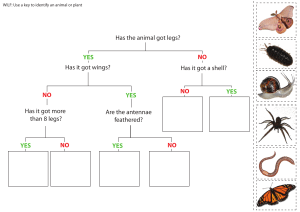
A. CHARACTERISTICS OF LIFE (MRS. GREN) Characteristic Description Movement An action by an organism or part of an organism causing a change of position or place. Respiration The chemical reactions in cells that break down nutrient molecules and release energy for metabolism. Sensitivity To detect or sense stimuli (changes) in the internal or external environment and make appropriate responses. Growth A permanent increase in size and dry mass by an increase in cell number or cell size. Reproduction The process that makes more of the same kind of organism. Excretion Nutrition Removal from the body of: • waste products of metabolism; • toxic materials; • substances in excess of requirements. Taking in of materials for energy, growth and development. B. THE BINOMIAL CLASSIFICATON SYSTEM Less groups but larger in size Kids Prefer Candy Over Fresh Green More groups but smaller in size • Salad Every organism has a binomial name that is decided by its Genus and species. Examples of how this works • The binomial name of the tiger is Panthera tigris. • The tiger’s genus is Panthera. • The tiger’s species is Panthera tigris. • The binomial name of each organism is an internationally agreed system in which the scientific name of an organism is made up of two parts showing the Genus and species. Two organisms belong to the same species if they can breed together to produce fertile offspring • Classification is traditionally based on studies of shape and anatomy (observations). • Classification is now based on DNA bases sequences and amino acid sequences of certain proteins. This is a much more accurate way of grouping organisms. • Organisms which share a more recent ancestor (are more closely related) have DNA base sequences that are more similar than those that share only a distant ancestor. C. CLADOGRAMS • A gene is a DNA base sequence that codes for a protein. • Cladograms are branching diagrams that show how closely related in evolution different organisms are. • DNA base sequences of a specific gene are compared in different organisms. • There will be less differences between organisms that are more closely-related as they share a more recent ancestor. Human Chimpanzee Macaque • The colours show the DNA bases that are the same in all three organisms. • Humans and chimpanzees show the most similarities for this DNA base sequence. What a cladogram looks like shortest distance from a branch point branching point = when organisms ‘split’ and started to evolve differently common ancestor = when all of these organisms were the same many years ago • • • • • Organisms A and B are the most closely related in evolution (As) they share the shortest distance from a branch point (So) they spilt from each other more recently (So) they share a more recent ancestor (So) they have the most similar DNA base sequences D. THE FIVE KINGDOMS ANIMAL PLANT FUNGI Nucleus X Cell wall X Some M M M - most U - some U M - some U - most C C C S C X X X Some Unicellular (U) or multicellular (M) Simple (S) or complex (C) structure Has chlorophyll for photosynthesis PROKARYOTE PROTOCTIST E. THE VERTEBRATES • These are animals that have a backbone. • Mammals and birds are warm-blooded. Their body temperature is kept constant. Vertebrate group MAMMALS BIRDS FISH REPTILES AMPHIBIANS Examples Human Dolphin Bat Whale Monkey Penguin Ostrich Robin Eagle Seagull Shark Tuna Salmon Cod Snake Crocodile Lizard Turtle Tortoise Frog Toad Salamander Newt Features • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Hair or fur Feed young on milk Give birth to live young Have a placenta Breathe using lungs Feathers Wings Most can fly Beaks Lay eggs with a hard shell Breathe using lungs Fins for moving Wet scales External fertilisation (happens outside the body) Breathe using gills • • • Dry, scaly skin Lay eggs with leathery shells Breathe using lungs • • • Smooth, wet, permeable skin Live in water when young but on land when adult Breathe using gills when young but use lungs when adult F. THE ARTHROPODS • This is the largest group of invertebrates, which do not have a backbone. ARTHROPODS • • • Exoskeleton Jointed legs Segmented body INSECTS ARACHNIDS CRUSTACEANS MYRIAPODS 3 body parts 6 legs Many have 4 wings Compound eyes 2 antennae 2 body parts 8 legs No wings Simple eyes No antennae Chalky exoskeleton 10-40 legs No wings Simple eyes 4 antennae Centipedes have 2 legs per segment Millipedes have 4 legs per segment No wings 2 antennae G. THE PLANT KINGDOM PLANTS do not produce flowers FERNS No flowers Leaves are called fronds Reproduce using spores produce flowers FLOWERING PLANTS MONOCOTYLEDONS DICOTYLEDONS One cotyledon in their seeds Two cotyledons in their seeds Leaves are strap-shaped Leaves have parallel veins A cotyledon is the embryo and its food stores in a seed Leaves are broad and wide Leaves have branching veins Tap root system Branched root system Flowers are usually in multiples of 3 Flowers are usually in multiples of 4 or 5 H. DICHOTOMOUS KEYS • Dichotomous means ‘dividing into two’. • These keys include a series of paired statements or questions that lead to an organism being identified. • When designing a key yourself, look for ‘clear cut’ obvious features that can easily be distinguished. Has the animal got legs? YES Has it got wings? NO Has it got more than 8 legs? YES NO Centipede Spider NO Has it got a shell? YES Is it active at night? YES Moth NO Butterfly NO YES Worm Snail