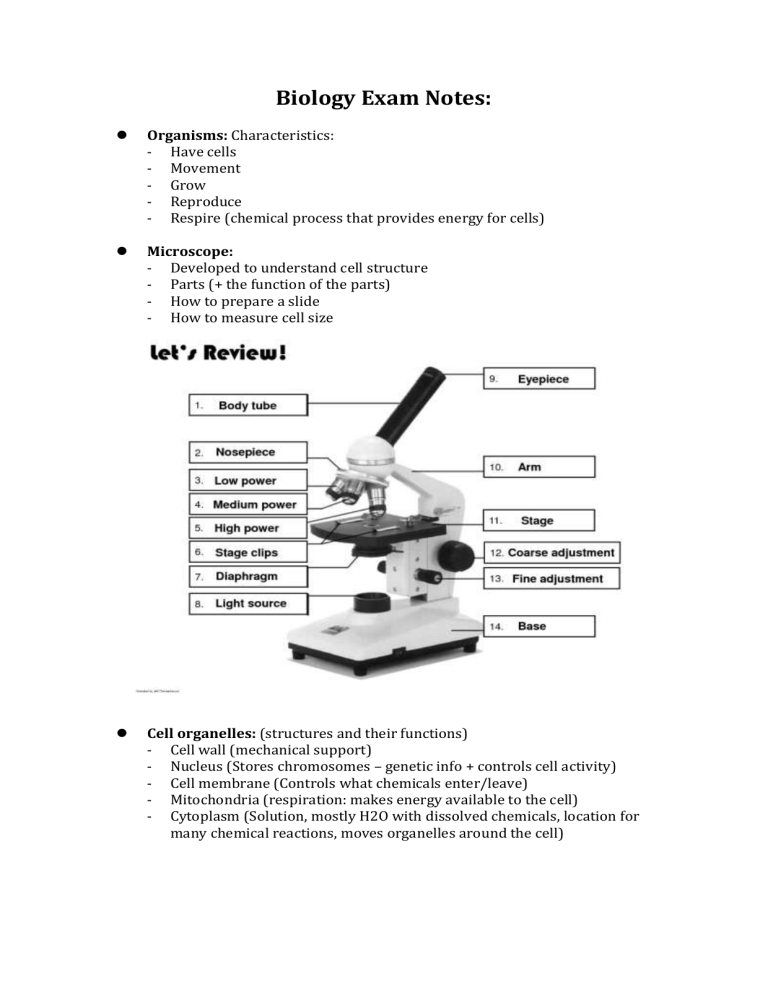
Biology Exam Notes: Organisms: Characteristics: - Have cells - Movement - Grow - Reproduce - Respire (chemical process that provides energy for cells) Microscope: - Developed to understand cell structure - Parts (+ the function of the parts) - How to prepare a slide - How to measure cell size Cell organelles: (structures and their functions) - Cell wall (mechanical support) - Nucleus (Stores chromosomes – genetic info + controls cell activity) - Cell membrane (Controls what chemicals enter/leave) - Mitochondria (respiration: makes energy available to the cell) - Cytoplasm (Solution, mostly H2O with dissolved chemicals, location for many chemical reactions, moves organelles around the cell) Cell transport: - Diffusion (Occurs when particles spread. From a region where of high to low concentration) - Osmosis (the diffusion of water molecules, higher to lower concentration, through a partially permeable membrane) - Active Transport (the movement of dissolved molecules into or out of a cell through the cell membrane, region of lower to higher concentration) - Endocytosis (where cells absorb molecules or substances from outside the cell by engulfing it with the cell membrane.) DNA Molecule: - Section of DNA molecule: Gene Making new cells (before cell division) Mitosis: The type of cell division that produces two daughter cells identical to the parent cell. - Meiosis: The type of cell division that produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell Fertilization: Inheritance: -Gene: - Section of DNA - Codes for a characteristic e.g. eye colour - Can have several different forms (alleles) 4 Types Genetic Problems: Complete Dominance: - E.g. Dimples (Dominant) D: Dimples (Recessive) d: no dimples E.g. Genotype = Dd Phenotype = Dimples Dd x Dd = 1DD, 2Dd, 1dd (3 dimples, 1 no dimples) Punnet Square D d D DD Dd d Dd dd Co-dominance (Incomplete): - One allele does not completely dominate the other (Gene) Flower Colour (Alleles) R = Red, r = white E.g. Genotype = Rr Phenotype = Pink Rr x Rr = 1RR, 2Rr, 1rr (1 red, 2 pink, 1 white) Punnet Square R r R RR Rr r Rr rr Multiple Alleles: - The gene has more than 2 alleles E.g. Blood groups (gene) Alleles: IA IB IO IA IO x IA IB Punnet Square IA IB IA IAIA IAIB Sex linked: - The gene occurs on the X or Y chromosome Gene: Haemophilia Alleles: H (normal) h (unable to clot blood) Punnet Square XH Xh IO IAIO IBIO XHXh x XhYXh XHXh XhXh Pedigree (Family Tree) Diagram: To show the inheritance of a particular characteristic in a family YXHYXhY- Gene Technology: 1. Genome project (Mapping where genes occurred on human chromosomes. 2. Gene therapy (Replacing faulty/ diseased genes, replacing with normal ones 3. Genetic Engineering (Transgenisis or swapping between species) 4. Gene Testing (Testing for the presence of a gene in an individual) Evolution: Within a species: Evidence: - Fossils: (Plant or animal dies in a watery environment and is buried in mud/ silt. Soft tissues decompose until bones/shell. Sediment hardens) - Comparing anatomy - Comparing DNA (molecules) How: Variation of inherited characteristics in species Competition: For (Food, water, nesting sites, sunlight, living space) Natural Selection: Structure, function, behaviour, environmental factors Inheritance: Offspring inherited survival characteristics Evolution: Over a number of generations the proportions of individuals with high survival features increases. To form new species: - Physical (geographical) separation - Natural selection - Unable to interbreed (reproductively isolated)



