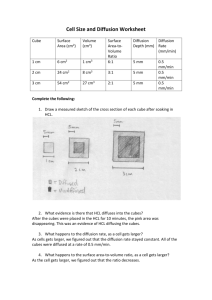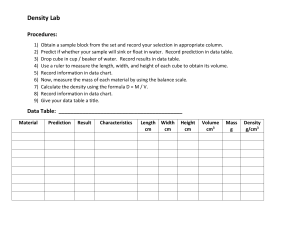
Results: Cube Size Total cube volume (cm3) Total volume of the decolorize cube (cm3) Percent Decolorization Surface area of cube (cm2) Surface area to volume ratio 1cm 1.586 cm3 0 cm3 100% 8.4 cm2 8.4 : 1.586 2cm 4.5 cm3 0.084 cm3 98.1333% 15 cm2 15 : 4.5 3cm 25.2 cm3 4.725 cm3 81.25% 53.4 cm2 53.4 : 25.2 Discussion: A cell needs a large surface to carry out metabolic functions and as the cell grows it needs to carry out more and more reactions. Diffusion is one of the most important processes of a cell in which it is used to transport substances such as molecules, nutrients, water, oxygen, and cellular waste through the cell membrane of a cell. Diffusion occurs when molecules in an area of higher concentration move to an area of lower concentration (Stouffer & Slisz, 2019). HCl is more concentrated outside the cubes than it is in the inside, HCl is diffusing through the outer surface of each agar cube. TOTAL CUBE VOLUME VS SURFACE AREA 72 3 25,2 18 2 4,5 1 1,586 11,76 0 20 SURFACE AREA 40 60 80 TOTAL CUBE VOLUME When a cell grows, there is comparatively less membrane for the substances to diffuse through resulting in the center of the cell not receiving the substances that it needs. Diffusion is less efficient, cell processes slow and cells stop growing. The cell needs to divide into two smaller cells, which each have a larger Surface Area:Volume ratio and can diffuse materials more efficiently.(edit mo to mamsh hahah) That is why cells are small because they rely on diffusion for getting substances into and out of their cells. Appendices: D. Diffusion and Surface Area Volume of 0.1 M HCl: C1 V1 = C2 V2 1 M * V1 = 0.1 M * 1000 mL V1 = 0.1 M∗1000 mL 1M = 100 mL % Decolorization = 1. volume of cube − volume of decolorized portion volume of cube (1.4 ∗ 1.4 ∗ 0.8) – (0) (1.4 ∗ 1.4 ∗ 0.8) x 100% ∗ 100% = 100% 2. (2 ∗ 1.5 ∗ 1.5) – (0.7 ∗ 0.4 ∗ 0.3) (2 ∗ 1.5 ∗ 1.5) 4.5−0.084 ∗ 100% = ∗ 100% 4.5 = 98.1333% 3. (4∗ 3 ∗ 2.1)– (2.1 ∗ 1.5 ∗ 1.5) (4 ∗ 3 ∗ 2.1) 25.2−4.725 ∗ 100% = ∗ 100% 25.2 = 81.25% Surface Area = Length * Width * # of sides 1. 1.4 * 1.4 * 2 = 3.92 cm2 1.4 * 0.8 * 2 = 2.24 cm 2 1.4 * 0.8 * 2 = 2.24 cm 2 Total surface area: 8.4 cm2 2. 2 * 1.5 * 2 = 6 cm2 1.5 * 1.5 * 2 = 4.5 cm 2 1.5 * 1.5 * 2 = 4.5 cm 2 Total surface area: 15 cm2 3. 4 *3 * 2 = 24 cm2 4* 2.1 * 2 = 16.8 cm 2 3 * 2.1 *2 = 12.6 cm 2 Total surface area: 53.4 cm2 Bibliography Stouffer, E., & Slisz, A. (2019, June 06). Retrieved from Rate of Diffusion through a Solution: https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Physical_and_Theoretical_Chemistry_Textbook_Maps/S upplemental_Modules_(Physical_and_Theoretical_Chemistry)/Kinetics/Rate_Laws/Reaction_Me chanisms/Rate_of_Diffusion_through_a_Solution