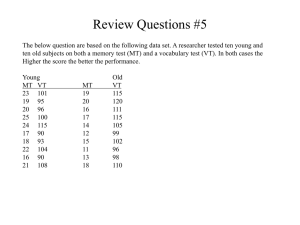
Part One Section 1 INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS RESEARCH METHOD What is Research? Re + search = research Various definitions by various authors A process of searching for answers (i.e. process of discovery) What do you want to know? How do know? Cont…What is Research? A structured, organized, and systematic process Scientific (following certain rules, norms, conventions and traditions) 1 Introduction to Research 1.1What is research? Research is the process of finding solutions to a problem after a thorough study and analysis of the situational factors. 1.2.What is business research? Research provides the needed information that guides managers to make informed decisions to successfully deal with problems. The information provided could be the result of a careful analysis of data gathered firsthand or of data that are already available (in the company). The hallmarks of scientific research 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Purposiveness Rigor Testability Replicability Precision and confidence Objectivity Generalizability Parsimony Hallmarks of Scientific Research 1. Purposiveness It has to start with a definite aim or purpose. The focus is on increasing employee commitment. Increase employee commitment will translate into less turnover, less absenteeism and increased performance levels. Thus it has a purposive focus. 2. Rigor A good theoretical base and sound methodological design would add rigor to the purposive study. Rigor adds carefulness, and the degree of exactitude in research. Example: A manager asks 10-12 employees how to increase the level of commitment. If solely on the basis of their responses the manager reaches several conclusions on how employee commitment can be increases, the whole approach to the investigation would be unscientific. : 3. Testability After random selection manager and researcher develops certain hypothesis on how manager employee commitment can be enhanced, then these can be tested by applying certain statistical tests to the data collected for the purpose. The researcher might hypothesize that those employees who perceive greater opportunities for participation in decision making would have a higher level of commitment. 4. Replicability It means that it can be used again if similar circumstances prevails. Example: The study concludes that participation in decision making is one of the most important factors that influences the commitment, we will place more faith and credence in these finding and apply in similar situations. To the extent that this does happen, we will gain confidence in the scientific nature of our research. 5. Precision and Confidence Precision Precision refers to the closeness of the findings to “reality” based on a sample. It reflects the degree of accuracy and exactitude of the results of the sample. Example: If a supervisor estimated the number of production days lost during the year due to absenteeism at between 30 and 40, as against the actual of 35, the precision of my estimation more favorably than if he has indicated that the loss of production days was somewhere between 20 and 50. Confidence Confidence refers to the probability that our estimations are correct. That is, it is not merely enough to be precise, but it is also important that we can confidently claim that 95% of the time our results would be true and there is only a 5% chance of our being wrong. This is also known as confidence level. 6. Objectivity The conclusions drawn through the interpretation of the results of data analysis should be objective; that is, they should be based on the facts of the findings derived from actual data, and not on our subjective or emotional values. Example: If we had a hypothesis that stated that greater participation in decision making will increase organizational commitment and this was not supported by the results, it makes no sense if the researcher continues to argue that increased opportunities for employee participation would still help! 7. Generalizability It refers to the scope of applicability of the research findings in one organization setting to other settings. Example: If a researcher’s findings that participation in decision making enhances organizational commitment are found to be true in a variety of manufacturing, industrial and service organizations, and not merely in the particular organization studied by the researcher, then the generalizability of the findings to other organizational settings in enhanced. The more generalizable the research, the greater its usefulness and value. 8. Parsimony Simplicity in explaining the phenomenon or problems that occur, and in generating solutions for the problems, is always preferred to complex research frameworks that consider an unmanageable number of factors. For instance, if 2-3 specific variables in the work situation are identified, which when changed would raise the organizational commitment of the employees by 45%, that would be more useful be more useful and valuable to the manager than if it were recommended that he should change 10 different variables to increase organizational commitment by 48%. The Building Blocks of Science in Research Deduction and Inductions Answers to issues can be found either by the process of induction or the process of induction, or by a combination of the two. Deduction Deduction is the process by which we arrive at a