filled with hardship. Most immigrants, as well as poor Americans, lived in overcrowded tenements. The monotony of factory work, along with long hours and low wages, took their toll on workers’ morale. Hope waned for labor reform due to the “laissez faire” attitude in government. As a result of the frustration, workers began to unite and form labor unions. People, like Terrance Powderly, Samuel Gompers, and Eugene Debs, helped workers organized and fight for better pay, shorter hours, and safer working conditions. Through tactics like arbitration and strikes, labor unions hoped to improve the lives of both skilled and unskilled workers. Though few gains were made by the end of the 19th Century, the work of labor unions would increase the demand for major reform. A foreshadowing of serious reform came with the collapse of patronage, which fueled the “political machines”. In 1883, the Pendleton Civil Service Act changed the way in which government positions were granted. No longer could elected officials pack their offices with friends. Instead, positions had to be filled by those qualified for the position. The Pendleton Civil Service Act was yet another sign of the reforms to come. Progressivism: Reform The momentum for the Progressive Era grew with the muckraking done by journalists at the end of the 19th Century and beginning of the 20th Century. Muckrakers brought to light the living conditions of the urban poor, infiltrated factories to uncover the horrifying truths of food production and worker hardship, exposed the corruption in big cities, and reported the abuses of big business. These actions opened the door for reform. Presidents Theodore Roosevelt, William Taft, and Woodrow Wilson answered the call for reform. The first twenty years of the 20th Century was commanded by Roosevelt, Taft, and Wilson, commonly referred to as the Progressive Presidents. The “laissez-faire” government of the late 19th Century was replaced by a regulatory government aimed at breaking up monopolies, improving the distribution of wealth, and protecting workers and consumers. By the start of the 1920s, the federal government had managed to add four new amendments to the Constitution including one creating an income tax and one granting women the right to vote. Additionally, federal policies aimed at regulating business and protecting consumers were created: The Federal Reserve System, Federal Trade Commission, and Food and Drug Administration. These major domestic changes paralleled changes in American foreign policy, which found America involved in imperialism and a world war. The government was not alone in the Progressive Movement, citizens also worked for change. People like Jane Addams and Lillian Wald created settlement houses to help immigrants and the poor. Minority groups, particularly African Americans, worked to protect their civil liberties and gain certain rights. Although progress was made for some (women were granted the right to vote) true equality would still be out of reach for some time. 1. 2. 3. 4. Unit Enduring Understanding(s) Change as a result of urbanization can necessitate reform. Change as a result of immigration can necessitate reform. A desire for power can lead to corruption and an unequal distribution of wealth. When citizens face inequalities, they often demand reform. 1. 2. 3. 4. Unit Essential Question(s) How can urbanization lead to political, economic and social reform? How can immigration lead to political, economic and social reform? How can the desire for power lead to corruption and an unbalanced distribution of wealth? Why do movements for political, economic, and social reform occur? Essential State Standards Priority Objectives AH2.H.3.4 Analyze voluntary and involuntary immigration trends since Reconstruction in terms of causes, regions of origin and destination, cultural contributions, and public and governmental response. AH2.H.4.1 Analyze the political issues and conflicts that impacted the United States since Reconstruction and the compromises that resulted. AH2.H.4.2 Analyze the economic issues and conflicts that impacted the United States since Reconstruction and the compromises that resulted. AH2.H.4.3 Analyze the social and religious conflicts, movements and reforms that impacted the United States since Reconstruction in terms of participants, strategies, opposition, and results. Supporting Objectives AH2.H.4.2 Analyze the economic issues and conflicts that impacted the United States since Reconstruction and the compromises that resulted. AH2.H.7.2 Explain the impact of wars on the American economy since Reconstruction. AH2.H.4.4 Analyze the cultural conflicts that impacted the United States since Reconstruction and the compromises that resulted. AH2.H.5.1 Summarize how the