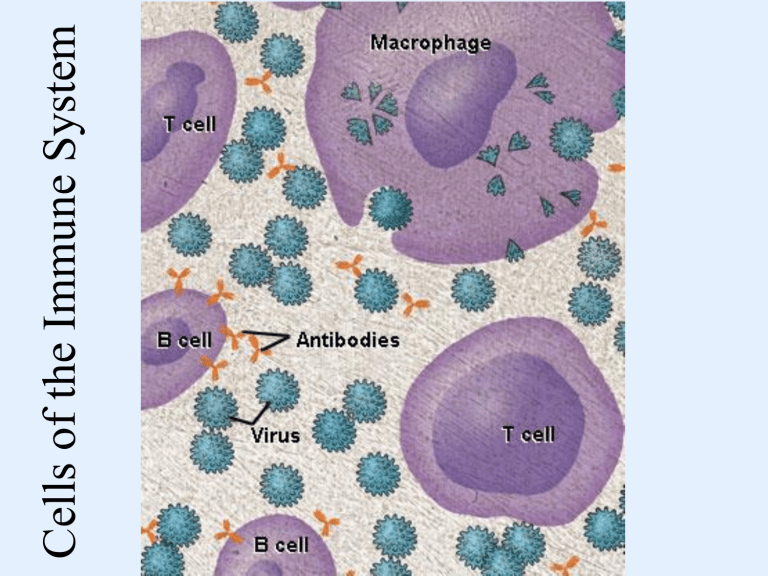
Cells of the Immune System Granulocytes • Neutrophils: most numerous and important • Basophils: allergic response • Eosinophils: allergic response Mast Cells • Non-phagocytic cells • Involved in allergic reaction (histamine release) • Cause vasodilation and increase vascular permeability (inflammation) Macrophages • Engulf bacteria, cells and products targeted by the innate and adaptive response elements: – PAMPS – Complement – Antibody • Present to TH cells for activation • Long lived and capable of producing more lysosomes Dendritic Cells • Antigen presenting cells (APC): – Phagocytize bacteria – Present parts of bacteria and their products on their surface receptors (MHC-II and MHC-I) – Activates T cells for adaptive immune response Lymphoid Cell Lines • T cells and B cells with specific antigen receptors • Natural killer cells: lymphoid cell line but NOT part of the adaptive immune system – Large granular lymphocytes – Kill cells that are abnormal such as viralinfected and tumors Lymphoid Tissues • Primary lymphoid organs (central): – Thymus – Bone marrow • Secondary lymphoid organs (peripheral) – – – – – Lymph nodes Spleen Mucosal lymphoid tissues: GALT Tonsils, adenoids Appendix T-cells • T-cell receptor (TCR) member of the immunoglobulin super family – Helper T cell (TH): activate macrophages and B cells. Also called CD4 cells – Cytotoxic T cell (TC): kill intracellularly infected cells. Also called CD8 cells B cells • B-cell receptor (BCR) binds the antigen – Presents to TH cells for activation – cell proliferation and differentiation – Plasma cells and some memory cells • Antibodies produced have the same specificity as the BCR (membrane Ig) Cellular Interaction • Macrophages bind pathogens and engulf them (cytokines are produced) – Neutrophils are recruited in to engulf bacteria • Dendritic cells engulf and begin to travel to nearest lymphatic tissue – Maturation includes presenting antigen – Presenting co-stimulatory molecules Adaptive Immune Response • • • • Mature dendritic cells activate T cells TH cells will activate B cells B cells produce antibodies as plasma cells TC cells travel to the site of infection and kill infected cells Immune System Cells • Myeloid cells have receptors that bind cells based on conserved patterns • Lymphocytes have specific unique receptors that can recognize pathogens and their products https://www.bing.com/images/search?q=initiation+of+adaptive+immune+response&view=detailv2&id=93EBADA5CA653A8183F10A4669E009A7DDEA3A55&selectedindex= 7&ccid=MUHk9tUZ&simid=608019722209264909&thid=OIP.M3141e4f6d5198ff8c82d91e2e8cfad06o0&mode=overlay&first=1