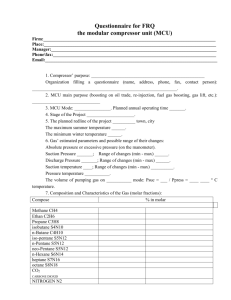
2019 HAZOP STUDY FOR REFRIGERATION CYCLE 2016-CH-404 SUBMITTED TO: SIR AZAM SAEED HAZOP Study of Refrigeration cycle Guideword Deviation Causes consequences Action No Flow No flow of cooling agent Very low temperature in condenser No cooling More More flow agent Improper checking, loose valve Fouling Fouling can be b/w evaporator and condenser tube Leakages of refrigerant it can lead to increased energy use by the compressor. Failure Compressor failure lubrication problems, overheating, slugging, flood back and contamination It may not work properly Restriction Liquid line restriction Some type of contamination Abnormally high discharge temperature, Low current draw, High superheats, Low condensing pressures Perform a freeze test More More flow An interruption in the flow output to storage tanks because of an error reading by High level allows entrainment of liquid ammonia into the compressor can Check level transmitter Keep surface and tube clean level transmitter make the broken blade and shutdown Other than Other than flow Control surge malfunction due to damage to the flow control Valve opening is not in accordance with requirements Install a proper valve in working less Less level Input ammonia liquid derived from control flow too low The loss of liquid level at which can lead to Compressor surges and Damaged Compressor checking Less Less flow Level valve failed to open or did not fit the required percentage Level high allows entrainment of liquid ammonia into the compressor can make a blade is damaged