philosophical, ideological and/or religious views on freedom and equality contributed to the development of American political and economic. AH2.H.8.1 Analyze the relationship between innovation, economic development, progress and various perceptions of the “American Dream” since Reconstruction. AH2.H.8.2 Explain how opportunity and mobility impacted various groups within American society since Reconstruction. AH2.H.8.3 Evaluate the extent to which a variety of groups and individuals have had opportunity to attain their perception of the “American Dream” since Reconstruction. AH2.H.8.4 Analyze multiple perceptions of the “American Dream” in times of prosperity and crisis since Reconstruction. *Standards 1 (historical thinking) and 2 (turning points) are included in every unit. Unit Resources Graphic Organizers and Activities Primary Resources, Readings, and Songs Websites and Videos Assessment Standard(s) AH2.H.3.4 Analyze voluntary and involuntary immigration trends since Reconstruction in terms of causes, regions of origin and destination, cultural contributions, and public and governmental response. AH2.H.4.2 Analyze the economic issues and conflicts that impacted the United States since Reconstruction and the compromises that resulted. AH2.H.8.1 Analyze the relationship Unit “Chunking” & Enduring Understandings The Gilded Age: Industrialization and Immigration Suggested Lesson Essential Questions Technological innovations can enable urbanization. How did technological innovations enable urbanization and the horizontal and vertical growth of cities? ______________ Rapid urbanization impacts the economy and culture of cities. _______________ How did rapid urbanization impact the economic and cultural development of cities in the 19th Century? Possible Factual Content (Bold Found in Standards) ● Industrialization - inventions * Edison * Westinghouse ● Urbanization - industrialization - growth horizontal and vertical - culture Example(s) From Unpacked Standard How various technological innovations enabled urbanization and the horizontal and vertical growth of cities in the 19th Century. ___________________ ● Urban Life - new issues * sanitation * fires * natural disasters ~ Johnstown flood 1889 ~ Galveston hurricane 1900 ~ San Francisco earthquake of 1906 - coping with life * entertainment ~ phonograph ~ motion pictures ~ mass _____________ How and why the United States became more industrial and urban during the 19th Century and to what extent rapid urban and industrial development produced widespread poverty and poor working conditions. African American Infusion Resources Activities: ● Research an African American innovator that developed something that helped with urbanization. Determine what would have happened without the innovation. Resources: ● African American Inventors, website ● America’s Always Had Black Inventors, article, discusses how enslaved people invented many items but slaveholders often took credit, also looks at inventions and patents of free people of color ____________________________ Resources: ● The Racial Origins of Zoning in American Cities, article, discusses how zoning was used to keep undesirables (immigrants and African Americans) out of certain areas ● The Racist History of Zoning Laws, website, provides links to Supreme Court decisions while providing historical context ● Residential Segregation, article, discussed zoning in NC and provides information on Winston-Salem between innovation, economic development, progress and various perceptions of the “American Dream” since Reconstruction. AH2.H.8.3 Evaluate the extent to which a variety of groups and individuals have had opportunity to attain their perception of the “American Dream” since Reconstruction. ______________ Immigrants often AH2.H.8.4 endure many Analyze multiple challenges to perceptions of immigrate to new the “American countries. Dream” in times of prosperity and crisis since Reconstruction. entertainment + Buffalo Bill’s Wild West + saloons + vaudeville * spectator and team sports ~ boxing ~ professional baseball ~ college football and basketball ~ bicycle races * leisure time ~ city parks ~ bicycles ~ Coney Island _______________ How did the process of immigrating to the United States impact immigrants? ● Immigration - reasons for - culture/ethnic groups * Eastern and Southern Europeans - endurance of passage - entry into USA * port ~ Ellis Island ~ Angel Island * process How and why the United States became more industrial and urban during the 19th Century and to what extent rapid urban and industrial development produced widespread poverty and poor working conditions. How 19th Century urbanization generated new forms of mass entertainment. How “the huddled masses” of American immigrants endured passage to the