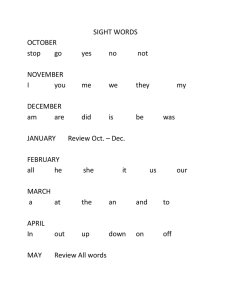
Test 1: Adair - Muscle Na+ channel selectivity filter glutamate Permeability of molecules w/o protein channels: nitrogen > water > urea > glucose > ions > albumin Review hypertonic, hyperosmotic Low serum K+: EK more negative, Vm more negative 6 mo endurance exercise training: all increase mt content, oxidative enzymes, capillary density, myoglobin content… and fiber diameter does not increase Most likely in increase velocity of shortening: longer muscle, decreased afterload Myasthenia Gravis: damage to acetylcholine receptor, post-synaptic Lambert-Eaton: damage to calcium channel, pre-synaptic Mechanism of Ca++ release from terminal cisternae: Ca-activated in heart, voltage activated in skeletal muscle General anesthesia, muscle rigidity, high temp: decreased calcium binding to calsequestrin Length tension diagram: Active = total – passive Total is line at very top, passive starts low and increases Normal Sk. Muscle contraction 1. Activation of dihydropyridine voltage sensor 2. Activation of ryanodine receptor 3. Ca++ release from terminal cisternae 4. Increased Ca++ conc. In sarcoplasm Excitation-contraction coupling in sm. Muscle: Myosin based, Ca++ binds calmodulin HEENT exam Type I sk muscle fibers: increased mt content (Know other comparison w/ type II) Malignant hyperthermia genetic disorder Block 2: Wilson - Hematology Low Hb, low Hct, low epo kidney failure Hx of smoking High hct, normal WBC, normal platelet, slightly increased Epo secondary polycythemia Iron uptake from small bowel mediated by: transferrin receptors on intestinal epit cells Phagocytic in tissues, sends early signals to initiate inflammatory response: macrophages Adhesion of neutrophils to inflamed epit: selectins and integrins Possible ruptured appendix, increase WBC count: due to mobilization of mature neutrophils from BM Peripheral smear shows numerous blasts and large # abnormal immature w/ incompletely segmented nuclei w/ few granules acute myeloid lymphoma Allergic rxn cross-linking of IgE receptors CD8+ interacts w/ MHC Class I Helper T direct their own cellular proliferation as well as proliferation of other immune cells Type A needs packed RBCs: can use type A or O Woman is A-Rh neg, Child O-Rh positive. Child is anemic and very high bilirubin Tx. repeated exchange transfusion w/ O-Rh neg blood IV drug user, chronic hep C, intractable nosebleed, INR is 7.0 Tx. Fresh frozen plasma Hx of excessive bleeding, often bleeding into joints, genetic inherited through mother Heparin prevents blood clotting via binding and potentiating anti-thrombin III Severe but undiagnosed gluten sensitivity w/ diarrhea and weight loss, excessive bleeding w/ markedly prolonged prothrombin time 37s vitamin K deficiency Sepsis, persistent bleeding from gums, around IV catheters, WBC is high w/ normal morphology, few immature neutrophils, reduced platelet count disseminated intravascular coagulation Predominant WBC in circulation = neutrophils DiGeorge Syndrome causes absent thymus impaired humoral and cellular immunity Intestinal hookworms, cell type likely increased eosinophils Xenograft likely to be associated w/ what type of organ rejection? Hyper-acute or acute Hemophilia A and B affect which pathway of blood coagulation? Intrinsic pathway only Block 3: Chade/Granger – Cardio Preload in ventricular PV graph point C/ end diastolic pressure PV diagram systole: C to A Atrial contraction may contribute up to 25% of ventricular filling AP arrives at AV bundle: 0.12 seconds Phase of ventricular muscle AP has highest K+ permeability: 3 Results in dilated heart: decreased Ca++ ions in blood Ach causes hyperpolarization of SA node Counting HR from EKG Einthoven’s Law: I + III = II aVR in EKG, positive terminal right arm ventricular depolarization wave -60° in frontal plane causes large negative in lead III purkinje fiber rate: 15-40 AP reaches ventricular septum at 0.16 seconds Sympathetic stimulation of heart releases norepi at sympathetic endings Know how to calculate mean electrical axis Know current of injury to determine location of injury/infarct EKG: paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia, Afib Circus mov’ts leads to vfib. Increases tendency: decreased conduction velocity, decreased refractory period, high extracellular K+, longer conduction pathway Afib rate of ventricular contraction is irregular and fast Inverted P wave AFTER qrs complex = premature contraction originating low in AV junction Systolic-diastolic murmur = PDA Patient in shock from blood loss give whole blood Systolic murmur, QRS axis -30° aortic stenosis Diastolic murmur, pulmonary congestion mitral valve stenosis Second heart sound assoc w/ closing of pulmonary valve Digitalis inhibits Na/K pump, increases intracellular Na+ and decreases