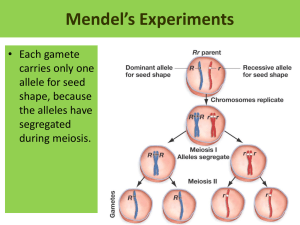
Select a number from the existing numbers 3 2 1 6 5 4 9 8 7 What type of organisms only reproduce asexually? A. bacteria B. protists C. plants D. simple animals Name the person known as the father of genetics. A. Felix Mendelssohn B. Gregor Mendel C. Dr. Reginald Punnett D. Albert Einstein Which pair of alleles is heterozygous? A. RR B. Rr C. rr D. yR Study the figures and answer How many cells are produced in the mitosis? 2. How many cells are produced in the meiosis? Mitosis= 2cells Meiosis = 4gamets What is this process called? A. fertilization B. gamete formation C. inheritance D. reproduction Segments of DNA that control the production of proteins are called _______. A. chromatids B. chromosomes C. genes D. traits What is the name for different forms of a single gene that are passed from generation to generation? A. alleles B. genotypes C. phenotypes D. traits To which step in this process does the law of segregation apply? A. grows into plant B. gamete formation C. fertilization D. seed development Try again Is Varies questions Duration of activity: 4 min STARTER Chapter 4 Section 1: Meiosis Section 2: Mendelian Genetics Section 3: Genetic linkage and chromosomes diversity Sexual Reproduction and Genetics Today we will talk about Mendelian Genetics 4.2 Mendelian Genetics What do I know about? What do I want to know about ? How can I find out? What you learned about? What action will I take? What new questions do I have? Review Vocabulary segregation: the separation of allelic genes that typically occurs during meiosis Sexual Reproduction and Genetics Today’s vocabulary item genetics phenotype allele dominant recessive law of segregation hybrid law of independent homozygous heterozygous genotype assortment 4.2 Mendelic Inheristance ) Lesson Objectives ( Explain the significance of Mendel’s experiments to the study of genetics Summarize the law of segregation and law of independent assortment. Predict the possible offspring from a cross using a Punnett square. Real world reading link There are many different breeds of dogs Labrador retrievers dachshunds German shepherd You might like a certain breed of dog because of its height, coat color, and general appearance. Poodles how genetic traits are passed on to the next generation. Section 2 Mendelic Inheristance Mendel explained how a dominant allele can mask the presence of a recessive allele. How Genetics Began Gregor Mendel father of genetics Pea plants Pea plants are: 1.Easy to grow 2.Many are truebreeding, Produce offspring with only one form of a trait. 3. Reproduce by self-fertilization Mendel studied seven different traits. Seed or pea color Flower color Seed pod color Seed shape or texture Seed pod shape Stem length Flower position F2 generation plants from these crosses also showed a 3:1 ratio. Strategy is Think discuss with your partner Participate You have two pictures, which one is self pollination, and the cross pollination? Duration of activity: 1 min cross pollination Self pollination Transferring a male gamete from the flower of one pea plant to the female reproductive organ in a flower of another pea plant. occurs when a male gamete within a flower combines with a female gamete in the same flower. cross pollination Self pollination What is heredity? The passing on of characteristics (traits) from parents to offspring What is Genetics ? is the study of heredity parent generation Male gamete Female gamete ( p) true-breeding green-seed true-breeding yellow-seed ( cross pollination) yellow-seed First filial generation (F1) ( self pollination) Second filial generation green-seed 2001 Ratio 1 : yellow-seed 6022 3 (F2) Mendel removed the male organs from the flower of the yellow-seed plant, Why??? To prevent self fertilization Infer why it is important that mendel’s experiments used to true breeding plant? The use of true-breeding plants allowed Mendel to easily segregate the genes passed from generation to generation Alleles •Each organism has two alleles for each trait •Alleles - different forms of the same gene •Genes - located on chromosomes, they control how an organism develops allele An alternative form of a single gene passed from generation to generation Phenotype & Genotype An organism’s allele pairs Genotype Phenotype The observable characteristic or outward expression of an allele pair yellow-seed Phenotype & Genotype •Phenotype - the way an organism looks • Example - red hair or brown hair •genotype - the gene combination of an organism • AA or Aa or aa Heterozygous & Homozygous •Heterozygous - if the two alleles for a trait are different (Aa) •Homozygous - if the two alleles for a trait are the same (AA or aa) WW - Homozygous dominant Ww – Heterozygous( hybrid) ww - Homozygous recessive Write Heterozygous or Homozygous??? BB Bb bb Male gamete Phenotype Genotype Female gamete green-seed yy Phenotype parent generation ( p) yellow-seed YY yellow-seed First filial generation Genotype (F1) Yy Second filial generation Ratio green-seed 2001 1 : yellow-seed 6022 3 (F2) Look at the shape, write the recessive trait and dominant trait yellow-seed Dominant green-seed recessive Comment on your work Explain the significance of Mendel’s experiments to the study of genetics First filial generation (F1) ( self pollination) Y Y y y Second filial generation (F2) Phenotype yellow-seed Genotype Yy Ratio Phenotype Ratio 2 yellow-seed green-seed yy YY : 1 : 1 yellow-seed green-seed 3 1 Why the seeds in the F1 generation were all yellow? The yellow seed was the dominant form of the trait. All the seeds in the F1 generation received one copy of the dominant gene. Mendel’s Law of Segregation Two alleles for each trait separate during meiosis During fertilization, two alleles for that trait unite. Heterozygous organisms are called hybrids. Monohybrid Cross A cross that involves hybrids for a single trait (seed color) green-seed yellow-seed Punnett Squares-Monohybrid Cross Predict the possible offspring of a cross between two known genotypes Comment on your work Predict the possible offspring from a cross using a Punnett square. Dihybrid Cross two traits (seed color) (seed form) yellow-seed round-seed green-seed wrinkle-seed Look at the shape, write the recessive trait and dominant trait yellow-seed round-seed Dominant green-seed wrinkle-seed recessive Look at the shape, write the Genotype yellow, round-seed pea plants YY RR green, wrinkle-seed pea plants yyrr Dihybrid Cross Sexual Reproduction and Genetics The simultaneous inheritance of two or more traits in the same plant yellow, round-seed pea plants YY RR green, wrinkle-seed pea plants yyrr Dihybrids are heterozygous for both traits. parent generation ( p) yyrr YY RR ( cross pollination) First filial generation (F1) ( self pollination) ( Gametes) Yy YyRr Rr Punnett square—Dihybrid cross Four types of alleles from the male gametes and four types of alleles from the female gametes can be produced. He counted and recorded four different Phenotypes 315 yellow round 108 green round 101 yellow wrinkled 32 green wrinkled Ratio 9:3:3:1. Genotypes: YYRR YYRr Yyrr YyRR YyRr Yyrr yyRr yyRR yyrr Punnett Square— Dihybrid Cross The resulting phenotypic ratio is 9:3:3:1. law of independent assortment random distribution of alleles occurs during gamete formation. Genes on separate chromosomes sort independently during meiosis. Each allele combination is equally likely to occur. Evaluate How can the random distribution of alleles result in a predictable ratio? Because there is an equal chance that each pair of alleles can randomly combine with each other, the outcome of a large sample size will be a predictable ratio Predict How many possible gamete types are produce? Four Comment on your work Summarize the law of segregation and law of independent assortment.