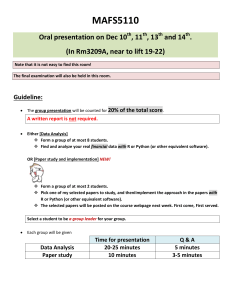
Data Structure Using Python https://www.tutorialspoint.com/python/python_data_structure_environment.htm Data Structure Using Python • Data structures are fundamental concepts of computer science which helps writing efficient programs in any language. • Python is a high-level, interpreted, interactive and object-oriented scripting language using which we can study the fundamentals of data structure in a simpler way as compared to other programming languages. • Python is also a general-purpose programming language that is becoming more and more popular for doing data science. Companies worldwide are using Python to harvest insights from their data and get a competitive edge. PYTHON SPECIFIC DATA STRUCTURES • These data structures are specific to python language and they give greater flexibility in storing different types of data and faster processing in python environment. • List: It is similar to array with the exception that the data elements can be of different data types. You can have both numeric and string data in a python list. • Tuple: Tuples are similar to lists but they are immutable which means the values in a tuple cannot be modified they can only be read. • Dictionary: The dictionary contains Key-value pairs as its data elements. What can I do/build with Python? Is Python better for certain programming needs? What can you/can't you do with Python Installing Python Windows Installation • Here are the steps to install Python on Windows machine. • Open a Web browser and go to https://www.python.org/downloads/. • Download the • Run the downloaded file. This brings up the Python install wizard, which is really easy to use. Just accept the default settings, wait until the install is finished, and you are done. • click this icon Python shell for instant calculations Create new file Python script for coding Setting path at Windows • To add the Python directory to the path for a particular session in Windows − • At the command prompt − type path %path%;C:\Python and press Enter. • Note − C:\Python is the path of the Python directory How to Run output Python Identifiers • A Python identifier is a name used to identify a variable, function, class, module or other object. • An identifier starts with a letter A to Z or a to z or an underscore (_) followed by zero or more letters, underscores and digits (0 to 9). • Python does not allow punctuation characters such as @, $, and % within identifiers. Python is a case sensitive programming language. Thus, Manpower and manpower are two different identifiers in Python. Here are naming conventions for Python identifiers • Class names start with an uppercase letter. All other identifiers start with a lowercase letter. • Starting an identifier with a single leading underscore indicates that the identifier is private. • Starting an identifier with two leading underscores indicates a strongly private identifier. • If the identifier also ends with two trailing underscores, the identifier is a language-defined special name. Reserved Words The following list shows the Python keywords. These are reserved words and you cannot use them as constant or variable or any other identifier names. All the Python keywords contain lowercase letters only. and exec not assert finally or break for pass class from print continue global raise def if return del import try elif in while else is with except lambda yield Lines and Indentation • Python provides no braces to indicate blocks of code for class and function definitions or flow control. Blocks of code are denoted by line indentation, which is rigidly enforced. • The number of spaces in the indentation is variable, but all statements within the block must be indented the same amount. Laboratory Exercise 1 Make the output below from the str =Hello Students of Data Structure and Algorithms Hello Students Of Data Structure and Algorithms Hello Hello Students of Data Structure and Algorithms Lab 2 Comments Instructions • print the (10 + 5), add the comment # Addition • print the (10 * 5), add the comment # Multiplication • print the (10 - 5), add the comment # Subtraction • print the (10 / 10), add the comment # Division Lab 3 Assigning values • Suppose you have $100, which you can invest with a 10% return each year. After one year, it's 100×1.1=110 100×1.1=110 dollars, • and after two years it's 100×1.1×1.1=121 100×1.1×1.1=121. • Add code to calculate how much money you end up with after 7 years. • Print the result