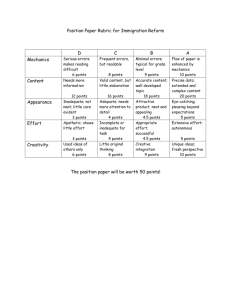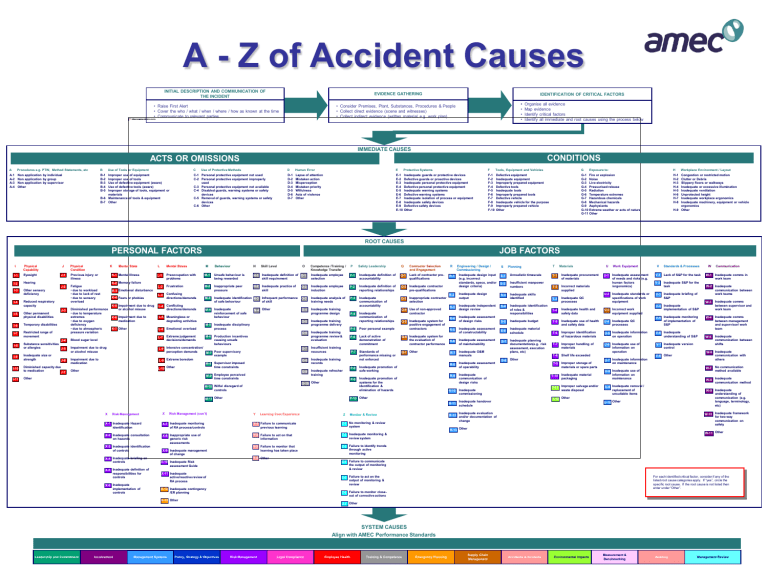
A - Z of Accident Causes INITIAL DESCRIPTION AND COMMUNICATION OF THE INCIDENT EVIDENCE GATHERING • Raise First Alert • Cover the who / what / when / where / how as known at the time • Communicate to relevant parties IDENTIFICATION OF CRITICAL FACTORS • • • • • Consider Premises, Plant, Substances, Procedures & People • Collect direct evidence (scene and witnesses) • Collect indirect evidence (written material e.g. work plan) Organise all evidence Map evidence Identify critical factors Identify all immediate and root causes using the process below IMMEDIATE CAUSES CONDITIONS ACTS OR OMISSIONS A Procedures e.g. PTW, Method Statements, etc B Use of Tools or Equipment A.1 A-2 A-3 A-4 Non application by individual Non application by group Non application by supervisor Other B-1 B-2 B-3 B-4 B-5 C Improper use of equipment Improper use of tools Use of defective equipment (aware) Use of defective tools (aware) Improper storage of tools, equipment or materials B-6 Maintenance of tools & equipment B-7 Other Use of Protective Methods C-1 Personal protective equipment not used C-2 Personal protective equipment improperly used C-3 Personal protective equipment not available C-4 Disabled guards, warning systems or safety devices C-5 Removal of guards, warning systems or safety devices C-6 Other D Human Error E Protective Systems F Tools, Equipment and Vehicles G D-1 D-2 D-3 D-4 D-5 D-6 D-7 Lapse of attention Mistaken action Misperception Mistaken priority Wilfulness Acts of violence Other E-1 E-2 E-3 E-4 E-5 E-6 E-7 E-8 E-9 E-10 Inadequate guards or protective devices Defective guards or proactive devices Inadequate personal protective equipment Defective personal protective equipment Inadequate warning systems Defective warning systems Inadequate isolation of process or equipment Inadequate safety devices Defective safety devices Other F-1 F-2 F-3 F-4 F-5 F-6 F-7 F-8 F-9 F-10 Defective equipment Inadequate equipment Improperly prepared equipment Defective tools Inadequate tools Improperly prepared tools Defective vehicle Inadequate vehicle for the purpose Improperly prepared vehicle Other G-1 Fire or explosion G-2 Noise G-3 Live electricity G-4 Pressurised release G-5 Radiation G-6 Temperature extremes G-7 Hazardous chemicals G-8 Mechanical hazards G-9 Asphyxiants G-10 Extreme weather or acts of nature G-11 Other Exposure to: H Workplace Environment / Layout Congestion or restricted motion Clutter or Debris Slippery floors or walkways Inadequate or excessive illumination Inadequate ventilation Unprotected height Inadequate workplace ergonomics Inadequate machinery, equipment or vehicle ergonomics H-9 Other H-1 H-2 H-3 H-4 H-5 H-6 H-7 H-8 ROOT CAUSES PERSONAL FACTORS I Physical Capability J I-1 Eyesight J-1 Previous injury or illness I-2 Hearing J-2 I-3 Other sensory deficiency Fatigue • due to workload • due to lack of rest • due to sensory overload I-4 Reduced respiratory capacity I-5 Other permanent physical disabilities K Mental State K-1 Mental Illness Temporary disabilities I-7 Restricted range of movement I-8 J-4 Substance sensitivities or allergies J-5 I-9 Inadequate size or strength I-10 Diminished capacity due to medication J-7 I-11 Other J-6 JOB FACTORS L Mental Stress L-1 Preoccupation with problems