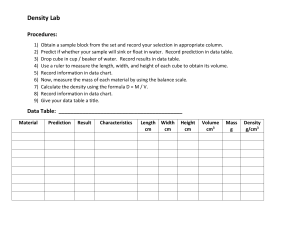
Name:____________________________________________________________________Per:_____ Date:____________ What is the ideal cell size? As you have observed, cells are small. Consider your little toe: it is made of about 2-3 billion cells! A newlymade cell will grow, but once it reaches a certain size it will divide to form two new cells rather than growing bigger. Why is this? Why aren’t you made of a few dozen, or a few hundred cells, instead of trillions? Why don’t single-celled organisms like amoebas and paramecia grow as big as a human? In this lab, we will investigate this question using model cells. Prelab Questions Contribued by 1. What is the basic structure of a cell? All cells have a cell membrane, ribosomes, cytoplasm, DNA. +2 2. What are some factors that could limit the ability of cells to survive? Environment, predation, mutations, disease, the ability to obtain nutrients and get rid of waste +2 3. Could any of these factors also limit the size of cells? Write your ideas here: The ability to process nutrients is probably the biggest limiting factor for growth and cell size. If a cell is unable to obtain the nutrients that it needs then its growth would be reduced and possible death would occur. +2 4. How do cells obtain materials they need and get rid of waste products? Cells obtain the material they need through the cell membrane (diffusion), once in the cell then the cell must transport those materials throughout the cell to all of the different organelles and the same must occur with waste except the cell with move this material out of the cell. +2 5. In this lab, we will investigate the ability of three model cells of different sizes to obtain nutrients from their environment. If the cell sizes are 2 cm3, 1 cm3 and .5 cm3, which cell do you think will be more successful? Should have one of the 3 +1 6. Explain your reasoning: Answers will very: should be good explanation as to why they picked the size they did. +2 Gathering Data Obtain safety goggles (for each group member), a potato stick, a metric ruler, 3 plastic knives, a 50mL beaker, a 250mL beaker and a single glove from the supply table. Decide who in the group will be knife wielder 1, 2 and 3, and who will be the metric master, and put on the safety goggles. From the potato stick, knife wielders measure and cut three cubes with the following dimensions: o Knife Wielder 1: 2 cm3 cube o Knife Wielder 2: 1 cm3 cube o Knife Wielder 3: 0.5 cm3 cube Metric master will verify accuracy and cubic dimensions, and fill the 250 mL beaker about ¾ full with tap water. When the cubes are perfect, the metric master will obtain iodine solution to cover the cubes. Allow cubes to soak in iodine solution for 15 minutes (Knife Wielder 2 keeps track of time). 7. What do the cubes represent? Different size cells. +1 8. What does the iodine represent? Nutrients for the cells. +1 Cube Data +9 Cube Size (cm) .5 Surface area (cm2) Volume (cm3) (length x width x number of sides) (length x width x height) 1.5 cm2 0.125 cm3 Surface Area: Volume Ratio (reduced) 1.5 : 0.125 or 12:1 1 6 cm2 1 cm3 6:1 24 cm2 2 8 cm3 24:8 or 3:1 After 15 minutes, Knife Wielder 3 obtains three folded squares of paper toweling. Knife Wielder 1 puts on the glove and carefully removes the three cubes from the iodine solution, swirls them in the large beaker of water to rinse off excess iodine, and then places them on the paper toweling squares. Distribute each potato cube to the knife wielder who created it. Metric master will return the beaker of iodine to the collection station at the teacher’s desk, and obtain a scalpel. Metric master will slice each potato cube in half and then return the scalpel to the collection station; Knife Wielders measure (in cm) and report how far the iodine penetrated into each cube. Diffusion of Iodine +9 Cube Size (cm) Time (min) Rate of Diffusion (cm/min) .1 15 .0066666667 .1 15 .0066666667 .1 15 .0066666667 Volume still Depth of Diffusion (cm) white .5 .5 - .2 = .3 1 1 - .2 = .8 2 2 - .2 = 1.8 All team members help with the following calculations: Percent Volume of Cube = ((total cube volume) – (volume of cube that has not changed color) x 100% That Received Iodine (total cube volume) Extent of Diffusion +9 Total Volume of Cube (cm ) Volume of cube that has not changed color (cm3) Percent of total volume of cube that received iodine 0.125 cm3 (.3 x .3 x .3) .027 78.4% 1 cm3 (.8 x .8 x .8) .512 48.8% 8 cm3 (1.8 x 1.8 x 1.8) 5.8 27% 3 Wash and dry all utensils, including beakers, and return everything neatly where you found it. Dispose of potato cubes, paper toweling and glove in the trash. Wipe your work surface clean! If you have time, work with your team members on the Discussion Questions. Discussion Questions 1. What is a potato? It is a vegetable also known as a tuber made up of cells. +2 2. Why did the diffusion of iodine into the potato cube cause the color change from white to black? Cells of the potato absorbed the iodine through the cell membrane (diffusion). +2 3. If each cube represented a living cell, and the iodine solution was a substance needed within the cell, what problem might the largest cell have? The largest cell would have trouble getting nutrients to all parts of the cell fast enough to support its size. +2 4. Examine your data in table 2. What pattern do you notice in the relationship between cube size and the rate of diffusion? The rate of diffusion is constant. +2 5. Examine your data in table 1. Describe what happens to the surface area and the volume as the cell grows larger. As the cell grows larger the volume amount increases at a higher rate then the surface area thus as cells increase in size they lose the high ratio of surface area to volume. +2 6. Still considering table 1, what happens to the ratio between surface area and volume as the cell grows larger? The surface area and volume ratio start to show less of a difference in the amount of each total (12:1 -> 6:1 -> 3:1) . +2 7. According to your data, which cell was most successful at receiving the needed nutrient (iodine solution) in the allowed time? The smallest cell (.5 cm). +2 8. What can you say about the surface area to volume ratio that will best meet the needs of living cells? In order to get the nutrients needed for survival into all parts of the cell it is necessary for the cell to remain small with a high surface area to volume ratio. +2 9. Why is surface area significant in this situation? Surface area allows for contact space for nutrients to enter the cell, the higher the amount of surface area compared to amount of volume the more nutrients the cell can obtain and quickly distribute to the volume of the cell. +2 10. Use what you learned in this lab to answer the research question. Individual cells do not grow large because the cell would be unable to distribute the needed nutrients to the cells increasing volume. As the size increases the volume increases at a faster rate then the surface area thus slowing the cell ability to move nutrients into the interior of the cell were it is needed for survival. So the cell divides and stays small which creates many cells with high amounts of surface area per volume ratios. +2 11. Evaluate your initial hypothesis (as stated in the PreLab). Answer will very but this should discuss whether the hypothesis was supported or not by the data and which cell size is best. +2 12. Graph the Percent Volume of Cube Changed by cell size (0.5, 1 and 2cm), then use your graph to predict the percent Volume of Cube Changed for a hypothetical cube of .25 cm, and one of 4 cm. It looks as if the 4 cm cell would have a negative amount of nutrients getting in but this is not possible but it certainly shows that the larger cell get much less then the smaller cell. The .25 trend seems to show that 104% of the cell will get nutrients which is also impossible but the entire cell could be getting nutrients (100%) much more efficient then the larger cell. +4 Trend line graph below. How cell size affects nutrients intake. 120 Percent of cell getting nutrients 100 78 80 60 49 40 27 20 0 0.25 0.5 1 2 -20 -40 size of cell in cm 3 4