reasoned conclusion by logical generalization of a known fact. Example: we know that all high performers are highly proficient in their jobs. If John is a high performer, we then conclude that he is highly proficient in his job Induction Induction is a process where we observe certain phenomena and on this basis arrive at conclusions. In other words, in induction we logically establish a general proposition based on observed facts. AIMS OF RESEARCH The general aims of research are: Observe and Describe Predict Determination of the Causes Explain Read more: http://www.experiment-resources.com/researchprocess.html#ixzz1XywCslzd The Hypothetico-Deductive Method Observation Observation is the first stage, in which one senses that certain changes are occurring or that some new behaviors, attitudes and feelings are surfacing in one’s environment (i.e., the work place). How does one observe phenomena and changes in the environment? Preliminary Information Gathering: It involves the seeking of information in depth, of what is observed. This could be done by talking informally to several people in the work setting or to clients or to other relevant sources, thereby gathering information on what is happening and why. (Unstructured interviews) Then it is followed by structured interviews. Additionally by doing library research or obtaining information through other sources, the investigator would identify how such issues have been tackled in other situations. Theory Formulation It is an attempt to integrate all the information in a logical manners, so that the factors responsible for the problem can be on conceptualized and tested. The theoretical framework formulated is often guided by experience and intuition. In this step the critical variables are identified and examined as to their contribution or influence in explaining why the problem occurs and how it can be solved. Hypothesizing It is the next logical step after theory formulation. From the theorized network of associations among the variables, certain testable hypotheses or educated conjectures can be generated. Hypothesis testing is called deductive research. Sometimes, hypotheses that were not originally formulated do get generated Further Specific Data Collection After the development of the hypotheses, data with respect to each variable in the hypotheses need to be obtained. Further data are collected to test the hypotheses that are generated in the study. Data Analysis Data gathered are statistically analyzed to see if the hypotheses that were generated have been supported. Co relational method will be used to analyze and determine the relation ship of two or more factors in the hypotheses for example: stock availability and customer satisfaction. Deduction Deduction is the process of arriving at conclusions by interpreting the meaning of results of the data analysis. Quali and Quanti Literature Review The basic criteria to evaluating information are as follows: (1) Authority – Who is the author? What are their credentials? (2) Accuracy – Are the facts verifiable? Is the information correct? (3) Objectivity – What is the purpose? Is there a bias? (4) Currency – Is the information up-to-date? (5) Coverage – What is the scope of the information? What does it focus on? The Role of Hypotheses Guide the direction of the study Identify relevant facts Suggest most appropriate research design Provide framework for organizing resulting conclusions Types of Research Quantitative research Testing a theory From theory to data (deductive approach) Qualitative research Developing a theory From data to theory (inductive approach) QUANTITATIVE vs. QUALITATIVE RESEARCH Quantitative Qualitative o Numbers o Words o Point of view of researcher o Points of view of participants o Researcher distant o Researcher close o Theory testing o Theory emergent o Static o Process o Structured o Unstructured o Generalization o Contextual understanding o Hard, reliable data o Rich, deep data o Macro o Micro o Behavior o Meaning o Artificial setting o Natural setting Source: Bryman, A. (2001) RESEARCH INTEREST IDENTIFICATION Industry: Banking, Manufacturing, SMEs, Foods, Retailing. Market: Competitive, volatile, mature, saturated, emerging, stagnant Functions: strategy, Entrepreneurship, marketing, Production, Management Macro-economic factors Country specific: Developing/ Developed countries, Asian, Time Frame: Cambodia Strategic Plan (2006-2010) Lets Practice…. Chapter 1 : Introduction Research Topic Research Title Background of the Study Problem Statement Research Questions Research Objectives Significance of the Study Background of the Study Starting Point of the Study General View of Variable Stepping Stone to Introduce the Flow of the Study What are some of the services found on the Internet? instant messaging e-mail Web message board chat file transfer MARKET COMPETITION AND THE INTERNET Internet can promote competition and efficiency in several respects Transacting on-line provides buyers and sellers much better information about available prices for competing goods. For example, internet prices for books and CDs tend to be 9 percent to 16 percent lower than traditional retail prices. The World Wide Web What is a wireless portal? A portal specifically designed for Webenabled handheld computers and devices Attempts to provide all information a wireless user might require Services include search engines, news, stock