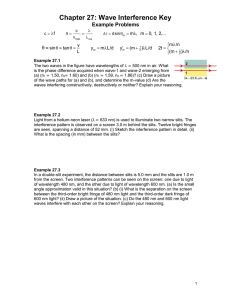
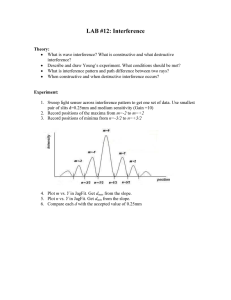
INTERFERENCE Objectives • Describe how light waves interfere with each other to produce bright and dark fringes. • Identify the conditions required for interference to occur. • Predict the location of interference fringes using the equation for double-slit interference. Video Observation - Discussion • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CAe3lkYNKt8 Waves in Phase and Out of Phase Resultant Waves Wave Length , Amplitude , node and antinode Phase difference for Interference Two speakers 3.0 m apart are making sound with a wavelength of 48.0 cm. and v = 343 m/s? is it loud, or quiet (frequency) If I am 2.12 m from one speaker, and 3.80 m from the other,, and how many wavelengths difference in distance is there? is it destructive or constructive ? Hint : v = f 3.5 wavelengths, destructive Coherent Vs Incoherent interference Conditions of Interference of light waves Path Difference for Light Waves from Two Slits Equation for Interference Sample problem Practice 1 • Lasers are devices that can emit light at a specific wavelength. A double-slit interference experiment is performed with blue-green light from an argon-gas laser. The separation between the slits is 0.50 mm, and the first-order maximum of the interference pattern is at an angle of 0.059° from the centre of the pattern. What is the wavelength of argon laser light? Practice 3 • A pair of narrow parallel slits separated by a distance of 0.250 mm is illuminated by the green component from a mercury vapor lamp (λ = 546.1 nm). Calculate the angle from the central maximum to the first bright fringe on either side of the central maximum.