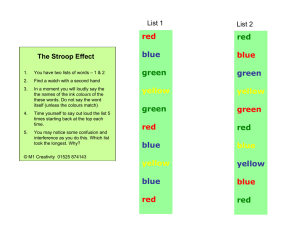
• Electromagnetic waves • it travels through a vacuum • Are waves that have an electric and magnetic field • It is a transverse waves • Vibrates perpendicular to the direction that they are traveling • Newton: light is a particle (corpuscles) • Young: light is a wave • Einstein: light is a particle (photon) • Broglie: Dual-Nature of Light • Maxwell: Electromagnetic Theory of Light • Incandescence is the emission of light from "hot" matter (T ≳ 800 K). • Luminescence is the emission of light when excited electrons fall to lower energy levels (in matter that may or may not be "hot"). • The speed of light in a vacuum is a universal constant in all reference frames. • The speed of light in a vacuum is fixed at 299,792,458 m/s by the current definition of the meter. • The speed of light in a medium is always slower the speed of light in a vacuum. • The speed of light depends upon the medium through which it travels. The speed of anything with mass is always less than the speed of light in a vacuum. • The amplitude of a light wave is related to its intensity. • Intensity is the absolute measure of a light wave's power density. • Brightness is the relative intensity as perceived by the average human eye. • The frequency of a light wave is related to its color. • Color is such a complex topic that it has its own section in this book. • Monochromatic light is described by only one frequency. Laser light is effectively monochromatic. There are six simple, named colors in English (and many other languages) each associated with a band of monochromatic light. In order of increasing frequency they are red, orange, yellow, green, blue, and violet. Light is sometimes also known as visible light to contrast it from "ultraviolet light" and "infrared light" Other forms of electromagnetic radiation that are not visible to humans are sometimes also known informally as "light" • Polychromatic light is described by many different frequencies. Nearly every light source is polychromatic. White light is polychromatic. •The wavelength of a light wave is inversely pro Light is often described by it's wavelength in a vacuum. Light ranges in wavelength from 400 nm on the violet end to 700 nm on the red end of the visible spectrum. portional to its frequency. •An object reflects light that matches colour of the object and it absorbs all other colours of light • Not actually white • Made up of millions of colours ex. ROYGBIV • Light and sound are energies. • Different colours of light are light waves having different frequency • Dispersion, in wave motion, any phenomenon associated with the propagation of individual waves at speeds that depend on their wavelengths. • Monochromatic light: single color •Polychromatic light: many colors • • • Different colours of light have same speed in air but when they hit the glass prism, different colours of light have different speed in glass prism • RED has the maximum speed • VIOLET has minimum speed • Dispersion of light Splitting of white light into its constituent colours • Spectrum Band of colours formed by dispersion • In glass or any medium (other that air) different colours travel at different speeds