United States to better themselves and their families. How the “huddled ______________ Increased immigration impacts the economy and culture of cities. _______________ How did increased immigration impact the economic and cultural development of cities in the late 19th Century and early 20th Century? - huddled masses * Lewis Hine photos from Ellis Island - opportunity and mobility * New York – garment industry * Chicago – meat industry * Cleveland – steel Mills * ethnic neighborhoods - naturalization - views on American Dream and life in US * Abraham Cahan Yekl: A Tale of the New York Ghetto * Jacob Riis Immigrant Interviews ___________________ ● Immigrants - cultural contributions - living conditions * ethnic neighborhoods * tenements * muckraking ~ Jacob Riis How the Other Half Lives masses” of “new” immigrants were processed at ports of entry such as Ellis Island and Angel Island, and how that process impacted the lives and cultural contributions of immigrants to the United States. _____________ How and to what extent the immigration of various Eastern Europeans influenced the industrial, urban and cultural development of particular cities and regions at _______________________ Activities: ● Have students look up why and how much the quotas from the late 19th and early 20th Century changed immigration rates for Africans and compare these to other immigrant groups. Then, examine current restrictions for immigration with a focus on Africans to compare changes over time. ● Have students create a chart showing immigration trends overtime for various groups, AH2.H.4.1 Analyze the political issues and conflicts that impacted the United States since Reconstruction and the compromises that resulted. The Gilded Age: Political Machines and Captains of Industry Political corruption impacts government, How did the desire for power and the resulting political corruption impact government, - working conditions * various industries ~ garment, meat, steel * child labor ~ Lewis Hines photos * muckraking ~ Upton Sinclair The Jungle - Nativism * Italians, Roman Catholics, Chinese - restrictions * Chinese Exclusion Act 1882 - views on American Dream and life in US * Abraham Cahan Yekl: A Tale of the New York Ghetto * Jacob Riis Immigrant Interviews ● Gilded Age ● Political Machines - corruption/graft * Boss Tweed and Tammany Hall + Plunkett of Tammany Hall * James Michael Curley and Chicago/Cook County the turn of the 20th Century. including Africans, to determine when major migrations waves can be seen, from where these immigration waves occurred, push/pull factors for these waves, and the response from the American government and citizens to these waves. How various muckraking journalists worked to expose the Resources: social, ● Chart Showing Immigration economic and Quotas from 1925-1927 political ills of ● Modern Immigration from Africa, article, discusses percent of an industrialized immigrants from Africa and society. reasons for immigration ● Immigration to the U.S. Since 1945, article, has charts _____________ To what extent politicians have used graft and corruption to move up the political ladder and lead political parties or “machines”. AH2.H.4.2 Analyze the economic issues and conflicts that impacted the United States since Reconstruction and the compromises that resulted. AH2.H.4.3 Analyze the social and religious conflicts, movements and reforms that impacted the United States since Reconstruction in terms of participants, strategies, opposition, and results. AH2.H.5.1 Summarize how the philosophical, ideological and/or religious views on freedom and economics, and society. economics, and society during the late 19th Century? * James Pendergast and Kansas City * Ed Crump and Memphis - immigrants for votes - patronage and favoritism - big business * laissez-faire How and why “political machines” at the state and local levels of government used patronage and favoritism to win the support of big business and working class voters. How and to what extent various local and state governments utilized immigrant votes to run machine politics. ______________ Industrial leaders can impact political, economic, and cultural progress. _______________ ___________________ How did industrial ● Business leaders’ desire for - “robber barons” power and money and “captains of impact political, industry” economic and * risks taken cultural progress of * distribution of the United States? wealth * improved fortune * people ~ Rockefeller ~ Carnegie + “The Gospel of Wealth” How Gilded Age entrepreneurs took risks to develop and monopolize industries and how their efforts impacted the economic development and cultural ress of the United States. equality contributed to the development of American political and economic. AH2.H.8.1 