quotes, weather, maps, e-mail, calendar, instant messaging, and shopping Mobile Issues……… http://digilib.itb.ac.id/ Education issues………….. http://gdl.itb.ac.id/ Background on OSS OSS Objectives Guiding Principles • Reduce total cost of ownership • Increase freedom of choice of software usage • Increase interoperability among systems • Increase growth of ICT industry • Increase growth of OSS user and developer community • Reduce digital divide • Fit for purpose • Least disruptive to operations • Co-existence with other legacy proprietary systems • Leverage on existing facilities, hardware, software and expertise • Not driven or controlled by hardware or software vendors Copyright VS OpenSource Issues…….. Comparative Study of CHIP MANUFACTURING COMPANY Review of Previous Study Previous Study (Author, Year) Findings and Conclusions of Previous Study Problem Statement There must always exist some clear rationale for the hypothesis. Such rationale is typically presented in a form of “problem statement” which explains what issue or controversy needs to be resolved within the field of study. The “ problem statements’ are included as a subsection of chapter 1 because they announce the puzzle to be solved so that the writer’s statement of hypothesis can go onto make a prediction about the puzzle probable resolution. Steps in Selecting a Topic and Defining a Problem Identify a topic of interest Set general research questions Specify the research objectives Read about the topic Find out the research gap Selecting a Topic / Focus Topic = Focus Focus – central concept being examined in a scholarly study Topic in IT management, e.g. Human resource management practices in IT Equality at IT work E-Government E-Retail issues Sources of Topic / Focus Personal experiences Curiosity (based on something in the media) Hot topics Personal values Everyday life Sources of Focus Past studies Involves conducting a literature review Assumption: Knowledge accumulates (we learn and build on what others have done) Reading relevant materials about the topic THE RESEARCH PROCESS INTERNET MARKETING INVOLVEMENT AND CONSUMER BEHAVIOR Example of Research Title The Application of TAM and Individual Differences to Substantiate the Usage of Internet Banking in Malaysia Research Title Sample……. The Problem “The formulation of the problem is often more essential than its solution” Albert Einstein Problem Definition The indication of a specific area that will be clarified by answering some research questions What is the existing gap? PROBLEM STATEMENT The rates of usage on the internet banking system in Malaysia are rather low compared to the western countries. Phenomena should be rectified and corrected for the benefit of the banking industry in Malaysia. Problem Statement Sample……. Problem Statement (Example) Anxiety, frustration, pressure and stress cause many doctoral degree seeking learners to abandon doctoral programs. Brown and Rudenstine (2016) found that over 40% of those who begin the process never graduate. Long, Convey, and Chwalek (2015) pointed out that selecting and developing a dissertation topic is one of the of important yet difficult steps in completing a doctoral degree Problem Statement (Example) There is a problem in ___________(societal organization). Despite _________________ (something that should be happening) ___________ is occurring. This problem has negatively impacted ____________(victims of problem) because _________________. A possible cause of this problem is ___________ Perhaps a study which investigates ___________ by ________(method) could remedy the situation. "I hear and I forget, I see and I remember, I do and I understand" John Dewey on Experiential Learning. By now, it is well known to those who study the Internet, and to most everyone else, that the volume of on-line business to consumer (B2C) transactions is increasing annually at a very high rate (Meyer, 2004). However, it is also known that there is considerable resistance among many Internet users to engage to B2C transactions over the web, primarily due to concerns about privacy and the trustworthiness of the Internet (Garson, 2005). There could be even more B2C activity on the internet if consumer concerns about privacy and trust could be dealt with successfully (Amstrong, 2006). The relationship between beliefs about privacy and trustworthiness and Internet purchasing is the subject of this paper. Specifically, how do individual beliefs about privacy and trustworthiness of the Internet, and attitudes towards purchasing on the Internet, affect individual intentions to make Internet purchases and actual purchasing behavior? Problem Statement Sample……. Focus to the Problem 1 2 3 4 5 IMPLEMENTATION PROCUREMENT 6 KNOWLEDGE SHARING OWNERSHIP 7 EDUCATION 8 TRAINING ADOPTION TECHNOLOGY Cont… Management is a culture not a discipline Leadership essential to good management Successful manager draws up many theories Holistic management culture requires strong and dispersed leader Financing must be part of solution ,not a part of the problem Financing must be alligned with public interest Financing must safeguard public interest Global competition has led the organization to demand higher performance and business outcomes as they become increasingly cross-functional and cross cultural Organizations with the capacity to adapt in the dynamic environment will successfully maintain their competitive edge. Communication, technology , transportation and international trade agreements have made it almost impossible for business to focus primarily on domestic business environments Every local product has to fight (branding /positioning?)with international giants. Multinational corporation has to give local touch and feel to its product in response to growing customer awareness and segmentation Research Questions Is there….? Somehow…? To what extend…? What is….? How….? Cont… A fundamental research problem that this study seeks to investigate is, whether? Therefore, this study intends to answer the following questions: 1. Is there a relationship between attitude and internet purchasing? 