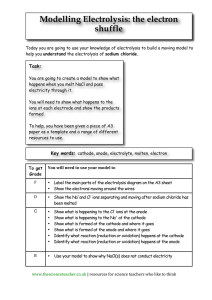
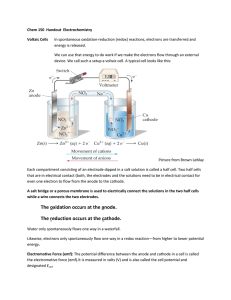
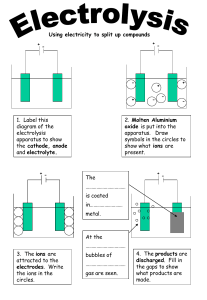
Unit 6: Electricity and Chemistry Prepared by : Amanda Anusha Unit 6 : Electricity and Chemistry 6.1 : Electrolysis What is electrolysis? • Electrolysis is the breaking down of an ionic compound in molten/aqueous solution by passage of electricity. • When electric current is passed through the ionic compound, a chemical reaction occurs and breaks down the compound. • The compound decomposes. Unit 6 : Electricity and Chemistry 6.1 : Electrolysis What is electrolysis? • The electrolysis cell has all the key parts. Unit 6 : Electricity and Chemistry 6.1 : Electrolysis What is electrolysis? • The functions of parts in the electrolytic cell are: Part Function Electrolyte Conducts electricity when molten and breaks down during electrolysis Electrodes Carry electric current to and from the electrolyte (normally inert) Anode Positive electrode Cathode Negative electrode Unit 6 : Electricity and Chemistry 6.1 : Electrolysis Predicting the products of electrolysis Unit 6 : Electricity and Chemistry 6.1 : Electrolysis Predicting the products of electrolysis At the cathode At the anode Observation When electricity is flowing, a silvery deposit of lead metal forms on the cathode. In fact, as it is molten, it is more likely to drip off in a molten blob. Observation When electricity is flowing, brown fumes of bromine gas are seen at the anode. Half equation Pb2+ + 2e ---> Pb Half equation 2Br- ---> Br2 + 2e Explanation The lead(II) ions, as they are positive, move to the negative cathode, where each ion gains two electrons to form a lead atom. Explanation The bromide ions, as they are negative, move to the positive anode, where each loses an electron to form a bromine atom.