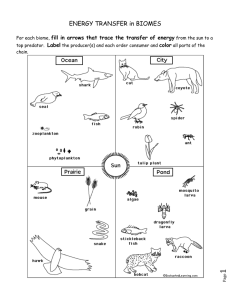
What Is Ecology? Across 3. A group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms. 6. Ecologists will conduct this to test a hypothesis about the way an ecosystem works. 8. This first step in studying ecology often helps ecologists decide on the right questions to ask next. 9. A group of similar organisms that can breed together. Down 1. All the organisms in the community and the physical environment where they live. 2. All the different populations that live together in an area. 3. This consists of all life on Earth and all parts of the Earth on which life exists. 4. This allows ecologists to test a number of different scenarios within an ecosystem. 5. This term describes the interaction between living things and their environment. 7. All the individuals in a species that live in the same area. Energy in Ecosystems V R P A C V H P N D H R N R N D E T R I V O R E R K R J O R F B S J E Q L C C I G S C E C H G T O J Z O O D O L N D E N Q I I V M U E H E R S C P M M B O X Y V E C H I I F U M T A E V C Y T O U F F R A B O E E T M S Y O B C F M R J M S W N A S E N X V E O R L M I R A N X I Y T G R E N E H R R O R G G V Y J R R E O W H P B B L N D V O X X H G F M I E S O T A B R U K F D O K S I D P M E C E X N J Z F C P U H F P K P I H P O R T O T U A G A L R I P AUTOTROPH CARNIVORE CONSUMER DECOMPOSER DETRIVORE ENERGY HERBIVORE HETEROTROPH OMNIVORE PRODUCER SCAVENGER What Is Ecology? Unscramble each of the clue words. Copy the letters in the numbered cells to other cells with the same number. HINT: This describes all life on Earth and the parts of Earth where live exists. Energy Flow In Ecosystems (Enter two-word answers with NO space) Across 3. Also called a consumer, this type of organisms obtains energy by consuming other organisms. 5. Shows the relative amount of energy or matter contained within each trophic level in a food web or chain. 8. These types of producers can create their own energy, from the sun or chemically. Down 1. This shows the network of different feeding relationships in an ecosystem. (2 words) 2. A series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten. (2 words) 4. These show each individual steps in a food chain or food web. (2 words) 6. The total amount of living tissue in a trophic level. 7. This word describes the chemical process by which plants create food through light energy. Cycles of Matter N N S B B W P H O E D I K O I G Z O N T I K C J A P N T D A I T I O O A N J P T Q T F A W M A R T C T T D I O U C E P L C T Q K A C I Q H G I E I E M T H Y U P F N M I P E I D U J S C D N R R E S A E I R E V J M U T A P Q B Y Y E T J H A R F U T R V I E I R V I I L G C N O P C X B R W G R Z L A Q A G E A C A R B O N D T X X L T T R C O N D E T P Y T S U R O H P W U Z Z O J N S A T I Q J S E S O N I L Q N K O O H P Y X Y E N W N W G S N P G F S D BACTERIA BIOCHEMICAL CARBON CONDENSATION DENITRIFICATION EVAPORATION NITROGEN NUTRIENT PHOSPHORUS PRECIPITATION TRANSPIRATION WATER Producers & Consumers Unscramble each of the clue words. Copy the letters in the numbered cells to other cells with the same number. HINT: All of these consumers are ___________________, which mean they consume other organisms to obtain energy. Community Interaction M M U T R S U A L I V U O P A M I G M K H H D T X L S M N C V X C H O Z I J Z I C Q L M I J G M B T Y G A C I D Q E V B A E S N C B E S N N Y S A V R V E S J K I X J M A T G Y I A S Q O W L M Z N B N W X Y M Z P A T A G Q T Z P M R I H C A D A S P O F K M R F T J I L H Y Q N O I E Y E N R G D R B S K F R L G Z V W D D A Q S O Y E Z U X U H I J G S N C S T P D A U B Z I N E Z W E U A I A F R Z L Y Z M T T R O N N K Y Y S I F T E P G R E M O C E C COMMENSALISM COMPETITION HABITAT MUTUALISM NICHE PARASITISM PREDATION SYMBIOSIS Biomes of the World Unscramble each of the clue words. Copy the letters in the numbered cells to other cells with the same number. HINT: These clues are all types of ____________. How's The Weather? Across 2. The ______ effect is a buildup of gases in the atmosphere that can trap heat and cause the average temperature on Earth to increase. 5. A _______ community is one where the animal and plant species are stable and exist in balance with each other and the environment. 6. Ecological ______ is a series of more-or-less predictable changes that occur in an ecosystem over time. 7. A ________ species is the first species to colonize a barren area. 8. This word typically describes rain or snow. Down 1. This is the average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time. 3. This type of succession occurs in situations where a disturbance affects the community without completely destroying it. 4. This describes a small, slightly different climate within one area. Biodiversity (Enter two-word answers with NO space) Across 6. This is the total of all genetically-based variation in all organisms in the biosphere. 