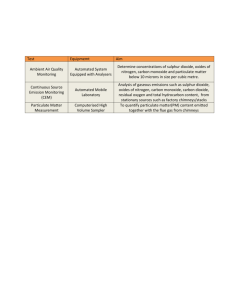
Air Pollution: Harmful substances in the air Main Pollutant gases: 1) carbon monoxide, CO Comes from: - When fuels like petrol and diesel are burnt in an internal combustion engine, the amount of oxygen present is limited, so carbon monoxide gas is formed, instead of carbon dioxide gas. - Unburnt hydrocarbons - forest fires Hazards: - Combines with haemoglobin when inhaled, which produces carboxyhaemoglobin that reduces efficiency of haemoglobin to transport oxygen. - Cells then die. Prevention: - Install catalytic converters in cars - Reduce number of cars on road - Create efficient engines in cars to ensure complete hydrocarbon combustion 2) sulphur dioxide, SO2 Comes from: - Combustion of fossil fuels containing sulphur impurities - volcanic eruptions Hazards: - Lung irritant - eye irritant - acid rain Prevention: - Prevent using fuels containing sulphur impurities, e.g. coal - Reduce the sulphur impurities inside fossil fuels - Spray exhaust gases from factories with water/hydrated CaO/alkalis to absorb sulphur dioxide before it’s released into the atmosphere - Add CaO to soil and rivers to neutralize acid rain 3) oxides of nitrogen, NO Comes from: - Lightning activity - forest fires - internal combustion engines (as nitrogen oxides are formed by oxygen and nitrogen under high temperature) --> Poisonous oxides of nitrogen are also formed from the electrical spark which passes through the air/petrol mixture. - power stations Hazards: - Eutrophication - lung damage - acid rain Prevention: - Install catalytic converters in cars - Design car engines which run at lower temperatures Notes: Reactions of oxides of sulphur and nitrogen The oxides of sulphur and nitrogen are acidic gases and are water-soluble. They dissolve to form acid rain. The main source of these pollutant gases is from the burning of fuels, especially those in petrol and diesel engines. All oils and fuels contain sulphur, and when they are burnt, sulphur dioxide gas is formed. In power stations, large quantities of this gas are produced, which dissolve in water in the atmosphere to form sulphurous acid (sulphuric acid) SO2 (g) + H2O (l) --> H2SO3 (aq) 4) Methane Comes from: - Decomposition of vegetable matter - rice field - cattle ranching - natural gas - mines Hazards: - highly flammable - greenhouse gas Prevention: - Cattle and other ruminant animals should be given improved diet - Animal manure and rotting vegetation can be used as biomass fuel 5) Unburnt hydrocarbons Comes from: - Internal combustion engines - Because of the limited supply of air inside the engines some of it remains unburnt and escapes as gaseous hydrocarbons. Hazards: - Carcinogenic - forms photochemical smog - can act as greenhouse gases contributing to global warming. Prevention: - Install catalytic converters in cars - Reduce number of cars on road - Create efficient engines in cars to ensure complete hydrocarbon combustion 6) Ozone Comes from: - It is formed when an electrical spark passes through air. This is because it reacts with the UV radiation in sunlight to produce a 'photochemical smog'. - It is an allotrope (two/three different forms of a pure element) of oxygen having structural formula O3 having characteristic odour. - High up in the atmosphere ozone is beneficial as it helps to filter out high levels of UV radiation Hazards - It reacts with unburnt hydrocarbons to form photochemical smog that causes headache, eye, nose and throat irritation. - It corrodes and kills plants and trees Prevention - Don’t use CFCs/replace it with HCFCs which destroys faster. Notes: Catalytic converters - One way to reduce pollution from cars is to fit catalytic converters to our exhausts. - Inside the converter is special metal-like platinum which acts as a catalyst. - It converts the poisonous exhaust gases - It does this by transferring oxygen atoms from the oxides of nitrogen to the CO. The function of this converter is to turn the poisonous exhaust gases of CO and oxides of nitrogen into harmless gases like carbon dioxide and nitrogen. 2CO (g) + 2NO (g) --> 2CO2 (g) + N2 (g) Natural compounds of carbon Carbon Cycle - Carbon dioxide is produced mainly by respiration. Here, sugars such as glucose are converted into carbon dioxide and water, giving out energy (exothermic) Respiration of glucose equation: - Carbon dioxide is also produced by combustion of fuels, in factories, and in the home - The carbon dioxide is then absorbed by plants, by photosynthesis. Energy is absorbed (endothermic) from the sun, and used to build up simple sugars. Photosynthesis equation: - Animals eat plants, and in turn, they themselves get eaten by other animals. So the carbon originally in the atmosphere ends up in every living plant and animal. Upon death, the carbon is released by bacteries and fungi, to return to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide. The cycle is then repeated. The addition of poisonous gases in the environment is called air pollution. These gases include carbon monoxide CO, sulphur dioxide SO2, etc, and are called pollutant gases. Some pollutants like the oxides of sulphur and nitrogen are also acidic oxides and water soluble, so they cause acid rain and thus cause plants to die and buildings to be eaten away. The main source of these pollutant gases entering the air is from the burning of fuels. All oils and fuels contain sulphur, and when they are burnt the sulphur reacts with the oxygen and forms sulphur dioxide gas. When fuels like petrol and diesel are burnt in an internal combustion engine, the amount of oxygen present is limited. The carbon in these fuels reacts with the limited oxygen to form carbon monoxide, which is poisonously fatal. Also, the oxides of nitrogen that are released from car exhausts cause major pollution problems. ● Carbon monoxide – incomplete combustion of carbon-containing substance s ● Sulfur dioxide – combustion of fossil fuels which contain sulfur compounds (leading to ‘acid rain’ ) ● Oxides of nitrogen – car engines ● Lead compounds – leaded petrol The Carbon Cycle: The carbon cycle is a natural global