Analyze the relationship between innovation, economic development, progress and various perceptions of the “American Dream” since Reconstruction. AH2.H.8.3 Evaluate the extent to which a variety of groups and individuals have had opportunity to attain their perception of the “American Dream” since Reconstruction. AH2.H.8.4 Analyze multiple perceptions of the “American ~ Morgan ~ Pullman - monopolies * impact on workers and consumers * impact on businesses * vertical and horizontal - Social Darwinism * “the survival of the fittest” * impact ~ government policies ~ industry ~ social customs How and why the philosophy of Social Darwinism emerged and how the notion of “the survival of the fittest” impacted the development of American industry, government policies and social customs during the Gilded Age. How “Captains of Industry” and Boss politicians defended the acquisitions of wealth and power during the Gilded Age. Dream” in times of prosperity and crisis since Reconstruction. AH2.H.4.1 Analyze the political issues and conflicts that impacted the United States since Reconstruction and the compromises that resulted. AH2.H.4.2 Analyze the economic issues and conflicts that impacted the United States since Reconstruction and the compromises that resulted. AH2.H.4.3 Analyze the social and religious conflicts, movements and reforms that Progressivism: Moving Towards Reform Laborers will often unite when they feel their pay and working conditions are unfair. How did laborers respond to the tactics of industrialists and working conditions during the late 19th Century and early 20th Century? ● Labor Unrest - unions * formation * Knights of Labor and Terrence Powderly * AFL and Samuel Gompers * American Railway Union and Eugene Debs * United Mine Workers and “Mother Jones” - Eugene Debs and Socialist Party of American * formation and Influence * “Yes, I am my Brother’s Keeper” - tactics * Molly Maguires * Railroad Strike 1877 * Haymarket Affair * Homestead Strike * Pullman Strike ~ Report and Testimony on the Chicago Resources: How “laissez faire” politics led ● The Pullman Strike and Boycott, article, includes information to the about how African Americans monopolization were not allowed to join the of specific union. It makes the argument that if they had been allowed to industries th join the strikers may not have during the 19 needed union help to shut down Century and the company. how monopolies ● Labor Unions 1869-1920, primary impacted source, statement by W.E.B. workers and DuBois and a brief by the National Archives and Records Division consumers. How and why labor unions formed during the 19th Century and to what extent their leadership bred opposition and results. How various muckraking journalists worked to expose the social, economic and political ills of about race and unions ● Race in History of Labor Unions, website, has a timeline of information regarding race and racism in labor unions impacted the United States since Reconstruction in terms of participants, strategies, opposition, and results. AH2.H.8.1 Analyze the relationship between innovation, economic development, progress and various perceptions of the “American Dream” since Reconstruction. AH2.H.8.4 Analyze multiple perceptions of the “American Dream” in times of prosperity and crisis since Reconstruction. Reforms are often necessary to eliminate corruption in government and industry. How did the elimination of patronage impact government and industry in the United States? Strike of 1894 an industrialized * collective society. bargaining - Triangle Shirtwaist Fire ● Civil Service Reform How late 19th and Regulatory Laws Century civil - Pendleton Civil service reform Service Act of and regulatory 1883 laws of the - muckraking national * Lincoln Steffens government The Shame of the impacted Cities American - changed relationship government and with industry industry. * McKinley Tariff ● Exposing Big How various Business muckraking - muckraking journalists * Ida M. Tarbell worked to History of the expose the Standard Oil social, Company economic and political ills of an industrialized society. AH2.H.4.1 Analyze the political issues and conflicts that impacted the United States since Reconstruction and the compromises that resulted. AH2.H.4.2 Analyze the economic issues and conflicts that impacted the United States since Reconstruction and the compromises that resulted. AH2.H.4.3 Analyze the social and religious conflicts, movements and reforms that impacted the United States since Reconstruction in terms of Progressivism: Reform The work of journalists can lead to reform movements. How did muckraking journalists pave the way for Progressive reforms? ______________ Political leaders can create policies that protect workers and consumers. _______________ How did Progressive Presidents work to reform business in an effort to protect workers and consumers? ● Muckraking ● Progressivism - reasons for - presidents * Roosevelt ~ Square Deal * Taft * Wilson ~ 1912 Election ~ Triple Wall of Privilege - impact on * government ~ Amendments 16-19 * society ~ income tax ~ FDA * business ~ Interstate Commerce Act of 1887 ~ Sherman AntiTrust Act ~ Frederick Winslow Taylor and The Principles of Scientific Management ~ FTC ~ Federal Reserve ~ Clayton Antitrust * labor ~ concessions gained How various muckraking journalists worked to expose the social, economic and political ills of an industrialized society. _____________ How Presidents Theodore Roosevelt, William H. Taft, and Woodrow Wilson led and advocated for progressive reform that regulated business and protected the worker and consumer. How progressivism changed the relationship between big business, labor and government. participants, strategies, opposition, and results. AH2.H.5.1 Summarize how the philosophical, ideological and/or religious views on freedom and equality contributed to the development of American political and economic. Political, economic, and social reforms can affect groups of people in many ways. How did the Progressive movement affect immigrants and minorities? ● Immigrants and Poverty - Social Gospel Movement * share wealth - settlement houses - Jane Addams, Ellen Starr, and Hull House - Lillian Wald and Henry Street Settlement - University Settlement Society of New York - YMCA ● Minorities - women * work for suffrage * people ~ Carrie Chapman Catt ~ Margaret Sanger ~ Alice Paul ~ Lucy Burns - African Americans * views ~ Ida B. Wells ~ Booker T. Washington and “The Atlanta Compromise” ~ W.E.B. Du Bois and “The Talented Tenth” ~ NAACP How and to what extent the Social Gospel Movement and its participants responded to rising social tensions and injustices of the late 19th Century. How immigration groups benefited from the services of individuals and public instructions during the late 19th and 20th Centuries. To what extent the American woman has successfully gained expanded roles in American society and gender equality. How African American civil rights leaders of the late 19th Activities: ● Compare the Differences in Agendas of Booker T. Washington, W.E.B DuBois, and Marcus Garvey This is an activity that includes a reading and Venn diagram comparing viewpoints of the three gentlemen. ● Who had the best plan for African Americans to achieve greater freedom and equality? This is a WSFCS Inquiry Based Project. ● Examine African American Identity in the Gilded Age This is a Library of Congress lesson with links to numerous resources. ● Analyze the African Americans Experience in the Gilded Age This is a lesson plan from the Bill of Rights Institute. Resources: ● African American Experience in North Carolina After Reconstruction, website, a lot of information on various issues facing African Americans in NC during the Progressive Era ● Civil Rights and the Gilded Age, article, shares views of Washington and DuBois ● National Association of Colored Women’s Club, website, includes information on the work of the members on progressive issues ● African American Women and the Nineteenth Amendment, website ● How Racism Tainted Women’s Fight to Vote, article, showdown between anti-lynching crusader Ida B. Wells and temperance leader Frances E. Willard revealed the grip that racial Century differed in how to best achieve greater freedom and equality. resentment had over the American suffrage movement ● Ida B. Wells, website ● Ida B. Wells, primary sources, various newspaper articles reporting on her work ● Ida B. Wells, primary resources, provides links to various sources ● Miss Ida B. Wells: A Lecture, primary source, an advertisement in a newspaper ● “Lynch Law in America”, primary source, by Ida B. Wells ● The Troublesome Question Ignored and Negro Communicants Refused Seats, primary sources, two different excerpts from Ida B. Wells ● A Red Record, book, account of lynchings in the United States, entire book by Ida B. Wells ● To the Members of the Anti-Lynching Bureau, primary source, appeal by Wells to African Americans to support the Anti-Lynching Bureau via membership and money at a time when lynchings were rising and newspaper accounts and interest declining *Standards 1 (historical thinking) and 2 (turning points) are included in every unit. i.e.: How was the passing of the 19th Amendment a turning point in U.S. history? HISTORY ● Change ● Conflict ● Patterns ● Leadership GEOGRAPHY ● Settlement Patterns CIVICS & GOVERNMENT ● Domestic Policy ● Political Action ECONOMICS ● Economic Systems ● Standard of Living ● Quality of Life CULTURE ● Assimilation ● Ethnicity ● Society ● Regulation ● Rights