Ca++ efflux Standing up from supine: Inc mean circulatory filling pressure, strength of contraction, dec parasym nerve activity Exercise: inc arteriole diameter, adenosine conc and dec in resistance Response to inc arteriole diameter: dec vascular resistance, inc capillary hydrostatic P & lymph flow Aortic valve stenosis: dec pulse pressure, stroke volume and systolic pressure Renovascular hypertension: Inc TPR, ANG II and dec in RBF Constriction of carotid artery: dec nerve impulses from carotid sinus, inc SV and filling pressure CHF: inc venous hydrostatic P, capillary hydrostatic P, interstitial fluid V O2 consumption, CO, pulmonary O2 conc calculation RVR calculation NOT responsible for increase in SV in response to inc venous return: decreased left atrial P Due to stretch of r atrium (Bainbridge reflex), stretch of SA node, Frank-Starling, increased r atrial pressure Increased resistance to venous return would decrease CO Most likely cause of cardiac pain from acute ischemia lactic acid Increase coronary BF: dec resistance, inc adenosine, vascular conductance, workload Substances in plasma that contributes LEAST to plasma colloid osmotic P: chloride Increased cerebral BF due to inc tissue hydrogen ion conc Administration of ACE inhibitor: inc Ang I, bradykinin and RBF Increase in diameter leads to increase in vascular conductance Which would lead to increase net mov’t Cl- across capillary: inc in conc. Diff of ClPrimary hyperaldosteronism hypertension: inc ECF volume, dec renin and plasma K+ Most likely cause of obesity related increase in BP inc sympathetic activity Which Na+ intake will have greatest reduction in BP in response to ACE inhibitor: lowest amt Response to reduction in arterial pressure decreased vascular resistance since BF is constant Greatest flow: high radius, low viscosity Changes in plasma conc expected to cause greatest activation of chemoreceptor reflex: Dec O2, inc CO2 and H+ Best drug for angina: nitroglycerin Decrease in which is most likely explanation of high pulse pressure? Arterial compliance Occurs in response to elevated atrial P: dec renal sympathetic N activity, inc ANP, Na+ excretion J point: entire ventricle is depolarized 2nd degree AV block – Mobitz I… Cardiac reserve is always reduced in cardiac failure Associated w/ decreased CO: hypothyroidism Decreased CO, decreased BP, inc HR, inc right atrial P: increase in lymph flow in lower extremities expected Decrease in arteriole diameter in local tissues: dec interstitial hydrostatic P, capillary hydrostatic P, lymph flow and blood flow What is correct about cardia afterload: it is the resisting force on ventricular wall during systolic ejection AV node is site where impulse is delayed the most QT interval represents: depolarization and repolarization of ventricles Block 4: Hall - Renal Decrease in afferent resistance: increase glomerular hydrostatic pressure, increase GFR, increase RBF Primary aldosterone: dec plasma K+, inc plasma pH, decrease renin, inc BP Which increases peritubular capillary reabsorption: inc peritubular capillary colloid osmotic P Liddle syndrome: dec plasma renin , plasma aldosterone Inc BP and no change in Na+ excretion Reduced efferent arteriole resistance: inc RBF, peritubular capillary hydrostatic P Dec GFR and glomerular capillary hydrostatic P Large decrease in plasma protein conc tends to cause all except: inc BV SIADH effect on intra and extracellular fluid: increase both volumes, decrease both osmolarities Osmolarity calculation. Glucose completely metabolized, just changing total volume BW = 50 kg Plasma Na+ conc. = 160 mmol/L Plasma osmolarity = 340 ICF = 40% and ECF = 20% Adding 2.0L of glucose ECF osmolarity = 319 mOsm/L and ICF V = 21.3 L Runner loses 3L from sweating, drinks 3 L water. Which changes would you expect? Inc Intracellular V, dec intracellular osmolarity Dec extracellular V and osmolarity Greatest decrease in GFR = 30% increase in afferent arteriolar resistance Decrease efferent resistance: increase RBF, decrease GFR and FF Reduction in proximal tubule NaCl reabsorption: dec GFR, inc afferent resistance, dec RBF Bicarb in the urine is normally higher than in glomerular filtrate FF = GFR/RBF Dehydrated person w/ severe central diabetes insipidus w/ no ADH, where is osmolarity lowest? Fluid leaving collecting duct/urine GFR reduced to 50% normal: no change creatinine excretion rate, decreased clearance, increased plasma creatinine Type A intercalated cells: secretion of H+, reabsorption of HCO3- and reabsorption of K+ Transport maximum calculation Rate of potassium excretion calculation (make sure you convert from L to mL) Clearance calculation using PAH to get RBF Free water clearance: urine flow – (U osmolarity x U flow)/Plasma osmolarity Primary aldosteronism: NC K+ excretion