cycle of the element carbon. It is what maintains a constant level of carbon dioxide in air (0.03%). The cycle goes as follows: Plants absorb carbon dioxide from air and undergo photosynthesis reaction which turns it into glucose and produces oxygen: 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2 The carbon is now stored in plants as glucose. One of two things happen, either the plants get eaten by animals or humans, or the plant dies and decays. If the plant is eaten by animals or humans, glucose in the plant is used by them in a process called respiration to release energy for their body. C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O Respiration is the opposite of photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide is one of the products of it, which is released by the humans through breathing into the air. Thus carbon dioxide returns to the atmosphere. If the plant dies. It is buried underground and by time it decays forming coal and other fossil fuels. These substances contain the carbon which was made and stored by the plants and they are then taken by power stations which put them to use. Power stations burn carbon-containing fuels that were obtained as coal or fossil fuels formed by dead plants. This is a combustion reaction. C + O2 → CO2 Carbon dioxide is result of these reactions. Carbon dioxide produced is released to the air through chimneys of power stations. Thus the cycle is completed and all carbon dioxide returns to the atmosphere. Green House Gases: The sun sends energy to the earth in two forms, light and heat. Some of the heat energy reflects back to the space, some however are trapped inside the Earth. This is caused by some gases and it is called the greenhouse effect. The main greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide and methane. Carbon dioxide is formed in many ways. It is formed on a large scale in power stations by the combustion of carbon containing fuels. Carbon dioxide is also caused by respiration of living organisms. The gas can also be produced by a reaction between an acid and a carbonate, like that of the corrosion limestone. Methane, the other greenhouse gas is formed by animals. When animals eat and digest their food, methane gas is one of the waste products of this process. It is released to the atmosphere by animals. When plants die and decompose over many years, methane gas is also produced. The greenhouse effect poses a threat to the world now days. This is because greenhouse gases, especially carbon dioxide, have increased in amounts in the atmosphere due to activity of humans. Lots of fuel combustion is taking place around the world, increasing the levels of CO2, while trees are being chopped off to made use of instead of leaving to replace CO2 with oxygen. These activities cause an increase of the levels of CO2 in the atmosphere, which leads to more heat trapping in earth. This rises the global temperature of the earth causing what’s called global warming. Global warming is the increase of the temperature of the earth due to the increase of levels of greenhouse gases. Global warming has effects on the earth. To start with, it north and south poles, which are made of ice, will start to melt raising sea levels. The sea temperature will also rise causing death to marine lives. This is also accompanied by other natural disasters such as hurricanes and heavy rains. Humans could prevent this by reducing combustion of fossil fuels and leaving forests to live. Ozone depletion: Ozone forms a protective layer in the upper atmosphere (around 20-40 Km above sea level) which filters out most of the harmful ultraviolet rays from the sun. Chemicals from aerosols like chlorofluorocarbons CFCs [CF2Cl2] are destroying this protective layer as. CF2Cl2 → CF2Cl + Cl Cl+ O3 → ClO +O2 ClO+ [O] → Cl +O2 Greenhouse effect: The trapping of the long wavelength radiation coming from the sun, leads to more heating and a higher resultant temperature is known as Green house effect. e.g it is green house effect that a car standing in warm sun light with closed windows (glasses) has higher temperature. Green house gases. · · · · · Water vapours Carbon dioxide gas Methane gas CFCs (Chloroflorocarbons) Ozone gas These gases strongly absorb infrared and does not allow as much of it to escape into space, hence cence contribute to green house effect. Result of green house effect is “Global warming” (rise of temperature). Consequences of Global warming. · · · · Rise in sea level or flooding of low lying land. Climate change or extreme weather or increased rainfall. Desertification or more forest fires or more droughts. Melting of glaciers or melting of polar ice caps or melting icebergs. NOT: increase in temperature or greenhouse effect skin cancers or increase in water level. Sources & effects of Pollution in air Air pollutant Carbon Monoxide Chemical formula CO Carbon dioxide CO2 Lead Compounds Pb Ozone O3 Methane CH4 Unburnt Hydrocarbons CxHy. Smoke (Soot) Sulphur Dioxide Source Exhaust fumes from incomplete combustion of petrol Exhaust fumes from complete combustion of petrol, from trees Exhaust fumes from motor vehicles Car exhaust fumes, electrified rails From the bacterial decay of vegetable matter. Exhaust fumes from internal combustion engines C Burning coal, wood, etc. SO2 Burning fossil fuels like coal, oil, natural gas and also from volcanoes Effects Extremely poisonous and can cause suffocation & death. Its excess creates suffocation, contributes to the 'greenhouse effect' & extinguishes fire. High levels can cause serious damage to children's brains. ozone from car exhausts reacting with sunlight to cause a photochemical smogwhich irritates lungs, etc. Hydrocarbons contribute to the 'greenhouse effect' and cause global warming. Poisonous and causes global warming. Irritates the lungs and causes bronchitis and other lungrelated diseases. Causes acid rain. Attacks buildings, statues made of limestone and damages aquatic life and forests. Oxides of Nitrogen NO, NO2 etc. Exhaust fumes from motor vehicles and lightning activity Like sulphur dioxide, it can cause acid rain.