L-2 Frustration L-3 Confusing directions/demands M-3 Inadequate identification N-3 of safe behaviour Conflicting directions/demands M-4 Inadequate reinforcement of safe behaviour K-2 Memory failure J-3 I-6 Physical Condition M Behaviour N Skill Level M-1 Unsafe behaviour is being rewarded N-1 M-2 Inappropriate peer pressure N-2 K-3 Emotional disturbance K-4 Fears or phobias Diminished performance • due to temperature extremes • due to oxygen deficiency • due to atmospheric pressure variation K-5 Impairment due to drug or alcohol misuse L-4 K-6 Impairment due to medication L-5 Meaningless or degrading activities K-7 Other L-6 Competence /Training / Knowledge Transfer P Inadequate definition of O-1 skill requirement Inadequate employee selection P-1 Inadequate practice of skill Inadequate employee induction P-2 Infrequent performance of skill N-4 Other Emotional overload Impairment due to medication Other O-3 Inadequate analysis of training needs O-4 Inadequate training programme design Inadequate disciplinary process M-6 Production incentives causing unsafe behaviours L-8 Intensive concentration/ perception demands M-7 Poor supervisory example L-9 Extreme boredom M-8 Supervisor imposed time constraints L-10 Other L-7 Impairment due to drug or alcohol misuse O-2 O-5 M-5 Blood sugar level O O-6 Inadequate training programme review & evaluation Insufficient training resources O-8 O-9 M-9 Employee perceived time constraints R Inadequate definition of accountability Q-1 Lack of contractor prequalifications R-1 Inadequate definition of reporting relationships Q-2 Inadequate contractor pre-qualifications Inadequate design input (e.g. incorrect standards, specs, and/or design criteria) R-2 Inadequate design output R-3 Inadequate independent design review S-4 R-4 Inadequate assessment of design risks S-5 Inadequate budget T-5 Inadequate use of health and safety data R-5 Inadequate assessment of constructability S-6 Inadequate material schedule T-6 Inadequate assessment of maintainability S-7 T-7 P-4 Inadequate communication of reporting relationships Q-3 Inappropriate contractor selection Q-4 Use of non-approved contractor Poor personal example Q-5 Inadequate system for positive engagement of contractors P-6 Lack of active demonstration of commitment Q-6 Inadequate system for the evaluation of contractor performance R-6 P-7 Standards of performance missing or not enforced Q-7 Other R-7 Inadequate O&M manuals Inadequate promotion of safe working R-8 P-8 Inadequate assessment of operability R-9 P-9 Inadequate promotion of systems for the identification & elimination of hazards Inadequate communication of design risks M-10 Wilful disregard of controls R-10 Risk Management X Risk Management (con´t) Y Learning from Experience Z Monitor & Review X-1 Inadequate Hazard identification X-7 Inadequate monitoring of RA process/controls Y-1 Failure to communicate previous learning Z-1 No monitoring & review system X-2 Inadequate consultation on hazards X-8 Inappropriate use of generic risk assessments Y-2 Failure to act on that information Z-2 Inadequate monitoring & review system Y-3 Failure to monitor that learning has taken place Z-3 Failure to identify trends through active monitoring X-3 Inadequate identification of controls X-4 Inadequate briefing on controls X-5 Inadequate definition of responsibilities