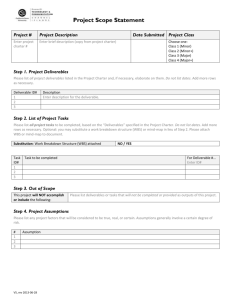
CHAPTER 7 Project Scope Management Key learning objectives • Learn about the specific processes, tools and techniques and major deliverables related to the key knowledge area of Project Scope Management • Become familiar with the processes for project scope management • Understand the importance of effective scope definition and scope management practices • Learn about the relationship between project scope and requirements and be introduced to different approaches to requirements definition Key learning objectives (cont.) • Consider the importance of the project scope statement and how this translates into project deliverables in the real world • Examine the importance of the work breakdown structure and look at techniques for producing this deliverable • Appreciate the importance of controlling scope and how this relates to overall integrated change control • Begin to understand the impacts of poor scope management on project delivery Scope management plan A scope management plan: • documents how the project scope will be defined, validated and controlled (PMI, 2013, p.103) • details procedures to control scope via scope change and integrated change controls • includes instructions for the use of change logs and completion of change requests or variation Product scope versus project scope • Product scope: features and functions that characterise a product or service • Project scope: work performed to deliver a product, service or outcome required to deliver project objectives Source: PMBOK Scope management plan Major development inputs include: • subsidiary plans developed for key knowledge areas • project charter • policies and procedures • lessons learned from past projects Scope management plan (cont.) Typical inclusions include: • processes and templates for developing detailed scope statements • guidelines and templates for the work breakdown structure (WBS) • procedures to control scope and approve change requests • processes for acceptance and sign-off on completed deliverables Scope management plan (cont.) Typical outputs include: – processes for planning and tracking of requirements – requirements, prioritisation and traceability processes – criteria applied to determine if requirements are met Collecting requirements • Involves defining and documenting the needs of stakeholders • Documents special characteristics of products being delivered Collecting requirements (cont.) Documentation on: • business requirements • functional requirements • non-functional requirements • quality requirements • design documentation • construction drawings • schematics and context diagrams Value of well-defined requirements Well-defined requirements: • increase understandings of stakeholders • reduce communication misunderstandings • ensure solutions conform to business needs and are fit for purpose • reduce cost without rework and with accelerated delivery Value of well-defined requirements (cont.) • increase chances of end users accepting the product • enable early error deduction • reduce cost of defect resolution • enable faster reaction to change in business situation or change requirements Requirement deliverables The PMBOK guide details three primary requirements outputs or deliverables: • requirements documentation • requirements management plan • requirement traceability matrix Project scope statement • Project scope is the work performed by a project to deliver a result as per the specification or requirements • Project scope statement is the primary output or deliverables of the project scope process, which involves a detailed description of the project or end products (PMBOK) Project scope • What is included and excluded from the project • Determined at initiation phase and expanded to the planning phase • Determined by project sponsor • Expanded by project manager • Re-confirmed by project sponsor • Defined by project boundaries/range to include constraints, assumptions and dependencies Project scope (cont.) • Related to objectives, outcomes and requirements • Gives project manager concrete goals • Ensure project sponsor objectives are met • Provides basis for expectation management, monitoring and reporting • Determines baseline against which project success is measured Work breakdown structure (WBS) • Deliverable-oriented hierarchal breakdown of the work project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables • Organises and defines the total scope of the project • Processes to identify all deliverables and work undertaken by project team • Basis for development of the project schedule • Basis for project team roles and responsibilities Work breakdown structure (WBS) (cont.) • Consists of work packages from phases, deliverables and activities down to task at the lowest level • Best represented in a diagrammatic version • Tabular version forms part of the project schedule and used to develop the Gantt chart Work breakdown structure (WBS) (cont.) WBS structure is organised by: • project phase • project discipline • work stream WBS dictionary • A document that contains detailed dictionary on each item in the WBS • Includes sub-projects, phases, disciplines and work packages Scope baseline • One of three baselines set at the end of a project planning phase • Other two baselines are project time and project cost • Combination of all the final scoping deliverables are at the end of the planning phase Scope baseline (cont.) Deliverables include: • project scope statement within the project charter and project management plan • detailed document requirements applicable to the project • detailed WBS Scope baseline (cont.) • Used to measure progress towards completion • Ensure expected elements of project scope delivered as per specification • Timing in establishing scope baseline is critical • Best practice to establish baseline for scope, time and cost at end of planning phase WBS practices and techniques The most common and useful practices and techniques for the creation of the WBS are: • WBS standards and templates • project knowledge management (past examples) • decomposition • brainstorming Project knowledge management Benefits of project knowledge management: • reduces project execution risk • increases likelihood of successful delivery • accelerates project scoping and planning • increases accuracy and completeness in project scoping and planning Decomposition Two major approaches: 1. Top-down: commence with project phases and discipline and then define major deliverables, subdeliverables, activities and tasks 2. Bottom-up: commence at activity or task level and then work backwards to associate these with a deliverable Brain storming Techniques and approaches to brain storming: • structured brain storming • facilitation • mind mapping • six hats thinking Validate project scope • Process of formally reviewing and accepting project deliverables • Responsibility for sign-off by project sponsor • Deliverable testing to ensure correct performance against functional requirements • Inspection to ensure non-functional requirements Causes of scope change • Changes in the market or business conditions • Change due to critical requirements overlooked during scoping and planning • Change due to inadequate involvement from project sponsor and key stakeholders Change control Goals of integrated change control: • influence factors that cause scope changes • ensure changes are processed according to developed procedures • manage changes when they occur • increase chances of meeting overall project objectives • define and obtain approval for changes to PMP and baselines for cost, scope and time Change control (cont.) • The project manager is responsible for controlling scope and managing changes • The project sponsor reviews and approves/rejects change request Scope creep • Occurs when unapproved changes to scope are incorporated into the project Scope change control process Good practices: • change request created to document any event that will impact on the project • need to provide details of the required change and the rationale • project manager enters and completes change request Scope change control process (cont.) • use of a change request log • kept simple and streamlined • have a two-step approval process • conduct impact assessment on cost and timeline