7. An _______ species doesn't belong in a habitat, and can threaten native biodiversity. Down 1. This type of diversity refers to the variety of habitats, communities, and ecological processes in the biosphere. 2. This type of diversity can mean the sum of all different forms of genetic information in a species, or in all the organisms on Earth. 3. Habitat ______ occurs when development splits ecosystems into pieces, leaving little habitat "islands" and limiting biodiversity. 4. An ecological ___ ____ is a place where significant numbers of species and habitats are in immediate danger of extinction. (2 words) 5. Species _____ is the number of different species in the biosphere or in a particular community. Community Interaction Across 3. The necessities of life, such as water, nutrients, light, and space. 5. The Competitive _______ Principle means that two species cannot occupy the exact same niche in the same habitat at the same time. 6. This is the general area where a species lives. 7. The range of physical and biological conditions in which a species lives and the way the species obtains what it needs to survive and reproduce. 8. An interaction in which one animal captures and feeds on another animal. Down 1. Occurs between individuals of one species (intraspecific) or between different species in a community (interspecific). 2. A ______ species is one that could cause great change to a community if it were removed. 4. Any relationship in which two species live closely together. 6. An interaction in which one animal feeds on producers such as plants. Biomes N B M C Y D P P J Y K E H N Z N K E F A S T N E J S E F R T T D Z Q C H T A R E P M E T E O H R N Y A V V I R L T Z W A A J N J W A U T A P A T I E N L D S I A S T H A B D P H E M P F N F B T L Q P E B I T U C D Y R C X D I S Y S P X A O I S T U C S M Q L Y W T E A P F A J Z N W V W J T U I M A X A P Y O A G O J G A G E N S L A Q I O F Z H Y S R M P R N E Q W H U Y W O E O T B H Y Y B N M P I C O A S T A L G W A R D N U T T M R C L Y O E H V F R COASTAL DESERT ESTUARY INTERTIDAL OCEANIC SAVANNA TAIGA TEMPERATE TROPICAL TUNDRA WETLANDS Answers What Is Ecology Cross Word: Across 3. A group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms. BIOME 6. Ecologists will conduct this to test a hypothesis about the way an ecosystem works. EXPERIMENTATION 8. This first step in studying ecology often helps ecologists decide on the right questions to ask next. OBSERVATION 9. A group of similar organisms that can breed together. SPECIES Down 1. All the organisms in the community and the physical environment where they live. ECOSYSTEM 2. All the different populations that live together in an area. COMMUNITY 3. This consists of all life on Earth and all parts of the Earth on which life exists. BIOSPHERE 4. This allows ecologists to test a number of different scenarios within an ecosystem. MODELING 5. This term describes the interaction between living things and their environment. ECOLOGY 7. All the individuals in a species that live in the same area. POPULATION Energy Word Search: V R P A C V H P N D H R N R N D E T R I V O R E V E C H I U R K R J O R F C H G T O J Z M B S E O O D O L N D E N Q I T J Q L I V M U E H E R S F A E C C I C P I V C Y T O U F F R O E E T M S Y O E N X V O R L M I B B L N H R R O R O T A M M B O X A B Y G S B F M R J R R C E M S W N A S E E R A N X I Y J O W H P T G G V Y G R E N D V O X X H G F M I E B R U K F D O K S I D P M E C E P K P I X N J Z F C P U H F H P O R T O T U A G A L R I P C E S What Is Ecology Jumble: Ecology Ecosystem Species Population Community Biome Biotic Abiotic Final Word: Biosphere Energy In Ecosystems Crossword: Across 3. Also called a consumer, this type of organisms obtains energy by consuming other organisms. HETEROTROPH 5. Shows the relative amount of energy or matter contained within each trophic level in a food web or chain. ECOLOGICAL PYRAMID 8. These types of producers can create their own energy, from the sun or chemically. AUTOTROPHS Down 1. This shows the network of different feeding relationships in an ecosystem. (2 words) FOOD WEB 2. A series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten. (2 words) FOOD CHAIN 4. These show each individual steps in a food chain or food web. (2 words) TROPHIC LEVEL 6. The total amount of living tissue in a trophic level. BIOMASS 7. This word describes the