for controls X-6 Inadequate implementation of controls X-9 Inadequate management of change S Planning R-12 T Materials S-1 Unrealistic timescale T-1 Inadequate procurement of materials S-2 Insufficient manpower numbers T-2 Incorrect materials supplied S-3 Inadequate skills identified S-8 Inadequate identification of roles & responsibilities Inadequate planning documentation(e.g. risk assessment, execution plans, etc) Inadequate QC processes T-4 Inadequate health and safety data U-3 Incorrect work equipment supplied V Standards & Processes W V-1 Lack of S&P for the task W-1 V-2 Inadequate S&P for the task V-3 Inadequate briefing of S&P U-4 Inadequate QC processes Improper identification of hazardous materials U-5 Inadequate information on operation V-6 Inadequate understanding of S&P Improper handling of materials U-6 Inadequate use of information on operation V-7 Inadequate version control T-8 Shelf life exceeded T-9 Improper storage of materials or spare parts Inadequate material packaging T-12 Other V-8 Other U-7 Inadequate information on maintenance W-3 Inadequate comms between supervisor and work team W-4 Inadequate comms between management and supervisor/ work team W-5 Inadequate communication between shifts W-6 Inadequate communication with others W-7 U-8 Inadequate use of information on maintenance Communication Inadequate comms in work team W-2 Inadequate communication between work teams V-4 Inadequate implementation of S&P V-5 Inadequate monitoring of implementation of S&P T-11 Improper salvage and/or waste disposal Inadequate handover schedule Work Equipment Inadequate assessment of needs and risks (e.g. human factors /ergonomics) T-3 T-10 Inadequate commissioning U U-1 U-2 Inadequate standards or specifications of work equipment Other P-10 Other R-11 X Engineering / Design / Commissioning P-5 O-10 Other M-11 Other Contractor Selection and Engagement Inadequate communication of accountability Inadequate training records Inadequate refresher training Q P-3 Inadequate training programme delivery O-7 Extreme judgement decisions/demands Safety Leadership No communication method available W-8 Inadequate communication method U-9 Inadequate removal / replacement of unsuitable items W-9 Inadequate understanding of communication (e.g. language, terminology, etc) U-10 Other Inadequate evaluation and/or documentation of change W-10 Inadequate framework for two-way communication on safety R-13 Other W-11 Other Y-4 Other Z-4 Failure to communicate the output of monitoring & review X-10 Inadequate Risk assessment Guide X-11 Inadequate active/reactive review of RA process For each identified critical factor, consider if any of the listed root cause categories apply. If “yes”, circle the specific root cause. If the root cause is not listed then enter under “Other”. Z-5 Failure to act on the output of monitoring & review X-12 Inadequate contingency /ER planning Z-6 Failure to monitor closeout of corrective actions X-13 Other Z-7 Other SYSTEM CAUSES Align with AMEC Performance Standards Leadership and Commitment Involvement Management Systems Policy, Strategy & Objectives Risk Management Legal Compliance Employee Health Training & Competence Emergency Planning Supply Chain Management Accidents & Incidents Environmental Impacts Measurement & Benchmarking Auditing Management Review