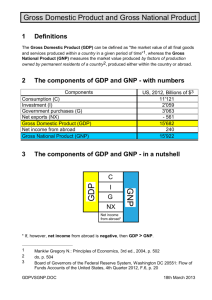
Section tow: Macroeconomic Macro means ‘large’ its branch of Economic dealing with performance, structure, behavior, and decision _making of an economic as whole rather than individual market. Field of Macroeconomic study aggregate indicators such as unemployment rates, GDP, Price levels, National Income, determination of consumption and Investment levels. History of Macroeconomics: 1. Great Depression 1929. In USA when goods remains un sold and workers unemployment a feat that left classical economics stumped, this evolved though out the 20th century diverting into several macroeconomic school. 2. Keynesian Theory 1936. Started with John Maynard kenes and publication of his book “General Theory Of , Interest and Money in 1936. Objective of Macroeconomic policy: 1. Full Employment . 2. Price Stability. 3. Economic Growth. 4. External Balance. *Major concept in Macroeconomic: 1- GNP: Gross National Product Is monetary value of all finished goods and service produced by country in specific time period usually calculated on annual basis. 2- GDP : Gross Domestic Product: Is monetary value of all finished goods and service produced within country Border in specific time period usually calculated on annual basis. GNP measure the productivity of nation’s citizen regard less of their locals as opposed to the GDP. Method Calculate GNP: 1. Expenditure Approach. 2. Income Approach. 3. Out Put e Approach. 1. Expenditure Approach:By this method GNP includes public consumption, government out lays, investment and export minus import The total sum of all s . products used in developing finished product for: 1. Consumption expenditure. 2. Investment expenditure. 3. Government expenditure. 4. Net of foreign trade. GDP = C+I+ G+X-M 2. Income Approach: It’s Measure GDP by way of totaling domestic income earned at all levels and used gross income . 1. Wages 2. Profit 3. Interest. 4. Rent. 5. Indirect taxes. 6. Depreciation. GDP = Wages +Rent + Profit +Interest + Indirect taxes + Depreciation Other concept of macroeconomic: 1. GNP: Measure of country economic performance or what e citizen produces goods and service and whether they produced within border. Real GDP: Can account for change in price level and provide a more accurate figure. R.G.N.P: Is inflation _ adjusted , measure that reflect the value of all goods and service produced in a given Year expresses in base year ,often referred to as (Constance_ price and inflation corrected. D.P.I Deflater Price Index GNP / R.G. N.P Example 1 Goods X Y Z Required: 1. Compute GNP1981 1980 P 2 3 1 1981 Q 5 4 2 P 3 4 2 Q 6 5 3 ∑ 𝑃𝑛 𝑄𝑛 = 3 ∗ 6 + 4 + 5 + 2 ∗ 3 = 44 2. Compute R.G.N.P1981. ∑ 𝑃0 𝑄𝑛 = 2 ∗ 6 + 3 ∗ 5 + 1 ∗ 3 = 30 3. Compute D.P.I 1981 𝐷. 𝑃. 𝐼 = 𝐺.𝑁.𝑃1981 𝑅.𝐺.𝑁.𝑃1981 *100 44 = *100 = 146.6 30 INF. RATE=146.6-100=46.6 4. compute Economic Growth Rate suppose population growth Growth Rate (G.R) N: Compare year b: basis year 𝐸. 𝐺. 𝑅 = 𝑅. 𝐺. 𝑁. 𝑃𝑁 − 𝑅. 𝐺. 𝑁. 𝑃𝑏 𝑅. 𝐺. 𝑁. 𝑃𝑏 𝐸. 𝐺. 𝑅 = 𝑅. 𝐺. 𝑁. 𝑃1981 − 𝑅. 𝐺. 𝑁. 𝑃1980 𝑅. 𝐺. 𝑁. 𝑃1980 𝑅. 𝐺. 𝑁. 𝑃1980=∑ 𝑃0𝑄0=2∗5+3∗4+2∗1=24 𝐸. 𝐺. 𝑅 = 30 − 24 ∗ 100 = 25% 24 G.R= E.G.R-G.POP=25-2=23