chemical process by which plants create food through light energy. PHOTOSYNTHESIS Cycles of Matter Word Search: N N S B B W P K C J A P N T D H O E D I K A I T I O O A N J O I I G Z O N T R V I J A E I P T Q T O U C E E T Q H G I E F A W M A R T H A R F U T R V C T T P L C T R E V J M U T A D I Q K A C I I E M T H Y U P I P Q B Y P I F N M I G C N O E I E Y S D U J I L P C X B R S C D N R R E W G R Z L A Q A G E A C A R B O N D T X X L T T R C O N D E N S A T I O N I T P Y T O J Q J E S L Q N K O S U R O H P S O H P Y X Y E N W U Z Z W N W G S P G F S D Producers & Consumers Jumble: Herbivore Scavenger Detrivore Carnivore Decomposer Omnivore Final Word: Heterotrophs N Community Interaction Word Search: M M U T U A L I S M N C N C R S U O P V X C H Z I U X A M I G M K J Z I M I Y C Q L H H D T X L J G M B T U H I V J G A C I D Q E A E E E S N C B E S N N Y W D D A Q S G S J K I S A V R V E M R I H S X J M A T N R G D R B S K F O Y R L Z C A D A S P O F K M G Y I G Z R F P I F N E A S Q O W L B Z W E U A M Z N B N W X Y M Z I A F R Z E P A T P L K Y Y L Y Z G R E A G Q T H Y S I M T T R O N N Z Q N O I T I T E M O Biomes of the World Jumble: Tropical Taiga Temperate Desert Tundra Savanna Marine Final Word: Biomes V T V J D A U B P O C Y E S Z C How’s The Weather Cross Word: Across 2. The ______ effect is a buildup of gases in the atmosphere that can trap heat and cause the average temperature on Earth to increase. GREENHOUSE 5. A _______ community is one where the animal and plant species are stable and exist in balance with each other and the environment. CLIMAX 6. Ecological ______ is a series of more-or-less predictable changes that occur in an ecosystem over time. SUCCESSION 7. A ________ species is the first species to colonize a barren area. PIONEER 8. This word typically describes rain or snow. PRECIPITATION Down 1. This is the average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time. CLIMATE 3. This type of succession occurs in situations where a disturbance affects the community without completely destroying it. SECONDARY 4. This describes a small, slightly different climate within one area. MICROCLIMATE Biodiversity Cross Word: Across 6. This is the total of all genetically-based variation in all organisms in the biosphere. BIODIVERSITY 7. An _______ species doesn't belong in a habitat, and can threaten native biodiversity. INVASIVE Down 1. This type of diversity refers to the variety of habitats, communities, and ecological processes in the biosphere. ECOSYSTEM 2. This type of diversity can mean the sum of all different forms of genetic information in a species, or in all the organisms on Earth. GENETIC 3. Habitat ______ occurs when development splits ecosystems into pieces, leaving little habitat "islands" and limiting biodiversity. FRAGMENTATION 4. An ecological ___ ____ is a place where significant numbers of species and habitats are in immediate danger of extinction. (2 words) HOT SPOT 5. Species _____ is the number of different species in the biosphere or in a particular community. DIVERSITY Community Interaction Cross Word: Across 3. The necessities of life, such as water, nutrients, light, and space. CROSSWORD 5. The Competitive _______ Principle means that two species cannot occupy the exact same niche in the same habitat at the same time. EXCLUSION 6. This is the general area where a species lives. HABITAT 7. The range of physical and biological conditions in which a species lives and the way the species obtains what it needs to survive and reproduce. NICHE 8. An interaction in which one animal captures and feeds on another animal. PREDATION Down 1. Occurs between individuals of one species (intraspecific) or between different species in a community (interspecific). COMPETITION 2. A ______ species is one that could cause great change to a community if it were removed. KEYSTONE 4. Any relationship in which two species live closely together. SYMBIOSIS 6. An interaction in which one animal feeds on producers such as plants. HERBIVORY Biomes Word Search: N B M C Y D P A Q I O A G O J P J Y K E H N Z N K D Z Q C H E F A S T N E T A R E P M E T J S E G A G E E O H R N Y A V F R T V I R L T Z W A A J N J T W A U T A P A T I S A O I S N S E I A S T U C D Y T U C S N L D S T R C X D I M Q L Y W H A B D P S Y T E A P F A J Z L H E N W V W J T U I O F Z H M A X A P P X Y S R M P R N E M P F L Q W H U Y W O E O T B N F B T H Y Y B N M P I M R C Y Q P E C O A S T A L L Y O E B I G W A R D N U T T H V F R Copyright © 2015 Mentor’s Market All rights reserved by author. Permission to copy for classroom use only. Electronic distribution limited to classroom use only.