rate, Na+ excretion rate, inc plasma pH, dec plasma K+ conc, inc BP Greatest impairment of urine concentrating ability chronic tx w/ furosemide ADH does NOT increase urea reabsorption by cortical collecting tubule ADH activates UT-A1 and UT-A3 in collecting ducts UT-A2 facilitates passive diffusion of urea into thin loops of Henle Salt-sensitivity of BP would be increased by: loss of fxnal nephrons due to CKD, inability to suppress Ang II, primary aldosteronism, Tx w/ an ACE inhibitor Know what causes K+ to move into and out of cells Person increases K+ intake: Inc K+ excretion, NC in Na+ excretion, inc plasma K+ by < 1mmol/L, inc aldosterone Aldosterone antagonists do NOT cause hypokalemia Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors tend to cause metabolic acidosis Thiazide diuretics inhibit Na-Cl cotransporters in distal tubules Osmotic diuretics increase K+ secretion Na+ channel blockers/amiloride block transport across luminal membrane of collecting tubules Loop diuretics tend to cause hypokalemia Chronic nephrogenic diabetes insipidus: inc urine V, dec urine osmolarity, inc free water clearance, dec renal medullary osmolarity Acidosis: inc. urine NH4+ excretion, new renal bicarb Dec urine excretion bicarb, urine pH Block 5: Hester - Respiratory PaO2 equation Venous blood in anemic person lower O2 sat and content O2 consumption equation Increase in Zone 1 conditions: positive pressure ventilation Cheyne Stokes Respiration: disordered breathing resulting from instability of resp control sys Increase airway resistance: activation of parasym nerves *Aspirated foreign body in right main bronchus BF decreases Day 1 after being in space: increased urinary output Blocking airway leads to increase in Zone 1 COPD, low PaO2, cause of edema: R ventricular failiure due to hypoxic pulmonary hypertension Low arterial O2, increased PCO2: increased carotid body impulses and inc ventilation rate Lung capacities and volumes O2 content and saturation calculations Inspired O2 lower than 21% = decrease in H+ ions at central chemoreceptors Beta adrenergic causes decrease in airway resistance Alveolar Ventilation and minute ventilation equations Pulmonary HTN, most likely cause of inc pulmonary vascular resistance decreased PAO2 Increase in HR due to mild exercise and doubling CO, what is change in PA pressure: 5 mmHg Not important in O2 delivery w/n exercising muscle: decreased H+ conc Respiratory distress of newborn: decreased compliance, inc surface tension Highest velocity of flow in lung right after start of inhalation Largest pressure differential b/t alveolar P and pleural P: at end of inhalation Arterial content calculation Does NOT cause airway narrowing in asthma attack: destruction of airways Normal V/Q ratio of 0.8: P02 = 100 and PCO2 = 40 V/Q ratio of 0: PO2 = 40 and PCO2 = 45 Most likely pleural effusion in which circumstance? Infection of pleural space destroying capillary membranes Block 6: Adair - GI Cell types and GI proteins they secrete GLIP stimulated by lipids, carbs and polypeptides Increase in spike potentials parasym stimulation Achalasia megaesophagus Decrease in salivary flow from parotid gland: fear Increased by: smooth objects, nausea, chewing, taste/smell Pernicious anemia caused by untreated atrophic gastritis Secretagogues for gastric acid under normal physiological conditions: Ach, histamine, gastrin Gastric acid secretion in response to meal 1. Increase in pH of gastric contents 2. Increase in rate of acid secretion 3. Decrease in pH of gastric contents 4. Decrease in rate of acid secretion Severe diarrhea by opening Cl- channels chorea toxin Fructose is not disaccharide Know disaccharides Assimilation of fat 1. Emulsification of fat 2. Micelle formation 3. Absorption of fat by enterocytes 4. Secretion of chylomicrons Causes voracious feeding and obesity: lesion that damages VM nuclei of hypothalamus *Urinary nitrogen excretion calculation RQ for untreated diabetes = 0.7 H. pylori causes damage via NH4+ Block 7: Ryan – Endocrine Hormone receptor types: IGF-1 uses enzyme linked receptor Increased fasting insulin, high FFA, high IGF-1: Inc. GH somatostatin gluconeogenesis, Dec GHRH total body fat mass Adenoma secreting GH and TSH: dec GHRH, inc GH IGF-1 TSH T3/T4 Increase in ECF osmolarity increases ADH GH most likely to exhibit nocturnal peak Pregnancy can result in euthyroid even though total T3/T4 are high Fxn of T3: increases gluconeogenesis, glycogenolysis, lipolysis, decreased serum cholesterol Chronic untreated hypoadrenalism: Dec BP, ECF volume, cellular pH Inc plasma K+ and no change in urinary Na+ Conn’s syndrome/primary aldosteronism: high ECF volume Vitamins for fetal physiology Vitamin D bone growth Vit K liver production of prothrombin Vit C bone matrix Vit E early embryonic development