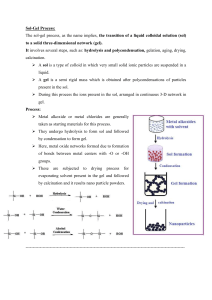
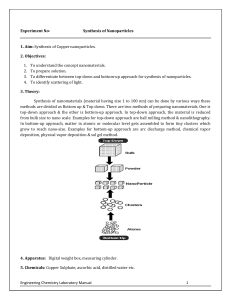
TOP-DOWN & BOTTOM-UP APPROACH FOR NENOPARTICALS SYNTHESIS Presented by: Almas Rana PH-04/2018 Nanotechnology PH-524 Nanoparticle Fabrications • Design and fabricate nanoparticles that have suitable properties for application. • Methods of obtaining nanomaterial vary and mostly depend on the material, its morphology and also the targeted applications Key Issues For Nanoparticles Synthesis • Uniformity of particle size • Size control • Shape control • Crystal structure uniformity • Purity Synthesis of nanomaterial Two general approaches based on the phase of starting material: TOP-DOWN APPROACH Slicing or successive cutting of bulk materials to get neno sized particles BOTTOM-UP APPROACH Built up of the material from the bottom, atom to atom or molecule to molecule to get to neno scale Processing Method Top-Down Physical processing methods: methods: Bottom-Up Chemical processing Mechanical methods : - Sol gel method - cutting , etching, grinding - Two phase method - ball milling - Co precipitation method Lithographic techniques: - Polyols method - Photo Lithography - Electron Beam Lithography - Hydrothermal reaction - Sonolysis Advantages Top-Down • Large scale production Bottom-Up • Ultra-fine nanoparticles, nanoshells, nanotubes can be prepare • Quick to manufacture • Cheaper technique • Chemical purification is not • Narrow size distribution (1-20 nm) required Disadvantages Top-Down Bottom-Up • Broad size distribution (10-1000 nm) • Large scale production is difficult • Varied particle shapes or geometry • Presence of impurities • Chemical purification of nanoparticles is required. • Expensive technique Sol-Gel Method Steps involved • Hydrolysis and condensation of molecule • Gelation • Ageing • Drying • calcination Steps • Metal alkoxides or inorganic salts as precursors is used. • Precursors undergoes a series of hydrolysis and condensation reaction to form a colloidal suspension or a sol. • Transition of system from liquid “sol” (mostly colloidal) into a solid “gel” phase. • Drying of the gel followed by calcination at different temperatures to obtain the metal oxide nanopowder Advantage • In sol-gel method it is possible to control the shape, morphology and textual properties of the final materials • Superior purity and compositional homogeneity can be achieved • This technique offers ability to control porosity to obtain high surface area materials • Iron oxide-silica gel composites are 2-3 times more reactive than conventional iron oxide. • Ceramic and glass materials can be obtained in a wide variety of forms: ultra-fine or spherical shaped powders, thin film coatings, ceramic fibres, microporous inorganic membranes. Disadvantage • Weak bonding • High permeability • Difficulty in controlling porosity • Substrate dependency • Contamination from by-products needs to be post treated Thank you