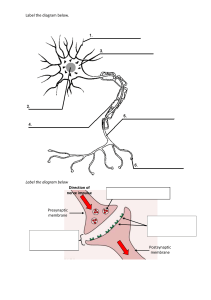
Passive Transport - Transportation of particles across the cell membrane that uses no energy Type of Transport Definition Diffusion Particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration Osmosis Movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane in order to cause concentrations to reach an equilibrium Facilitated Transport Protein channel helps larger particles diffuse across cell membrane Student Friendly Type of Particles Examples Active Transport - Transport across the cell membrane that requires energy Type of Transport Definition Molecular Transport Carries things across the membrane using proteins in the membrane that require energy. Usually the protein has to move things against the concentration or the protein has to move in order to move the particles across Phagocytosis a type of endocytosis when a particle is surrounded (engulfed) by the cell and then brings it inside the cell as a vacuole Pinocytosis A type of endocytosis where the cell takes up liquid from the environment by bringing in pockets of membrane filled with fluid from outside the cell Exocytosis Release of material from inside the cell caused when a vacuole is forced out of the cell Student Friendly Type of Particles Examples Structure Function Macromolecule