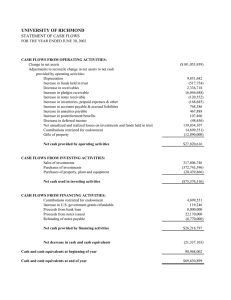
Purpose of balance sheet - Reports assets, liabilities and equity at a specific date - Provides information about resources, obligations to creditors and equity in net resources - Helps in predicting amounts, timing and uncertainty of future cash flows Usefulness of balance sheet - Compute rates of return - Evaluate the capital structure - Assess risk and future cash flows - Assess company’s liquidity, solvency and financial flexibility Limitations of balance sheet - Most assets and liabilities are reported at historical cost - Use of judgements and estimates (i.e. FIFO) - Many items of financial value are omitted (i.e. human capital) ***More companies favor reporting current assets first Non-current assets: not expected to be converted to cash or consumed within 1 year or the operating cycle 1. Long-term investments - Securities: bonds, ordinary shares, long-term notes o Held-for-collection: investments held with the objective of holding assets in order to collect contractual cash inflows (i.e. interests) o Trading: investments that are bought and held primarily for sale in the near term to generate income on short-term price differences o Non-trading: investments that are bought and held for strategic reasons (i.e. regulatory issues, enhancement the coordination or bargaining power) Type Valuation Classification Held-for-collection Debt Amortized cost Current or non-current Trading Debt / equity Fair value Current Non-trading Equity Fair value Current or non-current - Tangible assets: not currently used in operations (i.e. land held for speculation) - Special funds: sinking fund (money set aside to pay for the debt in the future), pension fund - Non-consolidated subsidiaries or associated companies (i.e. companies in joint ventures) 2. Property, plant and equipment - Tangible long-lived assets used in the regular operations of the business - Example: physical property such as land, buildings, machinery, furniture, tools and wasting resources - Companies depreciates or depletes PP&E except land (value of land goes up with infinite useful life unless the land is seriously damaged) 3. Intangible assets - Lack physical substance and are not financial instruments - Example: patents, copyrights, franchises, goodwill, trademarks, trade names and customer lists - Amortize limited-life intangible assets over their useful lives - Periodically assess indefinite-life intangibles for impairment 4. Other assets i.e. long-term prepaid expense, non-current receivable, property held for sale, restricted cash Current assets: expected to be converted to cash, sell or consumed within 1 year or the operating cycle 1. Inventories - Basis of valuation (i.e. lower-of-cost or net realizable value) - Cost flow assumption (i.e. FIFO or average cost) o LIFO is not permitted under IFRS. For LIFO, COGS used current prices but ending balance of balance sheet uses old prices, which is not reasonable. IFRS focuses more on the balance sheet than income statement. 2. Prepaid expenses - Payment of cash that is recorded as an asset because service or benefit will be received in the future, expecting economic inflow (cash payment before expense recorded) 3. Receivables - Major categories of receivables should be shown in the statement of financial position or the related notes - Company should clearly identify anticipated loss due to uncollectibles, amount and nature of any nontrade receivables and receivables used as collateral 4. Cash and cash equivalents - Generally consist of currency and demand deposits - Cash equivalent: short-term, highly liquid investments that mature within three months or less o Example: commercial paper, certificate of deposit, short-term government bonds - Restrictions or commitments must be disclosed o Restricted cash for long-term obligation should not be reported in the cash section 5. Short-term investments Non-current liabilities: obligations that a company does not expect to liquidate in its normal operating cycle or one year - Arise from specific financing situations - Arise from the ordinary operations of the company - Depend on the occurrence or non-occurrence of one or more future events to confirm the amount payable or the payee, or the date payable Current liabilities: obligations that a company expects to settle in its normal operating cycle or one year - Payables resulting from the acquisition of goods and services - Collection received in advance for the delivery of goods or services (i.e. unearned revenue) - Other liabilities whose liquidation will take place within the operating cycle or one year Equity - Share capital: par or stated value of shares issued, including ordinary shares and preferred shares Share premium: excess of amounts paid-in over the par or stated value Retained earnings Accumulated other comprehensive income Treasury shares: ordinary shares repurchased Non-controlling interest (minority interest) Why is cash flow important? - Sustain business operation (buy supply, pay wages) - Prepare firms to cope with bad business environment - Prepare firms to take good investment opportunities IASB requires the publication of statement of cash flows Statement of cash flows provides relevant information about the cash receipts and cash payments of an enterprise during a period - Where did the cash come from? - What was the cash used for? - What was the change in the cash balance? - Source of information: comparative statements of financial position, income statement and selected transaction data for financing and investing activities Operation activities are transactions that determines of net income. - Convert net income on an accrual basis to a cash basis - Add to or deduct from net income those items in the income statement that do not affect cash Account receivable – 1000 Account receivable increases Cash same Revenue – 1000 Revenue increases Net income increases Minus increase in account receivable Cash – 800 Cash increases Account receivable – 800 Account receivable decreases Add decrease in account receivable Account receivable – 1000 Account receivable increases Revenue – 1000 Revenue increases Minus increase in account receivable Supply expense – 1000 Supply expense increases Accounts payable – 1000 Account payable increases Add increase in account payable Accounts payable – 800 Account payable decreases Cash – 800 Cash decreases Minus decrease in account payable COGS – 5000 COGS increases Inventory – 5000 Inventory decreases Add decrease in inventory Inventory – 1000 Inventory increases Cash – 1000 Cash decreases Minus increase in inventory Depreciation – 5000 Depreciation increases Accumulated depreciation – 5000 Add increase in depreciation Net income increases minus / net income decreases add Cash increases add / cash decreases minus Increase in account receivable minus Increase in inventory minus Increase in account payable add Cash increases Net income same Cash same Net income increases Cash same Net income decreases Cash decreases Net income same Cash same Net income decreases Cash decreases Net income same Cash same Net income decreases Investing activities are transactions related to loans, investments and PP&E. Financing activities are transactions involving liability and equity items. Significant non-cash activities reported in a separate not to the financial statements. - Example: issuance of ordinary shares to purchase assets, conversion of bonds into ordinary shares, issuance of debt to purchase assets, exchanges on long-lived assets Usefulness of Statement of Cash Flows - Financial liquidity o Current cash debt coverage ratio = Cash from operating activities / Average current liabilities (indicate the ability to pay off the current liabilities from operation, ratio near 1:1 is good) - Financial flexibility o Cash debt coverage ratio = net cash provided by operating activities / average total liabilities (indicate the ability to repay liabilities from net cash provided by operating activities, without having to liquidate assets employed in operations longer view) Accruals = net income – net operating cash flow - Represents investments in net current assets and adjustments for accounting items that are not cash items