2. Is there a relationship between subjective norm and internet purchasing? 3. Somehow an influence of perceived behavioral control to internet purchasing? Research Objectives To examine the differences To Indicate the relationship To determine the influence of To test the negative impact To identify the factors that….. To prove that there are no differences To provide the evidence To evaluate the effects of….. To measure whether there….. To Compare between 2 variables To regress the DV and IV To confirm the importance of To explain what are the causes of failure To falsify To construct To establish the causes/ the effects, To predict, to correlate Research Objectives Using the theory of planned behavior as its basis, This study is to identify the relationships among beliefs about the Internet privacy and trustworthiness, along with beliefs about perceived behavioral control and the expectations of important others, and online purchasing behavior. OBJECTIVE OF STUDY Apply the TAM in the context of Internet banking In Malaysia. Internet self efficacy as a construct The understanding of an individual's acceptance behavior Research Objectives Sample……. Significance of the Study Significance to the Body of Knowledge/Theoretical Contribution Significance to the Practical/Implementation Level Significant Determinants for Successful IT/e-Commerce Adoption Market Industry Organization Stakeholders User’s Capabilities Significant Determinants for Successful IT/e-Commerce Adoption Market Competitor’s Activities Technology Standardization Government Regulation Rapid Change of Customer’s Needs Market Transparency Significant Determinants for Successful IT/e-Commerce Adoption Industry Scarcity of IT Assets Network Externalities Virtual Relationship w/Partners Business Process Standardization Significant Determinants for Successful IT/e-Commerce Adoption Organization/Firm Adaptive Business Processes Strategic Alignment Flexibility Innovative Culture/Mood Resources Significant Determinants for Successful IT/e-Commerce Adoption Stakeholders Profitable Performances Financial Value & Competence-focused Management Principal Criteria for Stakeholder’s Satisfaction Significant Determinants for Successful IT/e-Commerce Adoption User’s Capabilities System Interfaces User’s IT Knowledgement Acceptance Attitudes Education and Training User Experience of IT Full Research Structure Chapter 1 : Introduction Chapter 2 : Literature Review Chapter 3 : Methodology Chapter 4 : Findings & Discussions Chapter 5 : Conclusions &Recommendations RESEARCH TIME-LINE RESEARCH DEVELOPMENT PROGRESS TASKS NOVEMBER DECEMBER JANUARY FEBRUARY MARCH 15 November - 31 December FINDING TOPIC OF INTEREST 15 November - 31 December RESEARCH PROPOSAL QUESTIONNAIRE DEVELOPMENT QUESTIONNAIRE DISTRIBUTION AND DATA COLLECTION DATA ANALYSIS REPORT WRITING 1 January - 13 February 15 January - 10 February 1 January - 13 February 15 January - 1011 February - 28 February 11 - 28 February 1 - 5 March - 12 March 1 - 5 6March 6 - 12 March RESEARCH BUDGET Equipment Software Installation (SPSS) USD 10 Material and Supplies Paper Size A4 (Double A: 80grms) x 2 units USD 20 Paper Size A4 (Ikip: 70grms) x 2 USD 15 Ink Cartridge (Black) USD 100 Ink Cartridge (Colour) USD 120 Communication (mobile phone bill) USD 150 Stationeries USD 15 Travel Local Transportation including oil consumption) USD 100 Services Photostat (journal and articles) Photostat (Questionnaire form) Others Miscellaneous/Indirect Costs Grand Total USD 30 USD 30 USD 110 USD 100 RM 800 Steps in the Research Process Choose Topic Interpret Data Focus Research Question Analyze Data Design Study Collect Data Inform Others Neuman, 1994: 11 The Research Process Observation Problem definition Theoretical framework Generation of hypotheses Scientific research design Preliminary data gathering Data collection, analysis, interpretation Research objectives/ questions met? Sekaran, 2003: 56 Research Format Main contents: Disclaimer, Abstract foreword, etc. List of Tables and Figures Introduction (Chapter 1) Literature Review (Chapter Method (Chapter 3) Results (Chapter 4) Discussion and Conclusion References Appendices 2) (Chapter 5) Research Proposal Chapter 1 – Introduction Chapter 2 – Literature Review Chapter 3 – Method Completed Research Additional two chapters (at least): 4 – Results Chapter 5 – Discussion and conclusion Chapter Chapter 1 - Introduction Introduction Background of the study Statement of the Problem Research Questions Research Objectives Significance of the Study (7 – 10 pages) Exercise 1 Identify your research interest and research field Identify your research topic/focus. Explain why you choose that particular topic/focus? Why do you think it is important to conduct a research on that topic? Prepare Chapter 1